Join our daily and weekly newsletters for the latest updates and exclusive content on industry-leading AI coverage. Learn More
Thanks to the rapid advances in AI-powered security copilots, security operations centers (SOCs) are seeing false positive rates drop by up to 70% while saving over 40 hours a week of manual triage.
The latest generation of copilots has moved far beyond chat interfaces. These agentic AI systems are capable of real-time remediation, automated policy enforcement and integrated triage across cloud, endpoint and network domains. Purpose-built to integrate within SIEM, SOAR and XDR pipelines, they’re making solid contributions to improving SOC accuracy, efficiency and speed of response.
Microsoft launched six new Security Copilot agents today—including ones for phishing triage, insider risk, conditional access, vulnerability remediation, and threat intelligence—alongside five partner-built agents, as detailed in Vasu Jakkal’s blog post.
Quantifiable gains in SOC performance are growing. Mean-time-to-restore is improving by 20% or more, and threat detection times have dropped by at least 30% in SOCs deploying these technologies. When copilots are used, KPMG reports a 43% boost in triage accuracy among junior analysts.
SOC analysts tell VentureBeat on condition of anonymity how frustrating their jobs are when they have to interpret multiple systems’ alerts and manually triage every intrusion alert.
Swivel chair integration is alive and well in many SOCs today, and while it saves on software costs, it burns out the best analysts and leaders. Burnout should not be dismissed as an isolated issue that only happens in SOCs that have analysts doing back-to-back shifts because they’re short-handed. It’s far more pervasive than security leaders realize.
More than 70% of SOC analysts say they’re burned out, with 66% reporting that half their work is repetitive enough to be automated. Additionally, nearly two-thirds are planning to switch roles by 2025 and the need to make the most of AI’s rapid gains in automating SOCs becomes unavoidable.
AI security copilots are gaining traction as more organizations confront the challenges of keeping their SOCs efficient and staffed well enough to contain threats. The latest generation of AI security copilots don’t just accelerate response, they’re proving indispensable in training and retaining staff eliminating rote, routine work while opening new opportunities for SOC analysts to learn and earn more.
“I do get asked a lot well does that mean you know what SOC analysts are gonna be out of business? No. You know what it means? It means that you can take tier one analysts and turn them into tier three, you can take the eight hours of mundane work and turn it into 10 minutes,” George Kurtz, founder and CEO of CrowdStrike said at the company’s Fal.Con event last year.
“The way forward is not to eliminate the human element, but to empower humans with AI assistants,” says Ivanti CIO Robert Grazioli, emphasizing how AI copilots reduce repetitive tasks and free analysts to focus on complex threats. Grazioli added, “analyst burnout is driven by repetitive tasks and a continuous flood of low-fidelity alerts. AI copilots cut through this noise, letting experts tackle the toughest issues.” Ivanti’s research finds that organizations embracing AI triage can reduce false positives by up to 70%.
Vineet Arora, CTO for WinWire agrees, telling VentureBeat that, “the ideal approach is typically to use AI as a force multiplier for human analysts rather than a replacement. For example, AI can handle initial alert triage and routine responses to security issues, allowing analysts to focus their expertise on sophisticated threats and strategic work. The human team should maintain oversight of AI systems while leveraging them to reduce mundane workload.”
Ivanti’s 2025 State of Cybersecurity Report found that despite 89% of boards calling security a priority, their latest research reveals gaps in organizations’ ability to defend against high-risk threats. About half of the security executives interviewed, 54%, say generative ATI (gen AI) security is their top budget priority for this year.
The goal: turn massive amounts of real-time, raw telemetry into insights
By their nature, SOCs are continually flooded with data comprised mainly of endpoint logs, firewall events logs, identity change notices and logs and, for many, new behavioral analytics reports.
AI security copilots are proving effective in separating the signals that matter from noise. Controlling the signal-to-noise ratio increases a SOC team’s accuracy, insights and speed of response.
Instead of drowning in alerts, SOC teams are responding to prioritized, high-fidelity incidents that can be triaged automatically.
