The PJM Interconnection’s response to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission’s investigation into the grid operator’s rules for colocated loads indicates FERC may not approve new regulations by mid-year, as some people initially thought, according to utility-sector analysts.
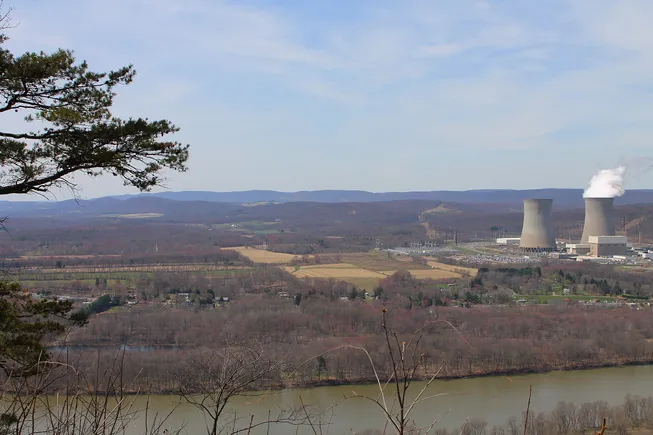
FERC on Feb. 20 launched a review of issues related to colocating large loads, such as data centers, at power plants in PJM’s footprint. The outcome of the review could set a precedent for colocated load in the power markets FERC oversees.
Talen Energy, Constellation Energy and PSEG Power, a Public Service Enterprise Group subsidiary, are among the companies that are considering hosting data centers at their nuclear power plants in PJM.
In its “show cause” order, FERC asked PJM and stakeholders to explain why the grid operator’s colocation rules are just and reasonable or to offer rules that would pass agency muster. FERC established a comment schedule that enables the agency to issue a response by June 20. The agency said it could make a decision on a PJM proposal within three months.
However, instead of proposing new colocation rules, PJM on March 24 said its existing rules are just and reasonable. The grid operator also offered five conceptual colocation options that have been proposed by stakeholders or developed by PJM.
PJM urged FERC to issue “detailed guiding principles” that the grid operator could use to craft colocation rules for the agency’s approval.
The lack of a proposal from PJM likely extends FERC’s review process, according to analysts.
“FERC may still act on the show cause order in June, but we don’t rule out a new iteration of process instead of a clear policy decision,” ClearView Energy Partners analysts said in a client note on Friday.
It will likely take FERC until late this year to approve changes to PJM’s colocation rules, according to Capstone analysts.
Morgan Stanley analysts said their “base case” expectation is a FERC decision in September. “We were hoping for a more definitive proposal to move the process forward more quickly,” the analysts said.
In its response to FERC, PJM noted that any colocation rules may be affected by state laws. “Regardless of what co-location arrangements are ultimately sanctioned by the commission, permitted by the states, and elected by developers, participants involved in co-location arrangements should pay the costs of any grid services they consume and the arrangements must be reliable and operationally manageable,” PJM said.
PJM also said it prefers that colocated load be deemed front-of-the-meter, “network” load, a designation that would require a colocated data center, for example, to pay for certain grid services.
Among the options PJM floated, it said it preferred three of them, partly because they would maintain resource adequacy. The colocation options are:
- Load that elects to be network load and brings its own generation (preferred).
- Load that will cut its electric use during grid emergencies (preferred).
- Load that elects to be network load and that participates as demand response (preferred).
- Load connected to the grid with protections to avoid delivery of system energy to serve the colocated load (less preferred).
- Load connected to the grid with protections to avoid delivery of system energy to serve the colocated load or for the co-located load to receive back-up service from PJM with permission (less preferred).
PJM’s colocation options “bode poorly” for Talen’s proposed colocation arrangement at the company’s majority-owned Susquehanna nuclear plant with Amazon Web Services and other behind-the-meter deals, Capstone said, noting PJM gave the only “true” behind-the-meter proposal a “less preferred” grade.
“We view PJM’s three front-of-the-meter … options as most amendable to the broadest pool of stakeholders, yet these would erode economics for merchant generators and data centers relative to the ‘isolated’ arrangements previously sought,” the research firm said.
Responses to PJM’s comments, and those filed by other stakeholders, are due April 23.