Join our daily and weekly newsletters for the latest updates and exclusive content on industry-leading AI coverage. Learn More
DeepSeek AI, a Chinese research lab gaining recognition for its powerful open-source language models such as DeepSeek-R1, has introduced a significant advancement in reward modeling for large language models (LLMs).
Their new technique, Self-Principled Critique Tuning (SPCT), aims to create generalist and scalable reward models (RMs). This could potentially lead to more capable AI applications for open-ended tasks and domains where current models can’t capture the nuances and complexities of their environment and users.
The crucial role and current limits of reward models
Reinforcement learning (RL) has become a cornerstone in developing state-of-the-art LLMs. In RL, models are fine-tuned based on feedback signals that indicate the quality of their responses.
Reward models are the critical component that provides these signals. Essentially, an RM acts as a judge, evaluating LLM outputs and assigning a score or “reward” that guides the RL process and teaches the LLM to produce more useful responses.
However, current RMs often face limitations. They typically excel in narrow domains with clear-cut rules or easily verifiable answers. For example, current state-of-the-art reasoning models such as DeepSeek-R1 underwent an RL phase, in which they were trained on math and coding problems where the ground truth is clearly defined.
However, creating a reward model for complex, open-ended, or subjective queries in general domains remains a major hurdle. In the paper explaining their new technique, researchers at DeepSeek AI write, “Generalist RM requires to generate high-quality rewards beyond specific domains, where the criteria for rewards are more diverse and complex, and there are often no explicit reference or ground truth.”
They highlight four key challenges in creating generalist RMs capable of handling broader tasks:
- Input flexibility: The RM must handle various input types and be able to evaluate one or more responses simultaneously.
- Accuracy: It must generate accurate reward signals across diverse domains where the criteria are complex and the ground truth is often unavailable.
- Inference-time scalability: The RM should produce higher-quality rewards when more computational resources are allocated during inference.
- Learning scalable behaviors: For RMs to scale effectively at inference time, they need to learn behaviors that allow for improved performance as more computation is used.
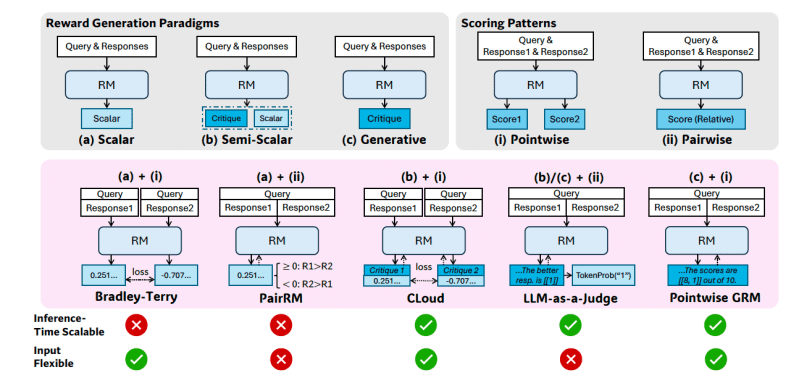
Reward models can be broadly classified by their “reward generation paradigm” (e.g., scalar RMs outputting a single score, generative RMs producing textual critiques) and their “scoring pattern” (e.g., pointwise scoring assigns individual scores to each response, pairwise selects the better of two responses). These design choices affect the model’s suitability for generalist tasks, particularly its input flexibility and potential for inference-time scaling.
For instance, simple scalar RMs struggle with inference-time scaling because they will generate the same score repeatedly, while pairwise RMs can’t easily rate single responses.
The researchers propose that “pointwise generative reward modeling” (GRM), where the model generates textual critiques and derives scores from them, can offer the flexibility and scalability required for generalist requirements.
The DeepSeek team conducted preliminary experiments on models like GPT-4o and Gemma-2-27B, and found that “certain principles could guide reward generation within proper criteria for GRMs, improving the quality of rewards, which inspired us that inference-time scalability of RM might be achieved by scaling the generation of high-quality principles and accurate critiques.”
Training RMs to generate their own principles
Based on these findings, the researchers developed Self-Principled Critique Tuning (SPCT), which trains the GRM to generate principles and critiques based on queries and responses dynamically.
The researchers propose that principles should be a “part of reward generation instead of a preprocessing step.” This way, the GRMs could generate principles on the fly based on the task they are evaluating and then generate critiques based on the principles.
“This shift enables [the] principles to be generated based on the input query and responses, adaptively aligning [the] reward generation process, and the quality and granularity of the principles and corresponding critiques could be further improved with post-training on the GRM,” the researchers write.
