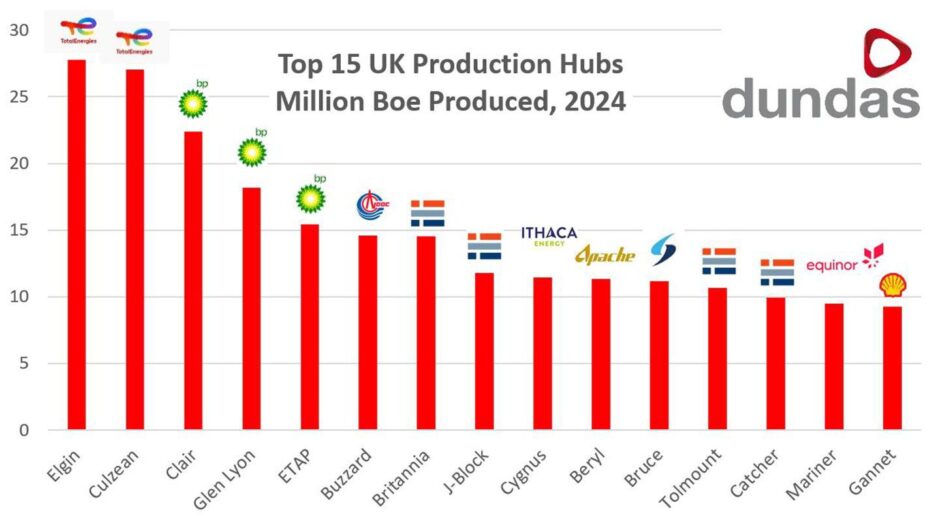
Of all the production hubs in the North Sea, the top four producers have remained unchanged since 2023; however, with the right policy, BP might climb the rankings.
Dundas Consultants has ranked the top 15 highest producing hubs in UK waters, and despite TotalEnergies’ recent statement that it sees “little future” in the country, it still controls the top two.
The French supermajor’s Elgin and Culzean hubs hold the first and second place spots on the league table, respectively.
The next three, Clair, Glen Lyon, and ETAP, are all operated by the London-listed BP, and according to Dundas director Richard Woodhouse, its highest-ranked of the trio has the potential to climb higher.
“The large oil in place in the West of Shetland Clair area arising from the very large size of the oil bearing structures mean that there could in time, still be large development projects taking place to increase the production over the hub, in particular at the Clair South area,” Woodhouse explained.
The Clair South development is now referred to by BP simply as Clair phase three.
 © Supplied by Dundas Consultants
© Supplied by Dundas ConsultantsThis comes as the top four hubs have all seen a double-digit downturn in production.
“If we look at the decline in production from 2023 to 2024, we have 21% for Elgin, 19% for Culzean and 13% each for Clair and Glen Lyon hubs,” Woodhouse added.
“If those decline rates continued into the future, the top 4 league table positions would not actually change.”
So, in order to see a shake-up in the table, there needs to be “game changers for the hubs”, and this is on the cards for BP.
 © Supplied by BP
© Supplied by BPThe Clair phase one platform celebrates 20 years of production in 2025, and its neighbouring Clair Ridge platform recently saw success as production from its latest well was described as “exceeding expectations” by the supermajor.
The field, located is 47 miles west of Shetland, is in the second phase of development. Clair also claims the title of the largest oilfield in the UKCS.
BP discovered Clair in 1977 but did not commence production until 2005 due to the complexity of the geology presented by the find. BP estimates the field holds 7 billion barrels of hydrocarbons.
The Dundas boss explained: “Clair South has already seen significant delay, and the current political headwinds suggest delays may continue for some time to come.”
Mid-table jostling
 © Supplied by BP
© Supplied by BPIt is also worth noting that ETAP managed to climb from 14th to fifth place since 2023 as a result of the Seagull project coming online.
The 50 million barrel tieback kicked off production in late 2023 and was developed by Neptune Energy. Due to ownership of North Sea assets changing hands in the past couple of years, Seagull is now operated by Ithaca Energy.
Equinor’s Mariner also managed to break into the top 15, according to Dundas figures, as it knocked out the former ninth-place Shearwater. Mariner stands in the 14th position of the top 15.
The new entrant is also set to change hands shortly as the Norwegian state-backed firm merges its UK assets with domestic supermajor Shell.
The combination is understood to be processing with more updates on the new vehicle set to be announced this year.
Will ‘pragmatism and common sense’ come out on top?
Despite the difficulties facing operators as a result of the UK’s current political and fiscal regime, Woodhouse remains “an optimist”.
North Sea players are currently contending with a 78% headline rate of tax and a government that stands to oppose new licences.
There has been much outcry from businesses, trade bodies and unions over the impact that deterring investment in the UK oil and gas market may have. However, Woodhouse hopes that “pragmatism and common sense” will prevail.
“It makes no political, economic or philosophical sense to kill off the UK oil and gas sector through licencing and taxation policies when, the alternative, on the demand side, is that we continue to import a higher and higher percentage of foreign-produced oil and gas for decades to come instead.”

Those who oppose the Labour government’s policy have argued that increasing imports of oil and gas will make the country more vulnerable to geopolitical turbulence while increasing the country’s emissions.
The logic touted by those in support of oil and gas is simple: if the UK pays for oil and gas to be imported from overseas in tankers, the carbon cost increases to account for the emissions of said vessel.
Woodhouse added: “I’m an optimist and believe that with time we will see greater political support for UK oil and gas and that we are currently at the bottom of that cycle.
“Pragmatism and common sense will hopefully prevail in the end – the UK needs the high-quality jobs, taxation receipts, economic activity, balance of payments contribution and vitally, energy security that our home-grown oil and gas sector can deliver.”