Dive Brief:
- Clean technology and renewable energy company Ameresco secured a $140 million energy savings performance contract award from the U.S. General Services Administration to cut purchased energy and water use at the Denver Federal Center, according to a Jan. 13 news release.
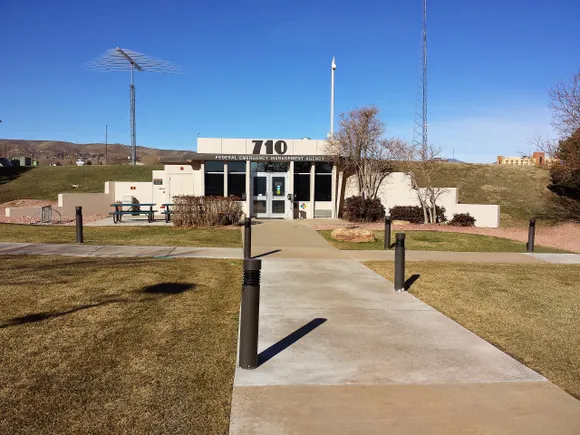
- The contract covers the addition of a centralized geothermal heat pump system and a solar photovoltaic system to supply year-round heating, cooling and electrical power to the 623-acre complex, which has 44 buildings used by 28 federal agencies.
- The future of the contract could be in question, however, due to an executive order President Donald J. Trump issued on his first day in office pausing the disbursement of funds from the Inflation Reduction Act, the source of the contract’s funding, and the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act.
Dive Insight:
In addition to the planned geothermal and solar systems, the project will electrify about half of the Denver Federal Center, install new windows and implement other energy conservation measures. The ESPC is expected to cut grid purchased energy at the complex by approximately 51% and water usage by approximately 10%. GSA said in the press release this would result in more than $2 million in cost savings in the first year.
“Fifty percent of their energy bill is serious money, so you can easily do a cost benefit [analysis] on that,” said Jennifer Perkins, the government industry specialist at Siemens subsidiary Brightly, a maker of software for asset lifecycle management. A project of that size also can create a lot of jobs, she said, noting she is not involved in the project.
In an energy savings performance contract, the contracted company conducts an energy audit of the facilities and designs and constructs a project based on its findings. As of Jan. 16, the GSA had obligated $416 million in total for ESPCs, according to an agency spokesperson.
Funding for the Denver Federal Center is part of $3.4 billion the IRA allocated to the GSA to “build, modernize and maintain more sustainable and cost-efficient high-performance facilities” that utilize low-embodied-carbon materials and help achieve net-zero emissions across the federal building portfolio by 2045, according to the release.
“These investments are a prime example of how Inflation Reduction Act investments get us a triple-win: creating good jobs, saving taxpayer dollars through energy efficiency, and ensuring a healthier, brighter future for our communities and our kids,” then-GSA Administrator Robin Carnahan stated in the news release.
In a 2023 blog post, the GSA had announced plans to invest almost $975 million from the IRA in emerging and sustainable technologies in federal buildings. In a Jan. 15 blog post, the agency stated that by leveraging private-sector funds through ESPCs, it could more than double that planned investment to $1.9 billion. The two blog posts have since been removed from the agency’s website.
But after campaigning against the IRA, the Biden administration’s signature climate legislation, Trump’s “Unleashing American Energy” executive order Jan. 20 paused the disbursement of Inflation Reduction Act funds. A separate Jan. 27 memo from the Office of Management and Budget ordered a pause on all federal grants and loans, starting at 5 p.m. Jan. 28, “including, but not limited to … the green new deal,” according to the memo.
Two federal judges temporarily blocked the effort with temporary restraining orders Jan. 28, leading OMB to rescind the memo on Jan. 29. However, White House Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt posted on X shortly after the memo was rescinded that “This is NOT a rescission of the federal funding freeze. It is simply a rescission of the OMB memo. … The President’s EO’s on federal funding remain in full force and effect, and will be rigorously implemented.”
Judge Jack McConnell of the U.S. District Court of Rhode Island issued another temporary restraining order Jan. 30 in response to Leavitt’s message, stating, in part, that “If Defendants engage in the ‘[identification] and review’ of federal financial assistance programs, as identified in the OMB Directive, such exercise shall not affect a pause, freeze, impediment, block, cancellation, or termination of Defendants’ compliance with such awards and obligations, except on the basis of the applicable authorizing statutes, regulations, and terms.”
On Feb. 7, the plaintiffs in that case filed another motion for a preliminary injunction, stating that “Despite the clear terms of the [temporary restraining order], the Government took the position in communication on February 5 that IIJA and IRA funds were excluded from the relief. This position and the ongoing freeze of numerous important funding streams … leave Plaintiff States uncertain as to the security of billions of dollars of critical resources for their residents.”
On Monday, the judge granted the motion, stating in part that “The Defendants must immediately restore withheld funds, including those federal funds appropriated in the Inflation Reduction Act and the 5 Infrastructure Improvement and Jobs Act.”
The General Services Administration and Ameresco did not respond to requests for comment.