As of 2023, nearly 2 billion metric tons of it were being produced annually, enough to cover Manhattan in a layer more than 13 feet thick.
Making this metal produces a huge amount of carbon dioxide. Overall, steelmaking accounts for around 8% of the world’s carbon emissions—one of the largest industrial emitters and far more than such sources as aviation. The most common manufacturing process yields about two tons of carbon dioxide for every ton of steel.
A handful of groups and companies are now making serious progress toward low- or zero-emission steel. Among them, the Swedish company Stegra stands out. (Originally named H2 Green Steel, the company renamed itself Stegra—which means “to elevate” in Swedish—in September.) The startup, formed in 2020, has raised close to $7 billion and is building a plant in Boden, a town in northern Sweden. It will be the first industrial-scale plant in the world to make green steel. Stegra says it is on track to begin production in 2026, initially producing 2.5 million metric tons per year and eventually making 4.5 million metric tons.
The company uses so-called green hydrogen, which is produced using renewable energy, to process iron ore into steel. Located in a part of Sweden with abundant hydropower, Stegra’s plant will use hydro and wind power to drive a massive electrolyzer that splits water to make the hydrogen. The hydrogen gas will then be used to pull the oxygen out of iron ore to make metallic iron—a key step in steelmaking.
This process of using hydrogen to make iron—and subsequently steel—has already been used at pilot plants by Midrex, an American company from which Stegra is purchasing the equipment. But Stegra will have to show that it will work in a far larger plant.
The world produces about 60,000 metric tons of steel every 15 minutes.
“We have multiple steps that haven’t really been proven at scale before,” says Maria Persson Gulda, Stegra’s chief technology officer. These steps include building one of the world’s largest electrolyzers.
Beyond the unknowns of scaling up a new technology, Stegra also faces serious business challenges. The steel industry is a low-margin, intensely competitive sector in which companies win customers largely on price.
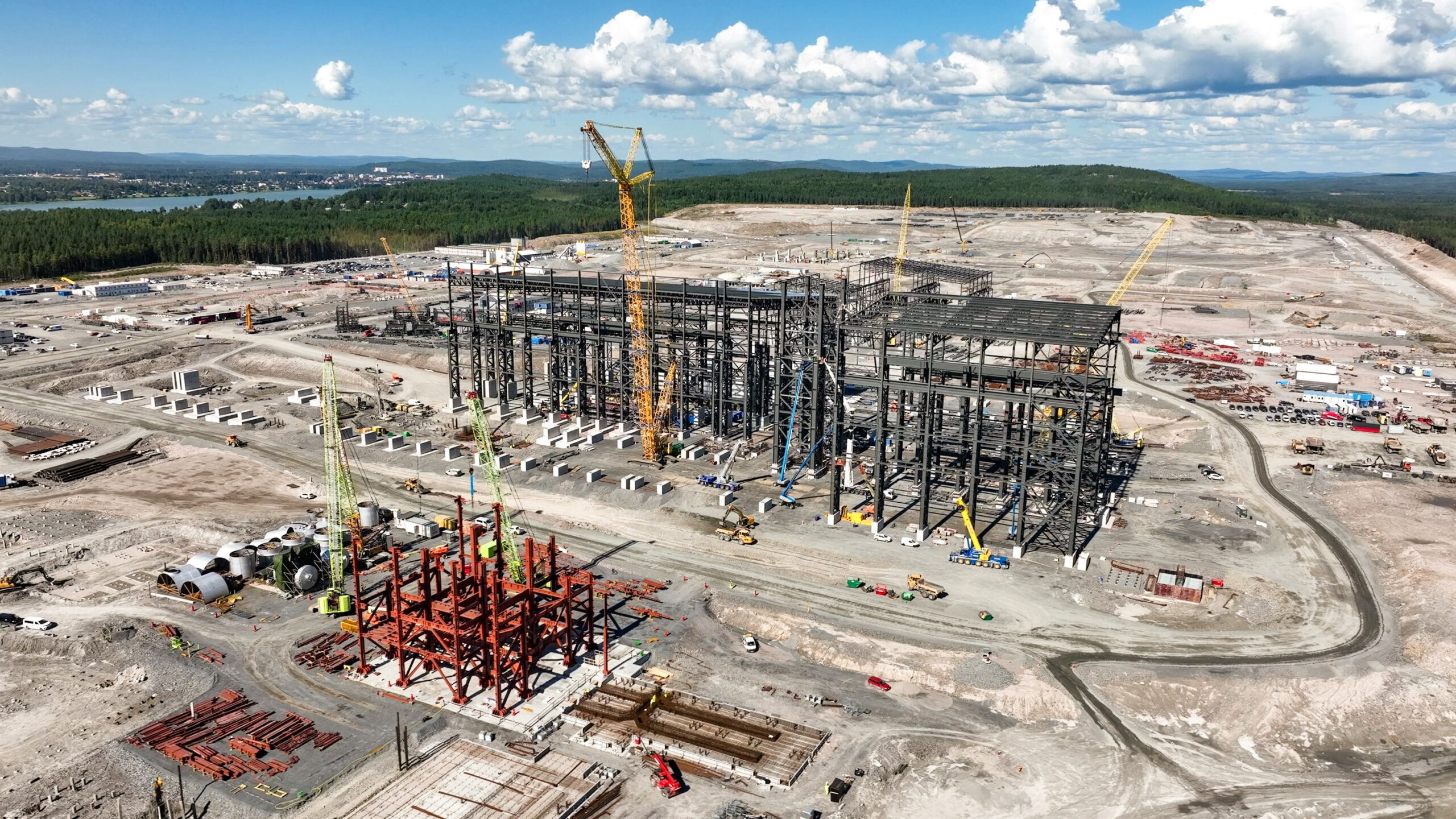

Once operations begin, Stegra calculates, it can come close to producing steel at the same cost as the conventional product, largely thanks to its access to cheap electricity. But it plans to charge 20% to 30% more to cover the €4.5 billion it will take to build the plant. Gulda says the company has already sold contracts for 1.2 million metric tons to be produced in the next five to seven years. And its most recent customers—such as car manufacturers seeking to reduce their carbon emissions and market their products as green—have agreed to pay the 30% premium.
Now the question is: Can Stegra deliver?
The secret of hydrogen
