Deepseek has recently made quite a buzz in the AI community, thanks to its impressive performance at relatively low costs. I think this is a perfect opportunity to dive deeper into how Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained. In this article, we will focus on the Reinforcement Learning (RL) side of things: we will cover TRPO, PPO, and, more recently, GRPO (don’t worry, I will explain all these terms soon!)
I have aimed to keep this article relatively easy to read and accessible, by minimizing the math, so you won’t need a deep Reinforcement Learning background to follow along. However, I will assume that you have some familiarity with Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and a basic understanding of how LLMs work.
I hope you enjoy the article!
The 3 steps of LLM training
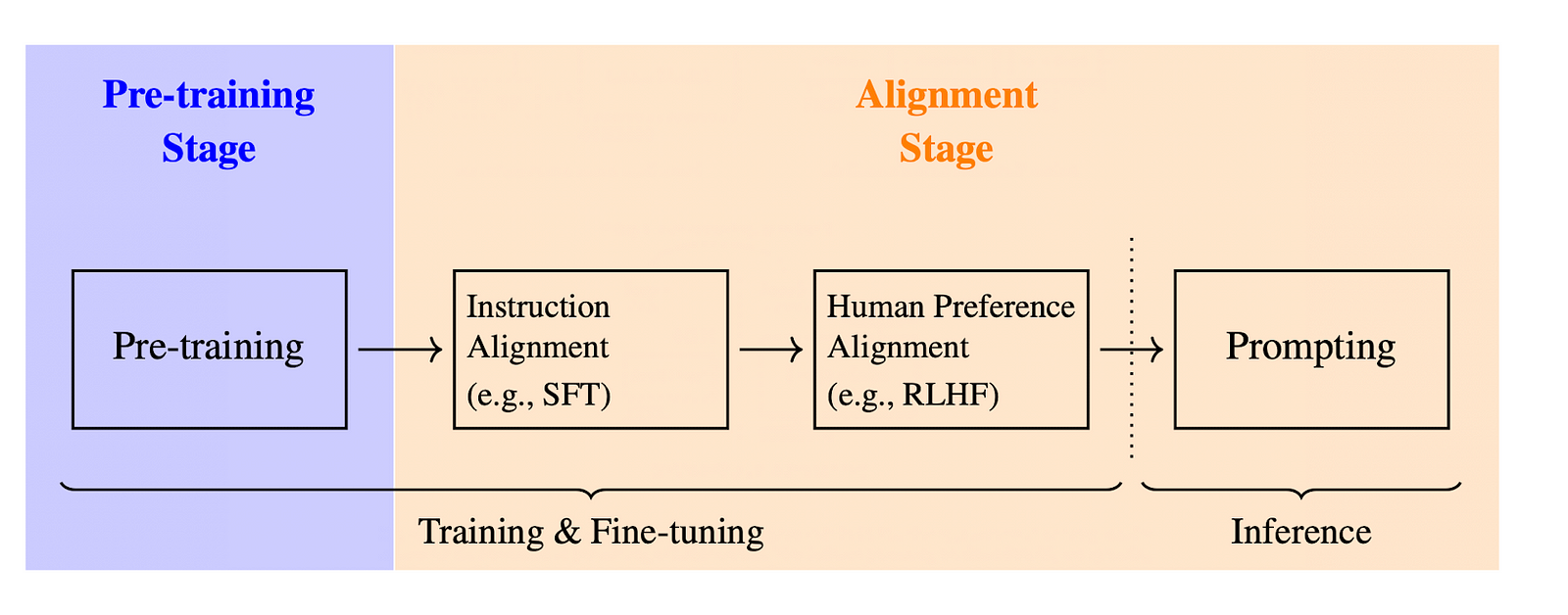
Before diving into RL specifics, let’s briefly recap the three main stages of training a Large Language Model:
- Pre-training: the model is trained on a massive dataset to predict the next token in a sequence based on preceding tokens.
- Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT): the model is then fine-tuned on more targeted data and aligned with specific instructions.
- Reinforcement Learning (often called RLHF for Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback): this is the focus of this article. The main goal is to further refine responses’ alignments with human preferences, by allowing the model to learn directly from feedback.
Reinforcement Learning Basics
Before diving deeper, let’s briefly revisit the core ideas behind Reinforcement Learning.
RL is quite straightforward to understand at a high level: an agent interacts with an environment. The agent resides in a specific state within the environment and can take actions to transition to other states. Each action yields a reward from the environment: this is how the environment provides feedback that guides the agent’s future actions.
