Such a shift, analysts say, could offer short-term benefits for enterprises, particularly in cost and access, but also introduces new operational risks.
“This acquisition may potentially lower enterprise pricing through lease cost elimination and annual savings, while improving GPU access via expanded power capacity, enabling faster deployment of Nvidia chipsets and systems,” said Charlie Dai, VP and principal analyst at Forrester. “However, service reliability risks persist during this crypto-to-AI retrofitting.”
This also indicates that struggling vendors such as Core Scientific and similar have a way to cash out, according to Yugal Joshi, partner at Everest Group.
“However, it does not materially impact the availability of Nvidia GPUs and similar for enterprises,” Joshi added. “Consolidation does impact the pricing power of vendors.”
Concerns for enterprises
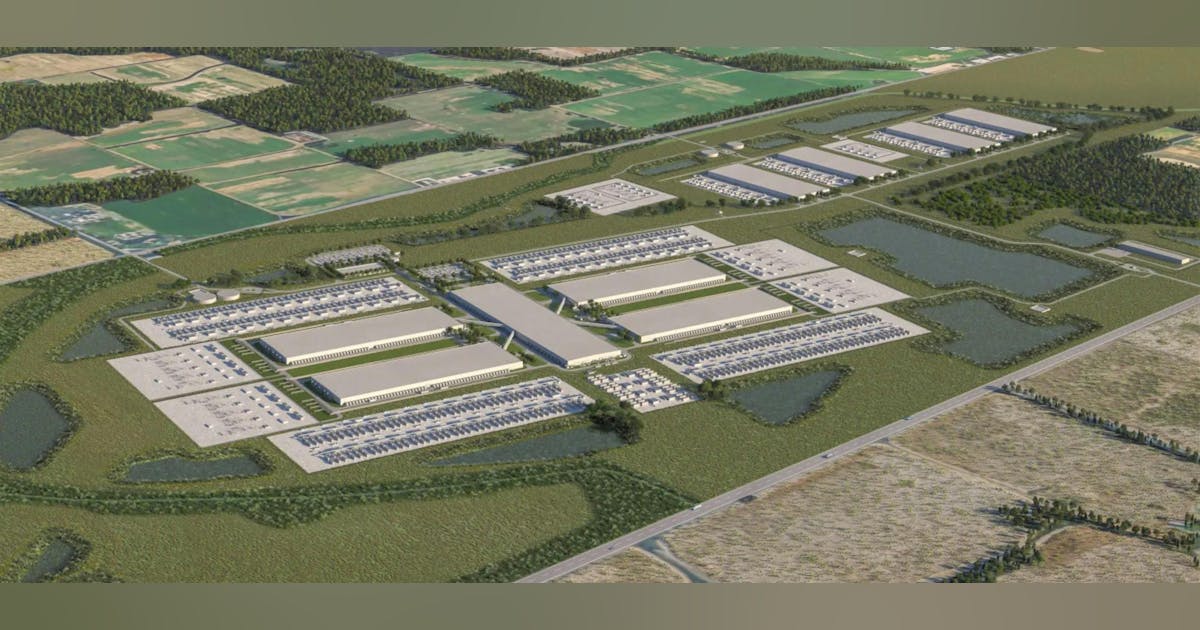
Rising demand for AI-ready infrastructure can raise concerns among enterprises, particularly over access to power-rich data centers and future capacity constraints.
“The biggest concern that CIOs should have with this acquisition is that mature data center infrastructure with dedicated power is an acquisition target,” said Hyoun Park, CEO and chief analyst at Amalgam Insights. “This may turn out to create challenges for CIOs currently collocating data workloads or seeking to keep more of their data loads on private data centers rather than in the cloud.”