To make steel—an alloy of iron and carbon, with a few other elements thrown in as needed—you first need to get the oxygen out of the iron ore dug from the ground. That leaves you with the purified metal.
The most common steelmaking process starts in blast furnaces, where the ore is mixed with a carbon-rich coal derivative called coke and heated. The carbon reacts with the oxygen in the ore to produce carbon dioxide; the metal left behind then enters another type of furnace, where more oxygen is forced into it under high heat and pressure. The gas reacts with remaining impurities to produce various oxides, which are then removed—leaving steel behind.
The second conventional method, which is used to make a much smaller share of the world’s steel, is a process called direct reduction. This usually employs natural gas, which is separated into hydrogen and carbon monoxide. Both gases react with the oxygen to pull it out of the iron ore, creating carbon dioxide and water as by-products.
The iron that remains is melted in an electric arc furnace and further processed to remove impurities and create steel. Overall, this method is about 40% lower in emissions than the blast furnace technique, but it still produces over a ton of carbon dioxide for every ton of steel.
But why not just use hydrogen instead of starting with natural gas? The only by-product would be water. And if, as Stegra plans to do, you use green hydrogen made using clean power, the result is a new and promising way of making steel that can theoretically produce close to zero emissions.
Stegra’s process is very similar to the standard direct reduction technique, except that since it uses only hydrogen, it needs a higher temperature. It’s not the only possible way to make steel with a negligible carbon footprint, but it’s the only method on the verge of being used at an industrial scale.
Premium marketing
Stegra has laid the foundations for its plant and is putting the roof and walls on its steel mill. The first equipment has been installed in the building where electric arc furnaces will melt the iron and churn out steel, and work is underway on the facility that will house a 700-megawatt electrolyzer, the largest in Europe.
To make hydrogen, purify iron, and produce 2.5 million metric tons of green steel annually, the plant will consume 10 terawatt-hours of electricity. This is a massive amount, on par with the annual usage of a small country such as Estonia. Though the costs of electricity in Stegra’s agreements are confidential, publicly available data suggest rates around €30 ($32) per megawatt-hour or more. (At that rate, 10 terawatt-hours would cost $320 million.)

Many of the buyers of the premium green steel are in the automotive industry; they include Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, BMW, Volvo Group, and Scania, a Swedish company that makes trucks and buses. Six companies that make furniture, appliances, and construction material—including Ikea—have also signed up, as have five companies that buy steel and distribute it to many different manufacturers.
