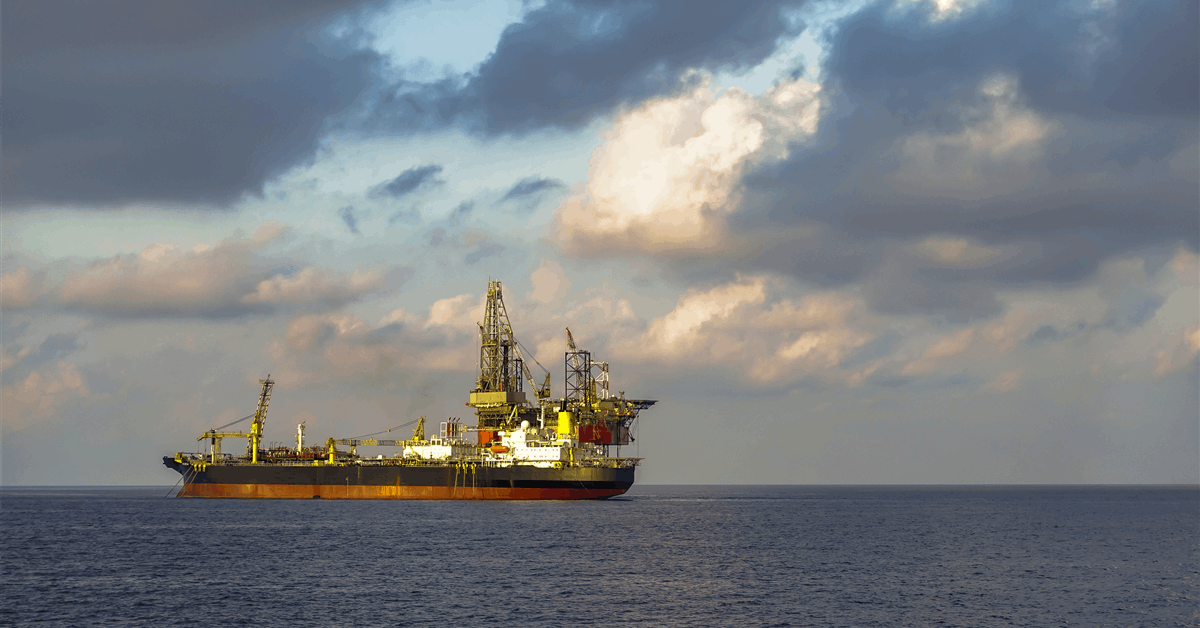
Australia’s Santos Ltd. said the BW Opal floating production, storage, and offloading (FPSO) vessel arrived at the Barossa gas field. This is a critical milestone on the path to first gas in the third quarter of 2025, Santos said in a media release, adding that the FPSO has been hooked up with final commissioning already in progress.
The FPSO is the production centerpiece of Santos’ Barossa liquefied natural gas (LNG) project. Santos said it and joint venture partners SK E&S and JERA Co. Inc. have invested $3.95 billion (AUD6.07 billion at today’s rates) on the Barossa LNG project to date.
“The project has come a long way since regulator acceptance of the Offshore Project Proposal in 2018. The project remains on track for first gas in the third quarter of 2025, and within the original cost guidance, which is a remarkable achievement”, Kevin Gallagher, Santos Managing Director and Chief Executive Officer, said.
“Barossa is a world-class asset and, together with the Pikka phase one project in Alaska, is expected to deliver a 30 percent increase in production over the next eighteen months or so compared to 2024. These projects will set the company up with long-term, stable cash flows to underpin compelling shareholder returns”.
Furthermore, the Darwin LNG life extension (DLE) project, which will support the Barossa LNG project, is on track to be completed by the start of the third quarter of 2025, with 90 percent of the work now done, Santos said.
The DLE project and its associated infrastructure have created 300 construction and maintenance jobs in Darwin, with a total investment of AUD 1 billion. Santos’ operations at Darwin LNG, which employ a 100 percent local workforce, are expected to generate around AUD100 million per year in supply and service opportunities for Northern Territory businesses, Santos said.
The Darwin LNG joint venture has teamed up with KAEFER Integrated Services on an AUD 3 million initiative to develop a skilled and sustainable Aboriginal workforce in the Northern Territory’s industry through local training delivery, Santos said. The program has created 20 trade and traineeship opportunities for local Territorians, including in boiler making, workplace health and safety, and administration, it said.
To contact the author, email [email protected]
What do you think? We’d love to hear from you, join the conversation on the
Rigzone Energy Network.
The Rigzone Energy Network is a new social experience created for you and all energy professionals to Speak Up about our industry, share knowledge, connect with peers and industry insiders and engage in a professional community that will empower your career in energy.
MORE FROM THIS AUTHOR