CrowdStrike’s Charlotte AI processes over 1 trillion high-fidelity signals daily from the Falcon platform and is trained on millions of real-world analyst decisions. It autonomously triages endpoint detections with over 98% agreement with human experts, saving teams an average of 40+ hours of manual work per week.
Microsoft Security Copilot customers are reporting that they’re saving up to 40% of their security analysts’ time on foundational tasks including investigation and response, threat hunting and threat intelligence assessments. On more mundane tasks such as preparing reports or troubleshooting minor issues, Security Copilot delivered gains in efficiency up to and above 60%.
In the following diagram, Gartner defines how Microsoft Copilot for Security manages user prompts, built-in and third-party security plugins, in addition to large language model (LLM) processing within a responsible AI framework.
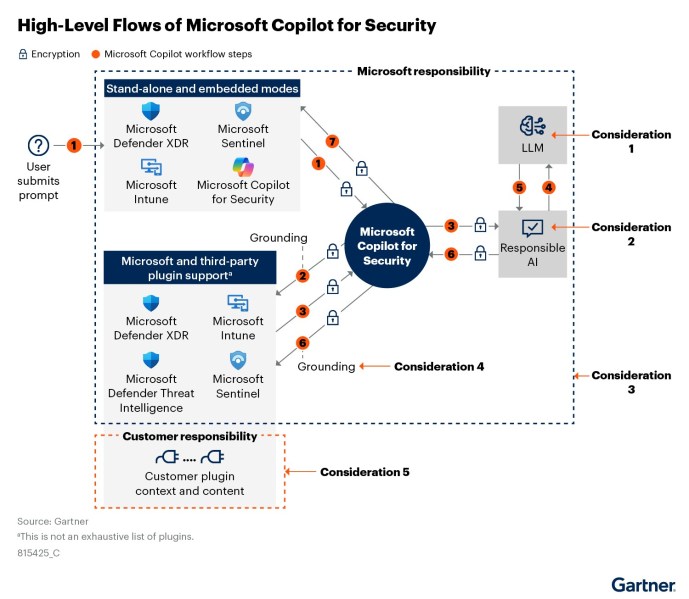
Like CrowdStrike, nearly every AI security copilot provider emphasizes using AI to augment and strengthen the SOC team’s skills rather than replacing people with copilots.
Nir Zuk, founder and CTO of Palo Alto Networks told VentureBeat recently that “our AI-powered platforms don’t aim to remove analysts from the loop; they unify the SOC workflow so analysts can do their jobs more strategically.” Similarly, Jeetu Patel, Cisco’s EVP and GM of security and collaboration, said, “AI’s real value is how it narrows the talent gap in cybersecurity—not by automating analysts out of the picture, but by making them exponentially more effective.”
Charting the rapid rise of AI security copilots
AI security copilots are rapidly reshaping how mid-sized enterprises detect, investigate and neutralize threats. VentureBeat tracks this expanding ecosystem, where each solution advances automated triage, cloud-native coverage and predictive threat intelligence.
Below is a snapshot of today’s top copilots, highlighting their differentiators, telemetry focus and real-world gains. VentureBeat’s Security Copilot Guide (Google Sheet) provides a complete matrix with 16 vendors’ AI security copilots.
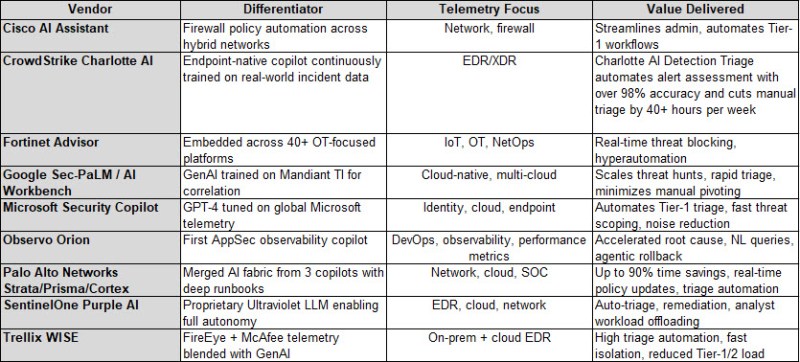
CrowdStrike Charlotte, SentinelOne’s Purple AI and Trellix WISE are already triaging, isolating and remediating threats without human intervention. Google and Microsoft are embedding risk scoring, auto-mitigation and cross-cloud attack surface mapping into their copilots.