Consider the following example: a robot (the agent) navigates (and tries to exit) a maze (the environment).
- The state is the current situation of the environment (the robot’s position in the maze).
- The robot can take different actions: for example, it can move forward, turn left, or turn right.
- Successfully navigating towards the exit yields a positive reward, while hitting a wall or getting stuck in the maze results in negative rewards.
Easy! Now, let’s now make an analogy to how RL is used in the context of LLMs.
RL in the context of LLMs
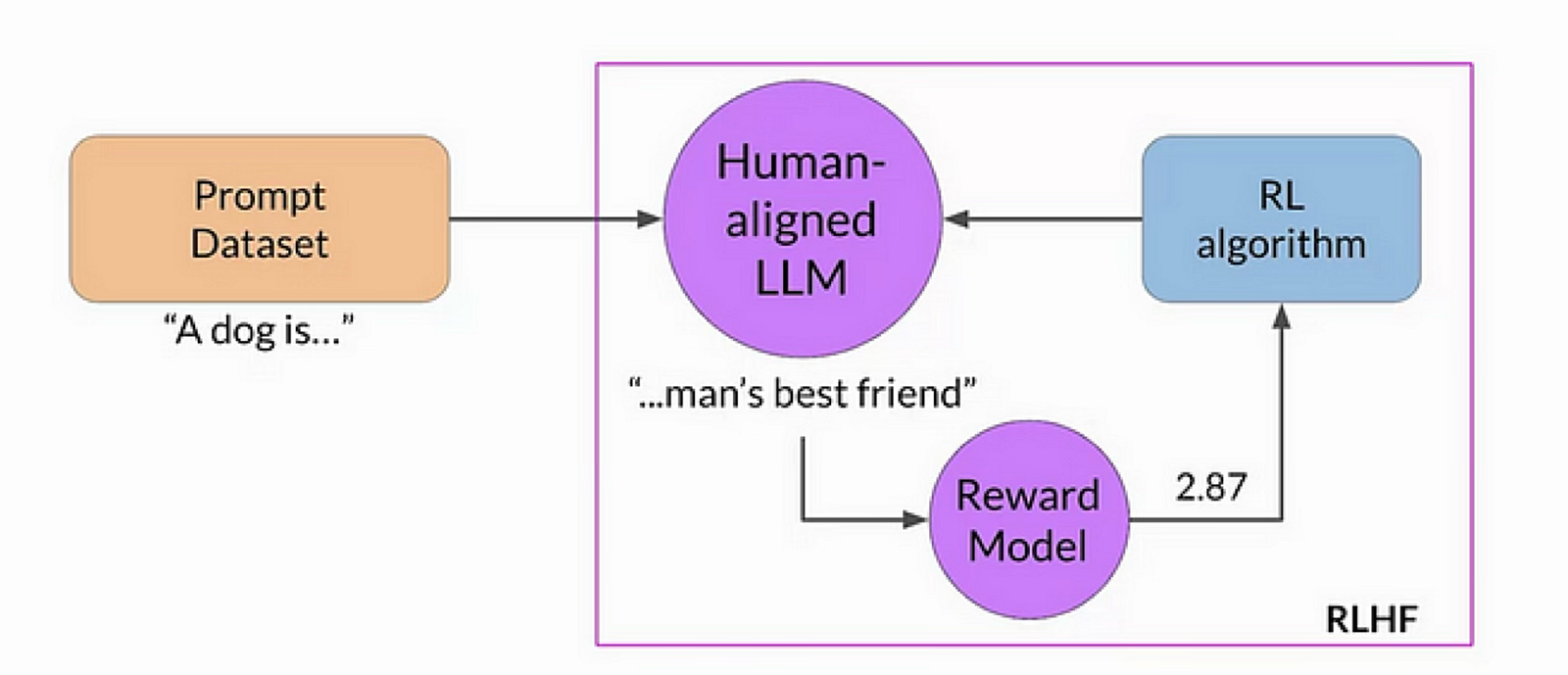
When used during LLM training, RL is defined by the following components:
- The LLM itself is the agent
- Environment: everything external to the LLM, including user prompts, feedback systems, and other contextual information. This is basically the framework the LLM is interacting with during training.
- Actions: these are responses to a query from the model. More specifically: these are the tokens that the LLM decides to generate in response to a query.
- State: the current query being answered along with tokens the LLM has generated so far (i.e., the partial responses).
- Rewards: this is a bit more tricky here: unlike the maze example above, there is usually no binary reward. In the context of LLMs, rewards usually come from a separate reward model, which outputs a score for each (query, response) pair. This model is trained from human-annotated data (hence “RLHF”) where annotators rank different responses. The goal is for higher-quality responses to receive higher rewards.
