In an AI-driven world of exponential compute demand, Aligned Data Centers is meeting the moment not just with scale, but with intent.
The company’s recent blitz of strategic announcements, led by plans for a transformative new campus on legacy industrial land in Ohio, offers a composite image of what it means to build data center infrastructure for the AI era: rapid, resilient, regionally targeted, and relentlessly sustainable.
From converting a former coal power plant site into a hub for digital progress in Coshocton County, to achieving new heights of energy efficiency in Phoenix, to enabling liquid-cooled, NVIDIA-accelerated AI deployments with Lambda in Dallas, Aligned is assembling a modular, AI-optimized framework designed to meet both today’s and tomorrow’s computational extremes.
Ohio Expansion: A New Chapter for Conesville, and for Aligned
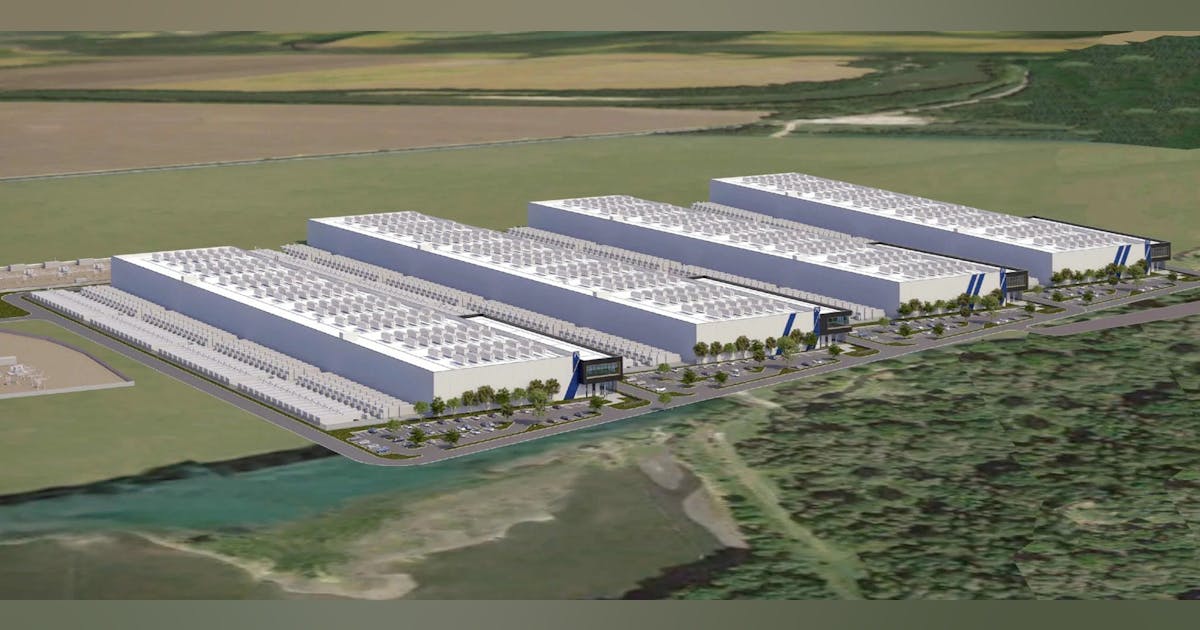
Announced July 24, Aligned’s newest mega-scale data center campus in Central Ohio will rise on a 197-acre parcel adjacent to the retired AEP Conesville coal-fired power plant, a brownfield site that once symbolized legacy energy and is now poised to power the future of digital infrastructure.
As noted by Andrew Schaap, CEO of Aligned Data Centers:
“Through this strategic expansion, Aligned not only reinforces its commitment to providing future-ready digital infrastructure in vital growth markets but also directly catalyzes billions of dollars in investment for the state of Ohio and the Coshocton County community.”
It’s a project with deep regional implications. The phased, multi-billion dollar development is expected to create thousands of construction jobs and hundreds of high-quality, long-term operational roles, while generating significant tax revenues that will support local services and infrastructure improvements.
The campus has already secured a foundational customer, with the first facility targeting initial capacity delivery in mid-2026.
This marks Aligned’s third campus in Ohio, a clear indication that the company sees the Buckeye State, with its abundant power, fiber routes, and shifting regulatory incentives, as fertile ground for AI and hyperscale growth.
But in Conesville, there’s also a deeper resonance: a shift from industrial legacy to digital future, grounded in economic revitalization.
Sustainability by Design: Phoenix Earns Triple Green Globes
As Aligned scales, the company is simultaneously sharpening its sustainability credentials. Nowhere is that more evident than in Phoenix, where its recently completed PHX-06 facility has earned a Three Green Globes® rating from the Green Building Initiative (GBI) — one of the highest levels of recognition for resource efficiency, environmental performance, and occupant wellness in new construction.
