In this week’s Charging Forward, Scotland secures a “formidable” £800 million investment in battery energy storage, Statera acquires a 680 MW battery project near Manchester and Centrica raises concerns around gas storage levels.
And in international news, developers in China have started installation work on the world’s largest compressed air energy storage project while Danish firm Hyme Energy is seeking EU funds for what it says will be the world’s largest thermal energy storage system.
This week’s headlines:
- £800m investment in Scottish battery energy storage (BESS) projects
- UK reaches 4.7 of operational BESS capacity in 2024
- UK battery storage sector “back on strack”, Gresham House says
- UK government vows to remove barriers to energy storage deployment
- Centrica raises gas storage concerns
- Statera acquires 680 MW BESS project
- Wind2 lodges Scottish wind-BESS application
- Developers appeal Aberdeen City Council BESS refusal
- NatPower UK submits plans for 1 GW Bellmoor BESS
- Cubico starts work on 95 MWh UK BESS
- RES submits plans for 100 MW BESS in Northern Ireland
- Conrad Energy to optimise KX Power Immingham BESS
- Bluefield Renewables Cramlington BESS approved
- Telis Energy starts early work on Lincolnshire solar-BESS
- International News: China compressed air energy storage and Danish thermal energy storage project developments
£800m for Scotland BESS projects
Investment fund manager Copenhagen Infrastructure Partners (CIP) has announced it will build two more battery storage sites in Scotland in partnership with Susgen subsidiary Alcemi.
The £800m investment in the 1 GW Coalburn 2 and 500 MW Devilla will see Scotland become home to some of the largest BESS projects in Europe.
Alongside the first phase of Coalburn, the three projects will have a combined energy storage capacity of 3 GWh.
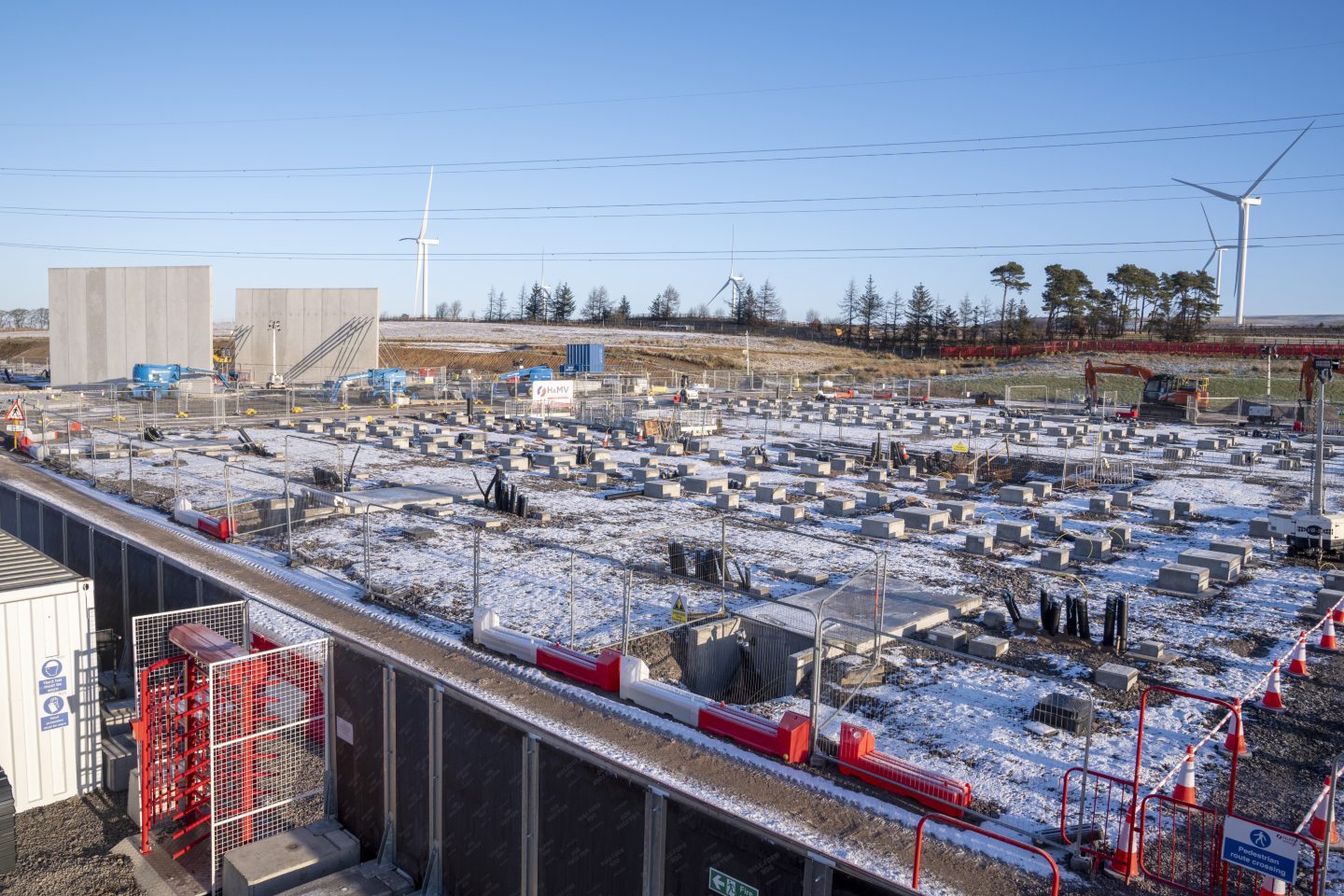 © Jane Barlow/PA Wire
© Jane Barlow/PA WireCanadian Solar will supply the batteries for the projects, which will be manufactured in China.
In response to the investment, Scotland’s First Minister John Swinney said: “This is an essential component of our journey to net zero. It’s an essential component of creating resilience within our networks.
“The fact that Scotland has been able to attract such a formidable investment demonstrates that Scotland is open for investment and open for business.”