Some of these automakers—including Volvo, which will buy from Stegra and rival SSAB—are marketing cars made with the green steel as “fossil-free.” And since cars and trucks also have many parts that are much more expensive than the steel they use, steel that costs the automakers a bit more adds only a little to the cost of a vehicle—perhaps a couple of hundred dollars or less, according to some estimates. Many companies have also set internal targets to reduce emissions, and buying green steel can get them closer to those goals.
Stegra’s business model is made possible in part by the unique economic conditions within the European Union. In December 2022, the European Parliament approved a tariff on imported carbon-intensive products such as steel, known as the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM). As of 2024, this law requires those who import iron, steel, and other commodities to report the materials’ associated carbon emissions.
Starting in 2026, companies will have to begin paying fees designed to be proportional to the materials’ carbon footprint. Some companies are already betting that it will be enough to make Stegra’s 30% premium worthwhile.
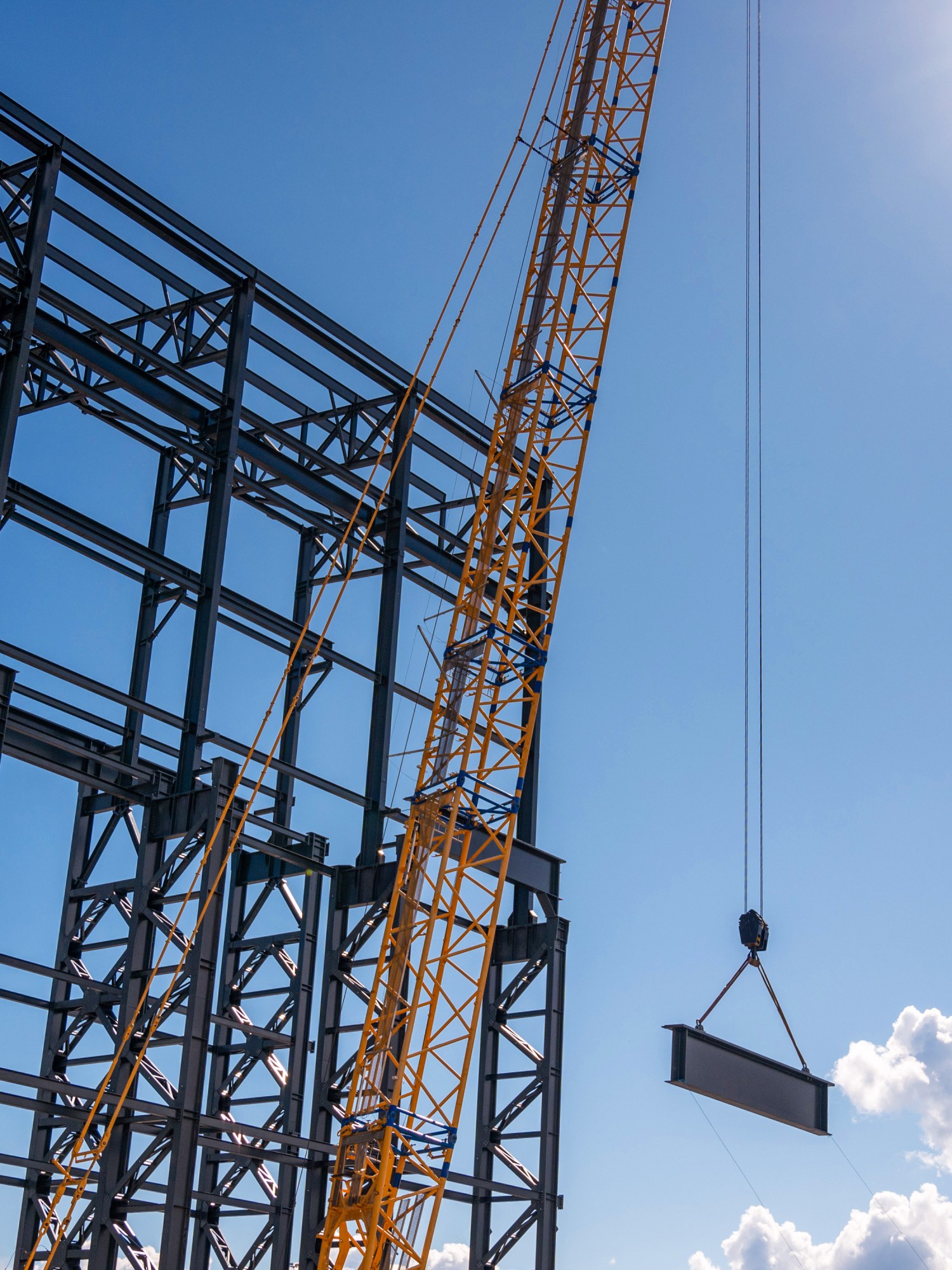

Though the law could incentivize decarbonization within the EU and for those importing steel into Europe, green steelmakers will probably also need subsidies to defray the costs of scaling up, says Charlotte Unger, a researcher at the Research Institute for Sustainability in Potsdam, Germany. In Stegra’s case, it will receive €265 million from the European Commission to help build its plant; it was also granted €250 million from the European Union’s Innovation Fund.