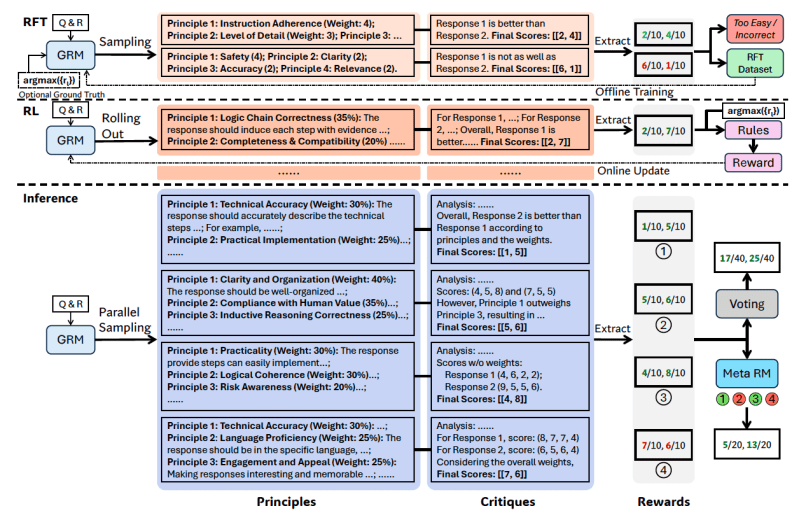
SPCT involves two main phases:
- Rejective fine-tuning: This phase trains the GRM to generate principles and critiques for various input types using the correct format. The model generates principles, critiques and rewards for given queries/responses. Trajectories (generation attempts) are accepted only if the predicted reward aligns with the ground truth (correctly identifying the better response, for instance) and rejected otherwise. This process is repeated and the model is fine-tuned on the filtered examples to improve its principle/critique generation capabilities.
- Rule-based RL: In this phase, the model is further fine-tuned through outcome-based reinforcement learning. The GRM generates principles and critiques for each query, and the reward signals are calculated based on simple accuracy rules (e.g., did it pick the known best response?). Then the model is updated. This encourages the GRM to learn how to generate effective principles and accurate critiques dynamically and in a scalable way.
“By leveraging rule-based online RL, SPCT enables GRMs to learn to adaptively posit principles and critiques based on the input query and responses, leading to better outcome rewards in general domains,” the researchers write.
To tackle the inference-time scaling challenge (getting better results with more compute), the researchers run the GRM multiple times for the same input, generating different sets of principles and critiques. The final reward is determined by voting (aggregating the sample scores). This allows the model to consider a broader range of perspectives, leading to potentially more accurate and nuanced final judgments as it is provided with more resources.
However, some generated principles/critiques might be low-quality or biased due to model limitations or randomness. To address this, the researchers introduced a “meta RM”—a separate, lightweight scalar RM trained specifically to predict whether a principle/critique generated by the primary GRM will likely lead to a correct final reward.
During inference, the meta RM evaluates the generated samples and filters out the low-quality judgments before the final voting, further enhancing scaling performance.
Putting SPCT into practice with DeepSeek-GRM
The researchers applied SPCT to Gemma-2-27B, Google’s open-weight model, creating DeepSeek-GRM-27B. They evaluated it against several strong baseline RMs (including LLM-as-a-Judge, scalar RMs, and semi-scalar RMs) and public models (like GPT-4o and Nemotron-4-340B-Reward) across multiple benchmarks.
They found that DeepSeek-GRM-27B outperformed baseline methods trained on the same data. SPCT significantly improved the quality and, crucially, the inference-time scalability compared to standard fine-tuning.
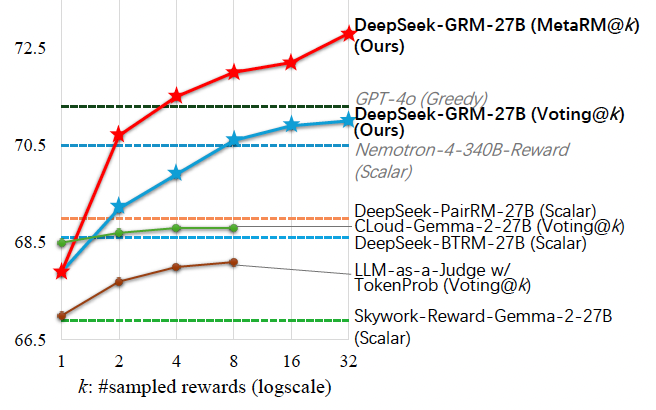
When scaled at inference time by generating more samples, DeepSeek-GRM-27B’s performance increased substantially, surpassing even much larger models like Nemotron-4-340B-Reward and GPT-4o. The meta RM further improved the scaling, achieving the best results by filtering judgments.
“With larger-scale sampling, DeepSeek-GRM could judge more accurately upon principles with higher diversity, and output rewards with finer granularity,” the researchers write.
Interestingly, SPCT showed less bias across different domains compared to scalar RMs, which often performed well on verifiable tasks but poorly elsewhere.
Implications for the enterprise
Developing more generalist and scalable reward models can be promising for enterprise AI applications. Potential areas that can benefit from generalist RMs include creative tasks and applications where the model must adapt to dynamic environments such as evolving customer preferences.
Despite the strong results, DeepSeek-GRM still lags behind specialized scalar RMs on purely verifiable tasks where explicit reasoning generation might be less efficient than direct scoring. Efficiency also remains a challenge compared to non-generative RMs.
The DeepSeek team suggests future work will focus on efficiency improvements and deeper integration. As they conclude, “Future directions could include integrating GRMs into online RL pipelines as versatile interfaces of reward systems, exploring inference-time co-scaling with policy models, or serving as robust offline evaluators for foundation models.”
Daily insights on business use cases with VB Daily
If you want to impress your boss, VB Daily has you covered. We give you the inside scoop on what companies are doing with generative AI, from regulatory shifts to practical deployments, so you can share insights for maximum ROI.
Read our Privacy Policy
Thanks for subscribing. Check out more VB newsletters here.
An error occured.