GB reaches 4.7 GW of BESS capacity in 2024
Across Great Britain, a total of 1 GW of battery capacity began commercial operations in 2024, taking the total rated power of BESS to 4.7 GW according to Modo Energy.
Meanwhile, the total energy capacity of GB batteries grew to 6.5 GWh, meaning the average duration of batteries was 1.39 hours by the end of 2024.
Modo said the buildout in 2024 was lower than expected, after a record breaking year in 2023 saw 1.6 GW of new capacity become commercially operational.
Over the year, 12 new battery owners began commercial operations including SSE, SUSI/Eelpower, NextEnergy/Eelpower and Econergy, contributing a total of 380 MW.
TagEnergy brought the largest site online in 2024 as its 100 MW Lakeside project, while Gresham House added three sites totalling 150 MW.
According to the National Energy System Operator (NESO), UK BESS capacity will need to reach between 23-27 GW in 2030 to ensure the government meets its clean power goals.
UK battery storage sector ‘back on track’
UK battery storage investor Gresham House Energy Storage Fund (LON:GRID) has said the industry is “back on track” as trading conditions improved, particularly in December.
The UK’s largest fund specialising in battery energy storage systems (BESS) highlighted improvements in service from NESO as well as its renewed commitment to to the sector as part of clean power aims by 2030.
Gresham also revealed that revenues exceeding £60,000 per MW of electricity its facilities provided in the second half of 2024 meant it would meet or even exceed revenue targets.
This comes after the fund said it had faced a “weak revenue environment” in the first part of the year. In April it reported a £110 million loss compared to a £217m profit the previous year and paused dividends.
UK vows to remove energy storage barriers
The UK government has vowed to remove barriers to energy storage deployment in response to an Environmental Audit Committee (EAC) report.
In its report, the EAC warned the lack of long duration energy storage (LDES) in the UK was driving the importation of gas.
The report found market, policy and regulatory barriers were holding back the development of LDES projects in the UK.
The government has now set out steps it plans to take to remove market barriers to “support the rollout of energy storage projects at scale”.