Meanwhile, Stegra is working to reduce costs and beef up revenues. Olof Hernell, the chief digital officer, says the company has invested heavily in digital products to improve efficiency. For example, a semi-automated system will be used to increase or decrease usage of electricity according to its fluctuating price on the grid.
Stegra realized there was no sophisticated software for keeping track of the emissions that the company is producing at every step of the steelmaking process. So it is making its own carbon accounting software, which it will soon sell as part of a new spinoff company. This type of accounting is ultra-important to Stegra, Hernell says, since “we ask for a pretty significant premium, and that premium lives only within the promise of a low carbon footprint.”
Not for everyone
As long as CBAM stays in place, Stegra believes, there will be more than enough demand for its green steel, especially if other carbon pricing initiatives come into force. The company’s optimism is boosted by the fact that it expects to be the first to market and anticipates costs coming down over time. But for green steel to affect the market more broadly, or stay viable once several companies begin making significant quantities of it, its manufacturing costs will eventually have to be competitive with those of conventional steel.
Stegra has sold contracts for 1.2 million metric tons of steel to be produced in the next five to seven years.
Even if Stegra has a promising outlook in Europe, its hydrogen-based steelmaking scheme is unlikely to make economic sense in many other places in the world—at least in the near future. There are very few regions with such a large amount of clean electricity and easy access to the grid. What’s more, northern Sweden is also rich in high-quality ore that is easy to process using the hydrogen direct reduction method, says Chris Pistorius, a metallurgical engineer and co-director of the Center for Iron and Steelmaking Research at Carnegie Mellon University.
Green steel can be made from lower-grade ore, says Pistorius, “but it does have the negative effects of higher electricity consumption, hence slower processing.”
Given the EU incentives, other hydrogen-based steel plants are in the works in Sweden and elsewhere in Europe. Hybrit, a green steel technology developed by SSAB, the mining company LKAB, and the energy producer Vattenfall, uses a process similar to Stegra’s. LKAB hopes to finish a demonstration plant by 2028 in Gällivare, also in northern Sweden. However, progress has been delayed by challenges in getting the necessary environmental permit.
Meanwhile, a company called Boston Metal is working to commercialize a different technique to break the bonds in iron oxide by running a current through a mixture of iron ore and an electrolyte, creating extremely high heat. This electrochemical process yields a purified iron metal that can be turned into steel. The technology hasn’t been proved at scale yet, but Boston Metal hopes to license its green steel process in 2026.
Understandably, these new technologies will cost more at first, and consumers or governments will have to foot the bill, says Jessica Allen, an expert on green steel production at the University of Newcastle in Australia.
In Stegra’s case, both seem willing to do so. But it will be more difficult outside the EU. What’s more, producing enough green steel to make a large dent in the sector’s emissions will likely require a portfolio of different techniques to succeed.
Still, as the first to market, Stegra is playing a vital role, Allen says, and its performance will color perceptions of green steel for years to come. “Being willing to take a risk and actually build … that’s exactly what we need,” she adds. “We need more companies like this.”
For now, Stegra’s plant—rising from the boreal forests of northern Sweden—represents the industry’s leading effort. When it begins operations in 2026, that plant will be the first demonstration that steel can be made at an industrial scale without releasing large amounts of carbon dioxide—and, just as important, that customers are willing to pay for it.
Douglas Main is a journalist and former senior editor and writer at National Geographic.