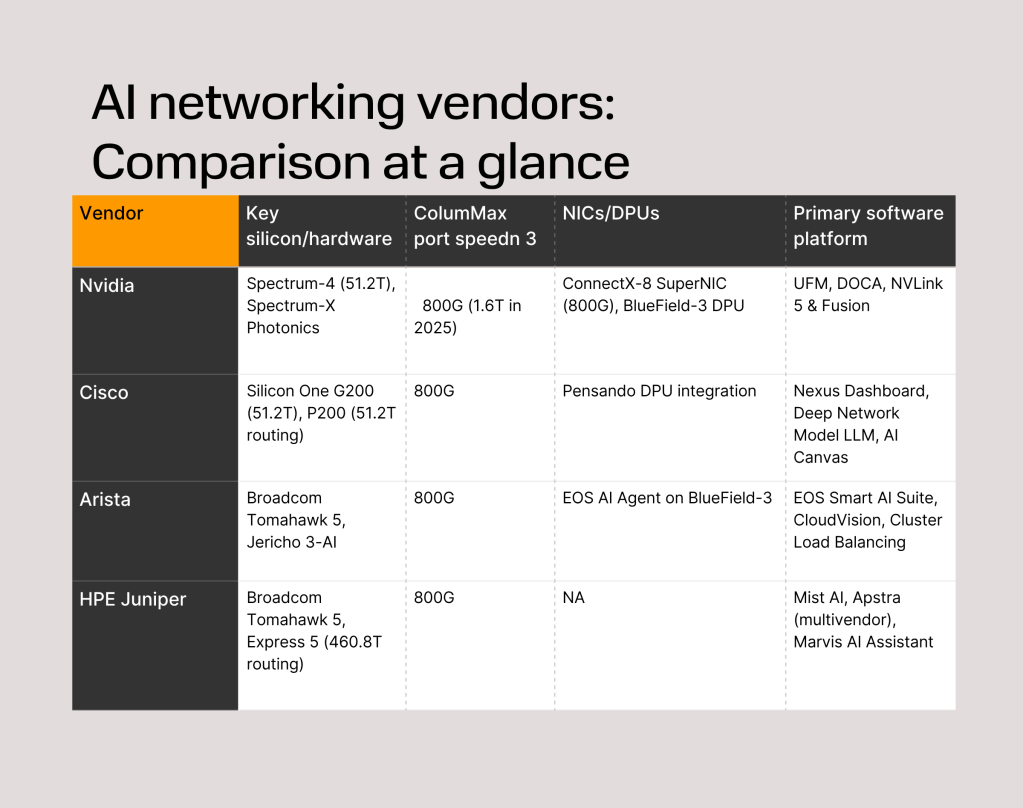
Join our daily and weekly newsletters for the latest updates and exclusive content on industry-leading AI coverage. Learn More
2025 will be the year that big tech transitions from selling us more and more powerful tools to selling us more and more powerful abilities. The difference between a tool and an ability is subtle yet profound. We use tools as external artifacts that help us overcome our organic limitations. From cars and planes to phones and computers, tools greatly expand what we can accomplish as individuals, in large teams and as vast civilizations.
Abilities are different. We experience abilities in the first person as self-embodied capabilities that feel internal and instantly accessible to our conscious minds. For example, language and mathematics are human created technologies that we load into our brains and carry around with us throughout our lives, expanding our abilities to think, create and collaborate. They are superpowers that feel so inherent to our existence that we rarely think of them as technologies at all. Fortunately, we don’t need to buy a service plan.
The next wave of superpowers, however, will not be free. But just like our abilities to think verbally and numerically, we will experience these powers as self-embodied capabilities that we carry around with us throughout our lives. I refer to this new technological discipline as augmented mentality and it will emerge from the convergence of AI, conversational computing and augmented reality. And, in 2025 it will kick off an arms race among the largest companies in the world to sell us superhuman abilities.
These new superpowers will be unleashed by context-aware AI agents that are loaded into body-worn devices (like AI glasses) that travel with us throughout our lives, seeing what we see, hearing what we hear, experiencing what we experience and providing us with enhanced abilities to perceive and interpret our world. In fact, by 2030, I predict that a majority of us will live our lives with the aid of context-aware AI agents that bring digital superpowers into our normal daily experiences.
How will our super human future unfold?
First and foremost, we will whisper to these intelligent agents, and they will whisper back, acting like an omniscient alter ego that gives us context-aware recommendations, knowledge, guidance, advice, spatial reminders, directional cues, haptic nudges and other verbal and perceptual content that will coach us through our days and educate us about our world.
Consider this simple scenario: You are walking downtown and spot a store across the street. You wonder, what time does it open? So, you grab your phone and type (or say) the name of the store. You quickly find the hours on a website and maybe review other info about the store as well. That is the basic tool-use computing model prevalent today.
Now, let’s look at how big tech will transition to an ability computing model.