Alongside the introduction of a cap-and-flor mechanism for LDES in October last year, the government confirmed it is reviewing the energy storage system alongside NESO “to help make it fit for the future”.
The government will also align grid connections with strategic plans so as to accelerate connections for projects that are ready to generate electricity.
Officials will also publish the status of the grid connection queue to allow for greater transparency.
EAC chair and Labour MP Toby Perkins welcomed the government’s response to the previous committee’s report.
“Addressing the grid constraints which could block the path to net zero is crucial, if the government is to achieve its ambitions and clean up our energy supply,” Perkins said.
“They explain that significant market barriers to long-term energy storage are to be identified, long-term energy storage will be rolled out and skills shortages in the sector are to be addressed: it is clear that the EAC’s advice has been taken seriously by the new government.”
Centrica raises gas storage concerns
British Gas owner Centrica (LON:CNA) said UK gas storage levels fell to “concerningly low levels” amid a “perfect storm” of winter conditions last week.
On Thursday, stocks at UK gas storage sites were 26% lower than the same period last year, leaving them about half full, the energy giant said.
Gas inventory levels have come under pressure from the cold weather conditions and the end of Russian gas pipeline supplies through Ukraine at the end of last month.
Centrica chief executive Chris O’Shea said the UK will need to use more energy storage systems to help meet demand, including gas and hydrogen storage.
“We are an outlier from the rest of Europe when it comes to the role of storage in our energy system and we are now seeing the implications of that,” O’Shea said.
 © Supplied by Centrica
© Supplied by Centrica“Energy storage is what keeps the lights on and homes warm when the sun doesn’t shine and the wind doesn’t blow, so investing in our storage capacity makes perfect economic sense.
“We need to think of storage as a very valuable insurance policy.”
Centrica operates the country’s largest gas storage site at the Rough field in the North Sea. The company is exploring the feasibility of converting the site for future use as a hydrogen storage facility.
Statera acquires 680 MW BESS project
Statera Energy has acquired a 680 MW BESS project in north-west England from Carlton Power.
The Carrington Storage project forms part of the Trafford Low Carbon Energy Park, located on the site of a former coal-fired power station near Manchester.
The project is Statera’s largest consent BESS project to date and is more than twice the size of its 300 MW Thurrock Storage project.
Statera said the Carrington Storage project alone will equate to nearly a quarter of the current installed energy capacity of the UK BESS fleet.
 © Supplied by Statera Energy
© Supplied by Statera EnergyIn 2023, Carlton Power received planning consent to develop up to 2GW of BESS on the Trafford site.
Other her planned developments include an agreement with Highview Power to build a £300m liquid air energy storage (LAES) project onsite.
Carlton Power also has planning consent for the 200MW Trafford Green Hydrogen production facility.
The project secured financial support from the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (DESNZ) as part of the first hydrogen allocation round.
The first 15MW phase is expected to begin operation in the next two years.
Carlton Power chief executive Keith Clarke said Trafford is “becoming a beacon for low carbon energy” in the north-west of England.
“The investment in the Trafford Low Carbon Energy Park over the next two to five years demonstrates Carlton Power’s long-term vision and commitment to the Trafford site, and we are actively exploring further options to fully realise the strategic benefits of the Trafford facility,” Clarke said.
Wind2 submits Scottish wind-BESS plans
Renewable energy developer Wind2 has submitted a planning application to the Highland Council for the Swarclett Wind Farm, which includes a 21.6 MW BESS.
The wind farm includes two wind turbines with a blade tip height of up to 149.9 metres on a site near Castletown in Caithness.
Wind2 said the project will generate approximately 66,000 MWh of electricity annually while offsetting approximately 6,000 tonnes of CO2 per year.
The project includes a community benefit fund worth £48,000 per year, and Wind2 said residents living closest to the turbines will be offered the opportunity to claim up to £600 per year towards their electricity costs.
Developers appeal Aberdeen BESS refusal
Flexion Energy is pushing for the Scottish government to approve its 40 MW battery storage site at Countesswells after Aberdeen City Council rejected the plans.