Google’s recent acquisition of Wiz will significantly impact AI security copilot adoption as part of a broader CNAPP strategy in many organizations.
Platforms such as Observo Orion illustrate what’s next: agentic copilots unifying DevOps, observability, and security data to deliver proactive, automated defenses. Rather than just detecting threats, they orchestrate complex workflows, including code rollbacks or node isolation, bridging security, development and operations in the process.
The endgame isn’t just about smart, prompt-driven personal programming assistants; it’s about integrating AI-driven decision-making across SOC workflows.
AI security copilots’ leading use cases today
The better a given use case can integrate into SOC analysts’ workflows, the greater its potential to scale and deliver strong value. Core to the scale of an AI security copilot’s architecture is the ability to ingest data from heterogeneous telemetry sources and identify decisions early in the process, keeping them in context.
Here’s where adoption is scaling the fastest:
Accelerating triage: Tier-1 analysts using copilots, including Microsoft Security Copilot and Charlotte AI, can reduce triage to minutes instead of many hours. This is possible due to pre-trained models that flag known tactics, techniques and procedures (TTPs), cross-reference threat intel and summarize findings with confidence scores.
Alert de-duplication and noise suppression: Observo Orion and Trellix WISE use contextual filtering to correlate multi-source telemetry, eliminating low-priority noise. This reduces alert fatigue by as much as 70%, freeing teams to focus on high-fidelity signals. Sophos XDR AI Assistant achieves similar results for mid-sized SOCs with smaller teams.
Policy enforcement and firewall tuning: Cisco AI Assistant and Palo Alto’s Cortex copilots dynamically suggest and auto-implement policy changes based on telemetry thresholds and anomaly detection. This is critical for SOCs with complex, distributed firewall topologies and zero-trust mandates.
Cross-domain correlation: Security Copilot (Microsoft) and SentinelOne Purple AI integrate identity telemetry, SIEM logs and endpoint data to detect lateral movement, privilege escalation, or suspicious multi-hop activity. Analysts receive contextual playbooks that reduce root cause analysis by over 40%.
Exposure validation and breach simulation: Cymulate AI Copilot emulates red-team logic and tests exposure against new CVEs, enabling SOCs to validate controls proactively. This replaces manual validation steps with automated posture testing integrated into SOAR workflows.
Natural language SIEM interaction: Exabeam Copilot and Splunk AI Assistant allow analysts to convert natural language queries into executable SIEM commands. This democratizes investigation capabilities, especially for less technical staff, and reduces dependency on deep query language knowledge.
Identity risk reduction: Oleria Copilot continuously scans for dormant accounts, excessive access rights, and unlinked entitlements. These copilots auto-generate cleanup plans and enforce least-privilege policies, helping reduce insider threat surface in hybrid environments.
Bottom Line: Copilots don’t replace analysts, they amplify and scale their experience and strengths
By integrating identity, endpoint and network telemetry, copilots reduce the time it takes to identify lateral movement and privilege escalation, two of the most dangerous phases in an attack chain. As Elia Zaitsev, CTO of CrowdStrike, explained to VentureBeat in an earlier conversation: it’s less about substituting human roles, and more about supporting and augmenting them.
AI-powered tools should be viewed as collaborative partners for people — a concept that is especially crucial in cybersecurity. Zaitsev cautioned that focusing on completely replacing human professionals rather than working alongside them is a misguided strategy.
Daily insights on business use cases with VB Daily
If you want to impress your boss, VB Daily has you covered. We give you the inside scoop on what companies are doing with generative AI, from regulatory shifts to practical deployments, so you can share insights for maximum ROI.
Read our Privacy Policy
Thanks for subscribing. Check out more VB newsletters here.
An error occured.