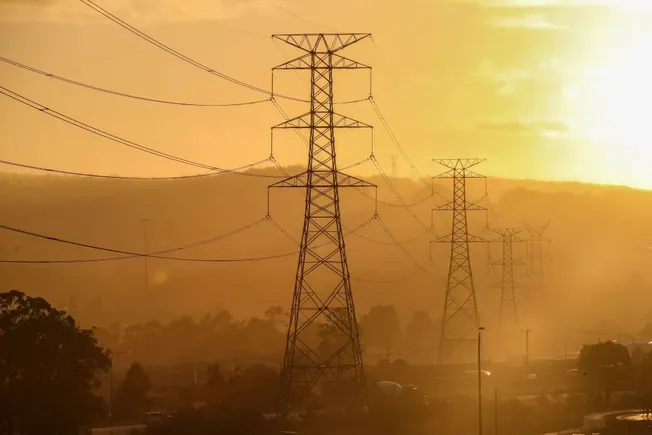
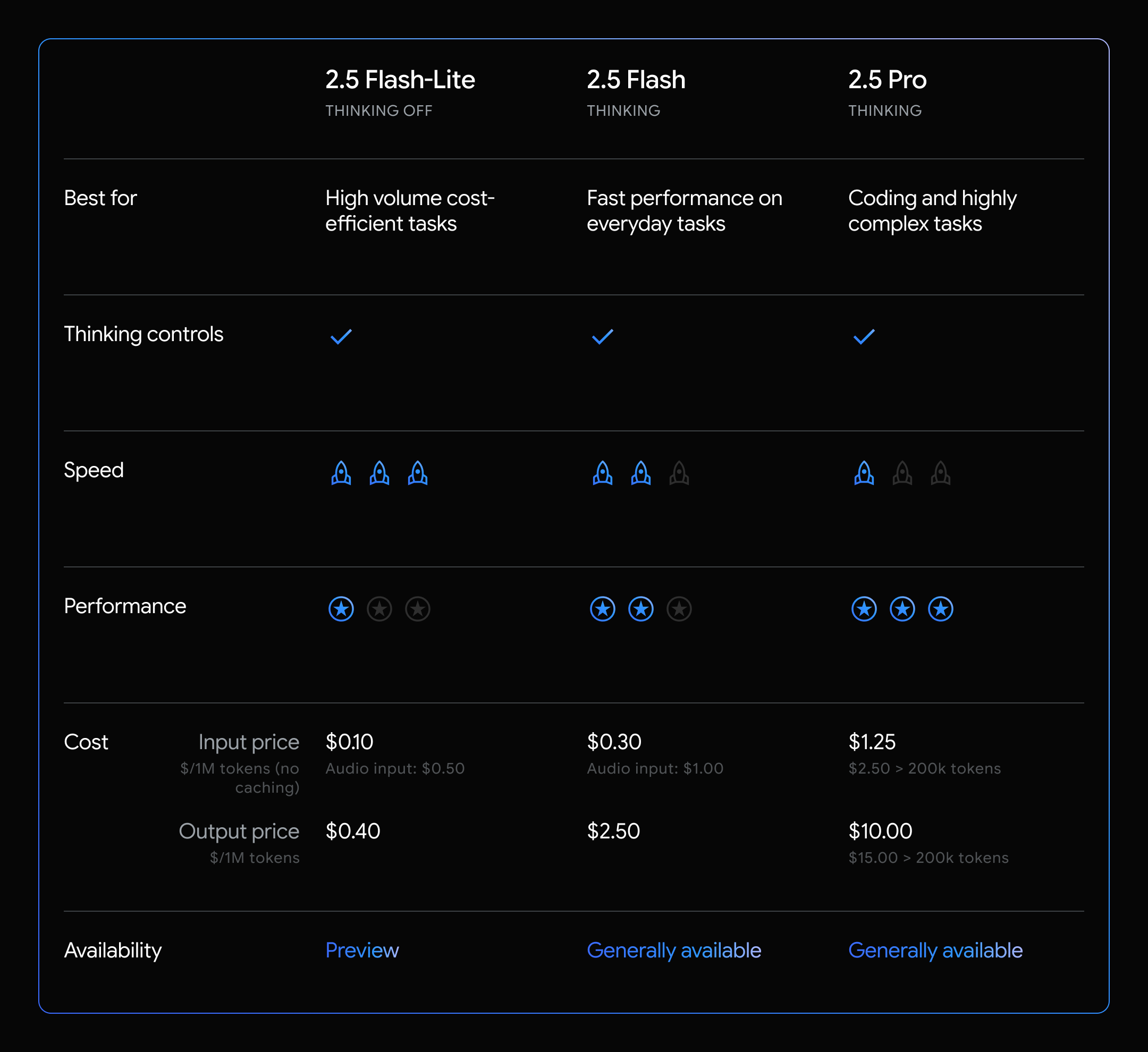
Google and conductor manufacturer CTC Global on Tuesday said they are partnering to ask states, utilities and transmission developers to identify areas to deploy advanced conductors, which can carry more power than standard transmission lines but use existing towers and poles.
Responses to a request for information are due on July 14, and a request for proposals will “shortly follow,” Google and CTC Global said in a release shared in advance with Utility Dive. “Applications are encouraged from areas where Google has existing or announced data centers, as well as their associated wholesale markets,” the release states.
The partnership will focus on U.S. transmission lines that have the most potential to accelerate grid capacity using CTC Global’s conductors, and it will prioritize projects that would “deliver the greatest immediate impact and that support load growth where Google operates,” the release said.
Advanced conductors are one of the alternative transmission technologies that the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission’s Order 1920 requires transmission providers “in each transmission planning region to consider more fully.”
FERC said in an explainer that the order’s goal “is to identify efficient and cost-effective solutions to meet transmission needs and optimize the transmission system without the need to build additional transmission facilities.”
Google and CTC Global invited states, utilities and transmission developers to start responding to the RFI immediately. They said “selected partners and projects” will gain access to cost assistance, workforce training on the deployment of CTC Global’s ACCC conductors and “support for technical project studies … to validate the technology’s integration and impact.”
CTC Global CEO J.D. Sitton said in the release that the partnership is a “positive turning point to lower electricity costs, generate economic growth, and advance U.S. energy dominance … [helping] ensure that the U.S. invests in cost-effective solutions for the long-term that help the U.S. continue to lead the AI revolution.”