Councillors knocked back the proposal in September as they believed the industrial site would be “out of place” on land just off Countesswells Road.
But Flexion said the proposal meets all national, regional and local planning rules, as well as specific criteria for energy sites such as this.
They added: “The unwarranted refusal is preventing the delivery of infrastructure that is critical to the delivery of renewable energy in the time of a climate crisis.
“Given the significant renewable energy benefits, the appropriateness of the site, and the proposed mitigation measures, the appeal seeks the overturning of the refusal.”
NatPower submits plans for 1 GW Bellmoor BESS
Renewable energy developer NatPower UK has submitted its plans for a 1 GW BESS near Thirsk to North Yorkshire Council.
If plans for the Bellmoor project are approved, NatPower said it will contribute up to £1m each year for 40 years to local community initiatives.
The submission comes just weeks after NatPower lodged a separate planning application with Redcar and Cleveland Council for a 1 GW BESS at Teesside.
The company has previously warned the UK government needs to deliver grid connection reform within six months to ensure its clean power 2030 target stays on track.
NatPower urged regulators to remove “non-credible” projects looking to connect to Britain’s electricity grid, and warned delays could put some of its plans to invest £10bn at risk.
Cubico starts work on 47.5 MW UK BESS
Renewable energy developer Cubico Sustainable Investments has started the construction process for its 47.5 MW Mannington BESS in Dorset.
The two-hour duration 95 MWh project is the company’s first “ready to build” BESS project in the UK, with Tesla selected as the battery supplier.
The Mannington project is the first in Cubico’s global BESS pipeline to reach the construction phase.
Across its global development portfolio, Cubico has 1.3 GW of battery projects at an “advanced stage” and an additional 2.3 GW of greenfield BESS projects in early stage development.
Cubico head of northern Europe James Pinney said issuing procurement and construction contracts for the Mannington BESS is a “key milestone” for the company.
“Integrating renewables into power grids requires substantial investment into storage solutions, and we have a growing pipeline of greenfield projects both in the UK and globally that we are now bringing to fruition,” Pinney said.
RES submits plans for Northern Ireland BESS
Renewable energy developer RES has submitted a planning application for a 100 MW BESS project to Fermanagh and Omagh District Council in Northern Ireland.
RES said the site for the Shaneragh BESS, located near Dromore in County Tyrone, was chosen for its proximity to the Dromore substation.
The site also lies outside of any national or local environmental designations, RES added.
RES development project manager Peter Henry said the importance of battery storage was demonstrated in October when the UK-Norway interconnector went offline.
“As a result, the frequency of our grid network dropped well below the operational limits and this would have led to power outages had it not been for fast-acting frequency services, like battery energy storage, which were able to recover the system within two minutes,” Henry said.
“As well as playing an important role in decarbonising our energy system and providing grid stability, our Shaneragh proposal would also enhance biodiversity in the local area through proposed new native hedgerow and grassland planting.”
If consented, RES said the Shaneragh BESS will take around 15 months to complete.
Across the UK and Ireland, RES has developed over 830 MW of battery storage and currently manages over 600 MW of operational storage projects.
Conrad Energy to optimise KX Power Immingham BESS
Conrad Energy has secured an agreement with KX Power to optimise its 80 MW/160 MWh Immingham BESS.
The Immingham project is set to go live in the first quarter of 2025, and Conrad Energy will utilise its trading platform to “ensure peak operational performance”.
Conrad Energy chairman Damian Darragh said the firm will operate the Immingham BESS over the next three years “providing critical stability and flexibility to the GB network”.
 © Supplied by KX Power
© Supplied by KX PowerKX Power chief investment officer Olivia He said: “Conrad Energy have a track record of successfully optimising their own assets as well as offering a strong balance sheet and flexible contracting.
“We’re confident that their trading desk will ensure the battery system at Immingham is optimised in the most efficient way possible.”
In addition to optimising third party assets, Conrad Energy owns a portfolio of 83 sites, both operational and in development, with the potential to generate 983 MW of electricity.