Stage 1: You are wearing AI-powered glasses that can see what you see, hear what you hear and process your surroundings through a multimodal large language model (LLM). Now when you spot that store across the street, you simply whisper to yourself, “I wonder when it opens?” and a voice will instantly ring back into your ears “10:30 AM.”
I know this is a subtle shift from asking your phone to look up the name of a store, but it will feel profound. The reason is that the context-aware AI agent will share your reality. It’s not just tracking your location like GPS, it is seeing, hearing and paying attention to what you are paying attention to. This will make it feel far less like a tool, and far more like an internal ability that is linked to your first-person reality.
And when we are asked a question by the AI-powered alter ego in our ears, we will often answer by just nodding our heads to affirm (detected by sensors in the glasses) or shaking our heads to reject. It will feel so natural and seamless, we might not even consciously realize we replied.
Stage 2: By 2030, we will not need to whisper to the AI agents traveling with us through our lives. Instead, we will be able to simply mouth the words, and the AI will know what we are saying by reading our lips and detecting activation signals from our muscles. I am confident that “mouthing” will be deployed, as it’s more private, more resilient in noisy spaces, and most importantly, it will feel more personal, internal and self-embodied.
Stage 3: By 2035, you may not even need to mouth the words. That’s because the AI will learn to interpret the signals in our muscles with such subtlety and precision, we will simply need to think about mouthing words to convey our intent. We will be able to focus our attention on any item or activity in our world and think something, and useful information will ring back from our AI glasses like an all-knowing voice in our heads.
Of course, the capabilities will go far beyond just wondering about things around you. That’s because the onboard AI that shares your first-person reality will learn to anticipate the information you desire before you even ask for it. For example, when a coworker approaches from down the hall and you can’t quite remember his name, the AI will sense your unease, and a voice will ring: “Gregg from engineering.”
Or when you pick up a can of soup in a store and are curious about the carbs or wonder if it’s cheaper at Walmart, the answers will just ring in your ears or appear visually. It will even give you superhuman abilities to assess the emotions on other people’s faces, predict their moods, goals or intentions, and coach you during real-time conversations to make you more compelling, appealing or persuasive (see this fun video example).
I know some people will be skeptical about the level of adoption I predict above and the rapid time frame, but I don’t make these claims lightly. I’ve spent much of my career working on technologies that augment and expand human abilities, and I can say that without question, the mobile computing market is about to run in this direction in a very big way.
Over the last 12 months, two of the most influential and innovative companies in the world, Meta and Google, revealed their intentions to give us self-embodied superpowers. Meta made the first big move by adding a context-aware AI to their Ray-Ban glasses and by showing off their Orion mixed reality prototype that adds impressive visual capabilities. Meta is now very well positioned to leverage their big investments in AI and extended reality (XR) and become a major player in the mobile computing market, and they will likely do it by selling us superpowers we can’t resist.
Not to be outdone, Google recently announced Android XR, a new AI-powered operating system for augmenting our world with seamless context-aware content. They also announced a partnership with Samsung to bring new glasses and headsets to market. With more than 70% market-share for mobile operating systems and an increasingly strong AI presence with Gemini, I believe that Google is well-positioned to be the leading provider of technology-enabled human superpowers within the next few years.
Of course, we need to consider the risks
To quote the famous 1962 Spiderman comic, “with great power comes great responsibility.” This wisdom is literally about superpowers. The difference is that the great responsibility will not fall on the consumers who purchase these techno-powers, but on the companies that provide them and the regulators that oversee them.
After all, when wearing AI-powered augmented reality (AR) eyewear, each of us could find ourselves in a new reality where technologies controlled by third parties can selectively alter what we see and hear, while AI-powered voices whisper in our ears with advice, information and guidance. While the intentions are positive, even magical, the potential for abuse is just as profound.
To avoid the dystopian outcomes, my primary recommendation to both consumers and manufacturers is to adopt a subscription business model. If the arms race for selling superpowers is driven by which company can provide the most amazing new abilities for a reasonable monthly fee — we will all benefit. If instead, the business model becomes a competition to monetize superpowers by delivering the most effective targeted influence into our eyes and ears throughout our daily lives, consumers could easily be manipulated with precision and pervasiveness that we have never before faced.
Ultimately, these superpowers won’t feel optional. After all, not having them could put us at a cognitive disadvantage. It is now up to the industry and regulators to ensure that we roll out these new abilities in a way that is not intrusive, manipulative or dangerous. I am confident this can be a magical new direction for computing, but it requires careful planning and oversight.
Louis Rosenberg founded Immersion Corp, Outland Research and Unanimous AI, and authored Our Next Reality.
DataDecisionMakers
Welcome to the VentureBeat community!
DataDecisionMakers is where experts, including the technical people doing data work, can share data-related insights and innovation.
If you want to read about cutting-edge ideas and up-to-date information, best practices, and the future of data and data tech, join us at DataDecisionMakers.
You might even consider contributing an article of your own!