“As the global demand for AI and high-performance computing continues to accelerate, we’re continuously looking for new ways to increase the efficiency and sustainability of our data centers,” said Schaap. “This certification not only validates the exceptionally high standards we set for environmentally responsible design and construction; it underscores our unmatched speed of delivery, which enables massive, future-proof scalability across the Americas.”
PHX-06 earned its rating through a range of sustainability innovations, including reduced water usage, efficient energy systems, 100% renewable power sourcing, and a core architectural strategy centered on Aligned’s Adaptive Modular Infrastructure (AMI).
The AMI model utilizes standardized, prefabricated building components, minimizing waste, accelerating timelines, and dramatically reducing Scope 3 emissions typically generated during onsite construction.
“Achieving this level of sustainability is an outstanding accomplishment,” noted GBI CEO Vicki Worden. “Aligned continues to demonstrate its leadership in sustainability with its exceptional outcomes in energy efficiency, water conservation, carbon emissions reduction, and occupant health.”
As the highest certifying data center developer in the GBI program to date, Aligned is building a reputation not just for how quickly it can deliver infrastructure, but also for how responsibly it builds it.
Thermal Intelligence: Advanced Cooling Lab Pushes R&D for GPU Heat Loads
In the AI era, power is only half the equation. Heat is the other half.
In June, Aligned unveiled its new Advanced Cooling Lab, a Phoenix-based R&D facility dedicated to refining the company’s approach to air, liquid, and hybrid cooling strategies for next-generation GPUs and AI accelerators.
Aligned’s cooling ecosystem combines its patented Delta Cube™ air-cooled technology with its patent-pending DeltaFlow~™ liquid-cooled system. The new lab allows both to operate in tandem within hybrid environments, demonstrating how Aligned customers can fluidly scale from traditional air-cooled racks to high-density liquid cooling in the same data hall as workloads evolve.
“The Advanced Cooling Lab is a testament to our commitment to delivering cutting-edge data center solutions,” said Aligned CTO Michael Welch. “By investing in research and development, we can continue to provide our customers with the most flexible and advanced infrastructure available, capable of handling the dynamic demands of AI workloads.”
In sum, Aligned’s cooling technologies do more than just dissipate heat — they enable density, accelerate deployment, and extend infrastructure lifespan, all while supporting extreme performance tiers like NVIDIA’s Blackwell architecture.
Combined with its AMI platform, the new lab demonstrates Aligned’s readiness to meet compute demands that scale not just linearly, but exponentially.
Lambda Partnership: GPU Cloud Meets AI-First Data Center Fabric
If the cooling lab is Aligned’s engine of innovation, its recently announced partnership with Lambda is a high-performance test drive.
In May, Lambda — which is becoming known as the AI Developer Cloud trusted by leading engineers and startups alike — announced it would occupy Aligned’s new DFW-04 facility in Plano, Texas. The new data center is engineered from the ground up to support high-density, liquid-cooled GPUs, including infrastructure accelerated by NVIDIA’s Blackwell and Blackwell Ultra platforms.
“Deploying AI at scale is no easy feat,” said Ken Patchett, VP of Data Center Infrastructure at Lambda. “With its unrelenting focus on driving disruptive innovation in data center design, energy efficiency and cooling, Aligned is the ideal partner.”
The partnership is emblematic of a deeper alignment between cloud-native AI infrastructure providers and forward-leaning data center operators. It also underscores the growing need for AI-specialized facilities that can deliver not just kilowatts, but cooling, flexibility, and seamless scalability at the highest compute tiers.
Aligned CEO Schaap noted, “Particularly in Dallas, where demand for AI computation space has spiked, combining a GPU cloud built specifically for AI workloads with an AI-ready data center designed with liquid cooling technologies will be a game changer.”
Conclusion: Infrastructure That Adapts as Fast as AI Evolves
So, spanning from a coal-fired past in Conesville to liquid-cooled futures in Plano, we see from these data points how Aligned is stitching together a data center platform not only built for speed and scale, but grounded in long-term sustainability, modularity, and technical vision.
The company’s strategy involves a fusion of real estate, advanced cooling, supply chain precision, and AI-aligned customer partnerships. This vision positions it as a vanguard builder in a world where digital infrastructure is increasingly inseparable from the future of industry, innovation, and economic development.
As generative AI, HPC, and GPU-based platforms push density to new extremes, Aligned Data Centers is ensuring the infrastructure beneath them evolves just as fast … and just as intelligently.