Bluefield Renewables 50 MW BESS approved
Northumberland County Council has approved plans from UK developer Bluefield Renewables to build a 50 MW BESS in Cramlington.
The Low Horton BESS will be located adjacent to the company’s Low Horton Solar Farm project, which received planning permission in 2022.
The solar farm will be built across two sites in Blyth and Bedlington, with the both sites located on sites formerly associated with coal mining.
Speaking at a meeting of the council’s strategic planning committee, Bluefield managing director Jonathan Selwyn said: “Battery storage is complementary to renewable technology and help achieve climate change targets, and support the UK’s urgent need for energy security.
“In particular, they help to balance generation against demand, stabilise the grid and reduce the likelihood of blackouts.”
Telis Energy starts work on solar-BESS
Renewable energy developer Telis Energy UK has commenced early stage works on an up to 600 MW solar-battery project in Lincolnshire.
The Leoda Solar Farm includes plans for a solar farm with a capacity between 500 and 600 MW, and an onsite BESS.
Because of its size, the project has been deemed “nationally significant” and will be determined by UK energy secretary Ed Miliband rather than the local council.
Shortly after Labour took office last year, Miliband pledged to triple UK solar power capacity.
The announcement came as Miliband approved three major solar power projects which had stalled under the former Conservative government.
Leoda Solar Farm head of planning Alex Herbert said: “As the UK continues its transition towards renewable energy, projects like Leoda Solar Farm are vital.
“This project not only supports national goals for net zero emissions but also provides a significant opportunity to invest in our environment, health, and local communities.
“We are committed to working closely with stakeholders and residents over the coming months to develop a project that benefits both the region and the country as a whole.”
Telis Energy UK is part of the wider Telis Energy Group, which has a 10 GW pipeline of projects across the UK, Germany, France and Italy.
China starts work on Jiangsu compressed air energy storage project
Chinese developer Huaneng Group has started construction on the expansion of the country’s first salt cavern compressed air energy storage (CAES) facility.
Billed as the world’s largest project of its kind, the expansion of the Jintan Salt Cavern CAES began on Wednesday 18 December.
The second phase involves building two 350 MW CAES units, with the capacity to store 2.8 GWh of electricity, the equivalent of charging 100,000 electric vehicles.
 © Supplied by Tsinghua University
© Supplied by Tsinghua UniversityThe power station uses electric energy to compress air into an underground salt cavern, before releasing the air to drive a turbine and generate electricity when required.
According to state-owned Chinese news outlet Xinhua, the station will help save 270,000 tonnes of standard coal and reduce CO2 emissions by 520,000 tonnes annually.
China National Salt Industry Group and Tsinghua University are co-developing the project alongside Huaneng Group.
Hyme Energy seeks EU funds for thermal energy storage project
Danish firm Hyme Energy is seeking EU funding for what it says will be the world’s largest industrial thermal storage system.
Hyme is collaborating with Danish firm Arla on the 200 MWh project at the dairy company’s milk powder facility in Holstebro.
The thermal energy storage system will convert renewable electricity into heat, which is stored in molten salt tanks above 500 degrees celsius.
Hyme said the stored heat can then be used to replace fossil fuels in Arla’s milk powder production.
The project will enable up to a 100% reduction in CO2 emissions from process heat at the production facility, Hyme said.
 © Supplied by Hyme Energy
© Supplied by Hyme EnergyHyme Energy chief commercial officer Nis Benn said the project could be a “game-changer for industrial decarbonisation”.
“It will show that reducing CO2 emissions in large-scale industries is not only feasible but also economically attractive.
“We believe this project will serve as a blueprint for future deployments, and we encourage other industry leaders to join the energy transition.”
Hyme and Arla are jointly seeking up to €30m (£25m) in EU funding for the project. If successful, Arla said it could scale the technology across its manufacturing network.
Hyme has already secured EU Horizon funding to build a 20 MWh thermal storage demonstration unit to provide district heating in the Danish town of Bornholm.
Recommended for you

Power Moves: New Energy Industries Council directors and more