Note: in some cases, rewards can actually get simpler. For example, in DeepSeekMath, rule-based approaches can be used because math responses tend to be more deterministic (correct or wrong answer)
Policy is the final concept we need for now. In RL terms, a policy is simply the strategy for deciding which action to take. In the case of an LLM, the policy outputs a probability distribution over possible tokens at each step: in short, this is what the model uses to sample the next token to generate. Concretely, the policy is determined by the model’s parameters (weights). During RL training, we adjust these parameters so the LLM becomes more likely to produce “better” tokens— that is, tokens that produce higher reward scores.
We often write the policy as:
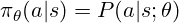
where a is the action (a token to generate), s the state (the query and tokens generated so far), and θ (model’s parameters).
This idea of finding the best policy is the whole point of RL! Since we don’t have labeled data (like we do in supervised learning) we use rewards to adjust our policy to take better actions. (In LLM terms: we adjust the parameters of our LLM to generate better tokens.)
TRPO (Trust Region Policy Optimization)
An analogy with supervised learning
Let’s take a quick step back to how supervised learning typically works. you have labeled data and use a loss function (like cross-entropy) to measure how close your model’s predictions are to the true labels.
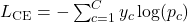
We can then use algorithms like backpropagation and gradient descent to minimize our loss function and update the weights θ of our model.
Recall that our policy also outputs probabilities! In that sense, it is analogous to the model’s predictions in supervised learning… We are tempted to write something like:
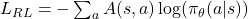
where s is the current state and a is a possible action.
A(s, a) is called the advantage function and measures how good is the chosen action in the current state, compared to a baseline. This is very much like the notion of labels in supervised learning but derived from rewards instead of explicit labeling. To simplify, we can write the advantage as:
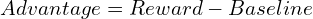
In practice, the baseline is calculated using a value function. This is a common term in RL that I will explain later. What you need to know for now is that it measures the expected reward we would receive if we continue following the current policy from the state s.
What is TRPO?
TRPO (Trust Region Policy Optimization) builds on this idea of using the advantage function but adds a critical ingredient for stability: it constrains how far the new policy can deviate from the old policy at each update step (similar to what we do with batch gradient descent for example).
- It introduces a KL divergence term (see it as a measure of similarity) between the current and the old policy:
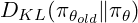
- It also divides the policy by the old policy. This ratio, multiplied by the advantage function, gives us a sense of how beneficial each update is relative to the old policy.
Putting it all together, TRPO tries to maximize a surrogate objective (which involves the advantage and the policy ratio) subject to a KL divergence constraint.
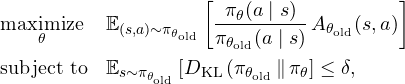
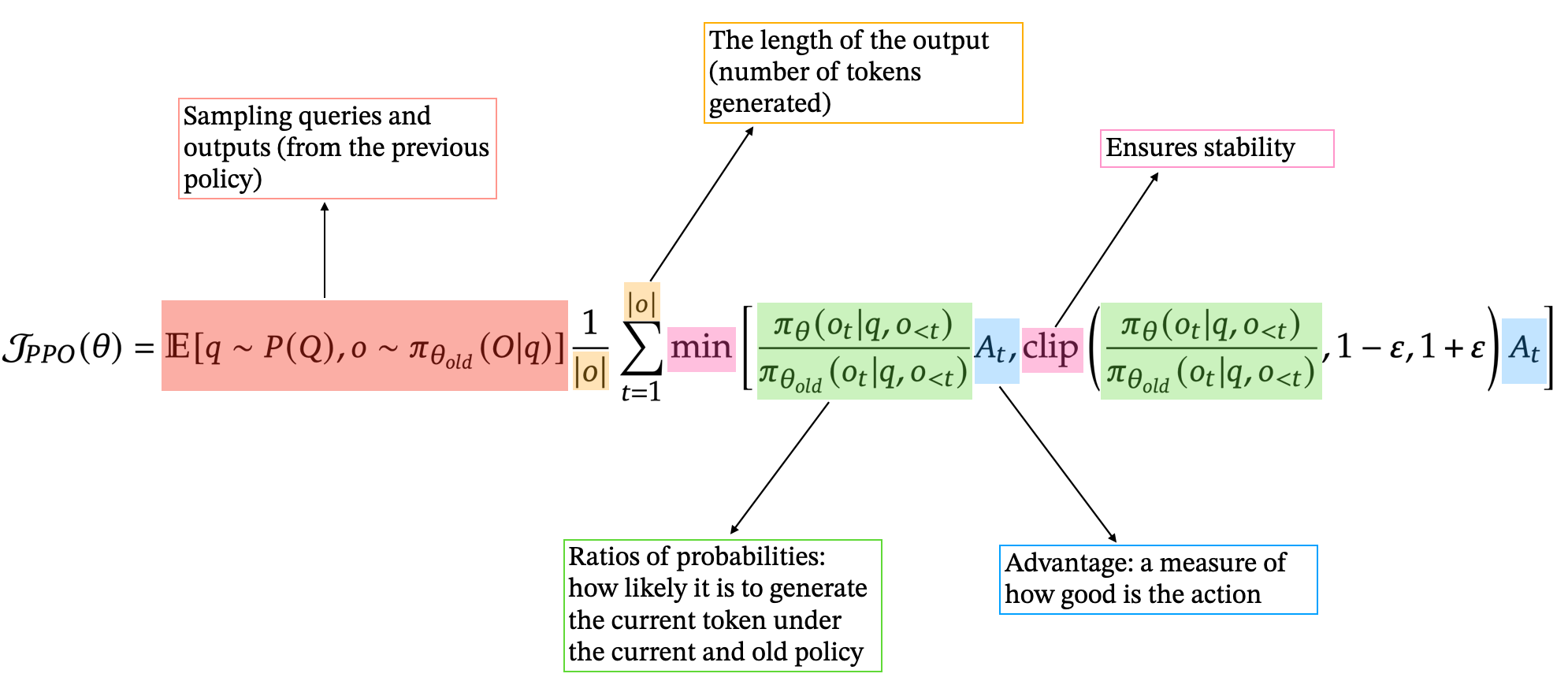
PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization)
While TRPO was a significant advancement, it’s no longer used widely in practice, especially for training LLMs, due to its computationally intensive gradient calculations.
Instead, PPO is now the preferred approach in most LLMs architecture, including ChatGPT, Gemini, and more.
It is actually quite similar to TRPO, but instead of enforcing a hard constraint on the KL divergence, PPO introduces a “clipped surrogate objective” that implicitly restricts policy updates, and greatly simplifies the optimization process.
Here is a breakdown of the PPO objective function we maximize to tweak our model’s parameters.
GRPO (Group Relative Policy Optimization)
How is the value function usually obtained?
Let’s first talk more about the advantage and the value functions I introduced earlier.
In typical setups (like PPO), a value model is trained alongside the policy. Its goal is to predict the value of each action we take (each token generated by the model), using the rewards we obtain (remember that the value should represent the expected cumulative reward).
Here is how it works in practice. Take the query “What is 2+2?” as an example. Our model outputs “2+2 is 4” and receives a reward of 0.8 for that response. We then go backward and attribute discounted rewards to each prefix:
- “2+2 is 4” gets a value of 0.8
- “2+2 is” (1 token backward) gets a value of 0.8γ
- “2+2” (2 tokens backward) gets a value of 0.8γ²
- etc.
where γ is the discount factor (0.9 for example). We then use these prefixes and associated values to train the value model.
Important note: the value model and the reward model are two different things. The reward model is trained before the RL process and uses pairs of (query, response) and human ranking. The value model is trained concurrently to the policy, and aims at predicting the future expected reward at each step of the generation process.
What’s new in GRPO
Even if in practice, the reward model is often derived from the policy (training only the “head”), we still end up maintaining many models and handling multiple training procedures (policy, reward, value model). GRPO streamlines this by introducing a more efficient method.
Remember what I said earlier?
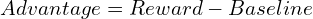
In PPO, we decided to use our value function as the baseline. GRPO chooses something else: Here is what GRPO does: concretely, for each query, GRPO generates a group of responses (group of size G) and uses their rewards to calculate each response’s advantage as a z-score:

where rᵢ is the reward of the i-th response and μ and σ are the mean and standard deviation of rewards in that group.
This naturally eliminates the need for a separate value model. This idea makes a lot of sense when you think about it! It aligns with the value function we introduced before and also measures, in a sense, an “expected” reward we can obtain. Also, this new method is well adapted to our problem because LLMs can easily generate multiple non-deterministic outputs by using a low temperature (controls the randomness of tokens generation).
This is the main idea behind GRPO: getting rid of the value model.
Finally, GRPO adds a KL divergence term (to be exact, GRPO uses a simple approximation of the KL divergence to improve the algorithm further) directly into its objective, comparing the current policy to a reference policy (often the post-SFT model).
See the final formulation below:
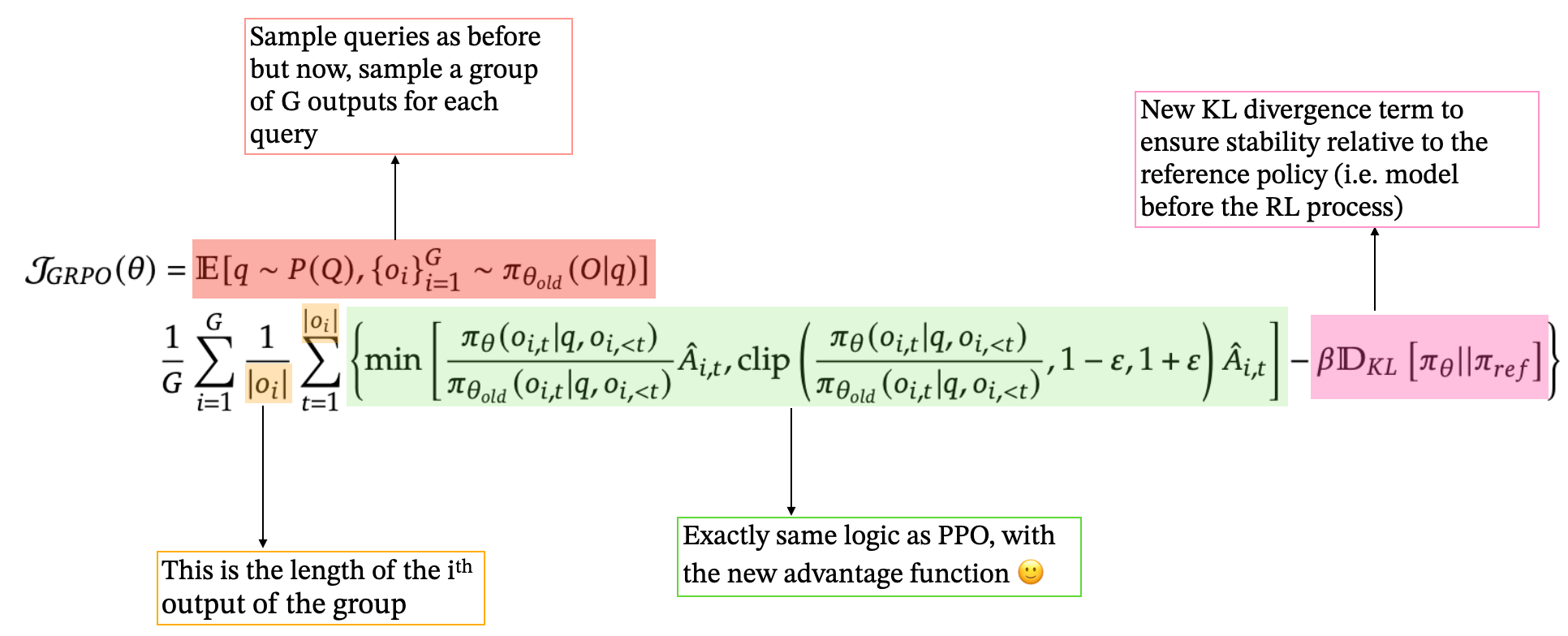
And… that’s mostly it for GRPO! I hope this gives you a clear overview of the process: it still relies on the same foundational ideas as TRPO and PPO but introduces additional improvements to make training more efficient, faster, and cheaper — key factors behind DeepSeek’s success.
Conclusion
Reinforcement Learning has become a cornerstone for training today’s Large Language Models, particularly through PPO, and more recently GRPO. Each method rests on the same RL fundamentals — states, actions, rewards, and policies — but adds its own twist to balance stability, efficiency, and human alignment:
• TRPO introduced strict policy constraints via KL divergence
• PPO eased those constraints with a clipped objective
• GRPO took an extra step by removing the value model requirement and using group-based reward normalization. Of course, DeepSeek also benefits from other innovations, like high-quality data and other training strategies, but that is for another time!
I hope this article gave you a clearer picture of how these methods connect and evolve. I believe that Reinforcement Learning will become the main focus in training LLMs to improve their performance, surpassing pre-training and SFT in driving future innovations.
If you’re interested in diving deeper, feel free to check out the references below or explore my previous posts.
Thanks for reading, and feel free to leave a clap and a comment!
Want to learn more about Transformers or dive into the math behind the Curse of Dimensionality? Check out my previous articles:
References: