Join our daily and weekly newsletters for the latest updates and exclusive content on industry-leading AI coverage. Learn More
Meta — parent company of Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, Threads and more —runs one of the biggest recommendation systems in the world.
In two recently released papers, its researchers have revealed how generative models can be used to better understand and respond to user intent.
By looking at recommendations as a generative problem, you can tackle it in new ways that are richer in content and more efficient than classic approaches. This approach can have important uses for any application that requires retrieving documents, products, or other kinds of objects.
Dense vs generative retrieval
The standard approach to creating recommendation systems is to compute, store, and retrieve dense representations of documents. For example, to recommend items to users, an application must train a model that can compute embeddings for both users and items. Then it must create a large store of item embeddings.
At inference time, the recommendation system tries to understand the user’s intent by finding one or more items whose embeddings are similar to the user’s. This approach require an increasing amount of storage and computation capacity as the number of items grows because every item embedding must be stored and every recommendation operation requires comparing the user embedding against the entire item store.
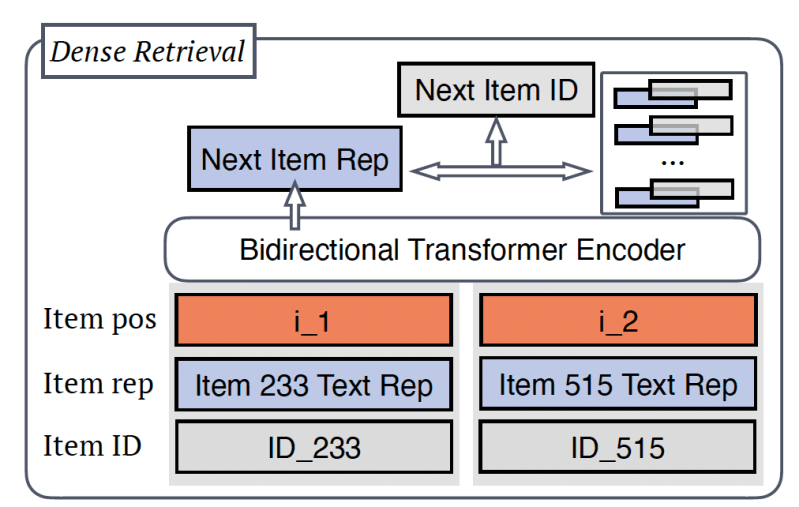
Generative retrieval is a more recent approach that tries to understand user intent and make recommendations by predicting the next item in a sequence instead of searching a database. Generative retrieval does not require storing item embeddings and its inference and storage costs remain constant as the list of items grows.
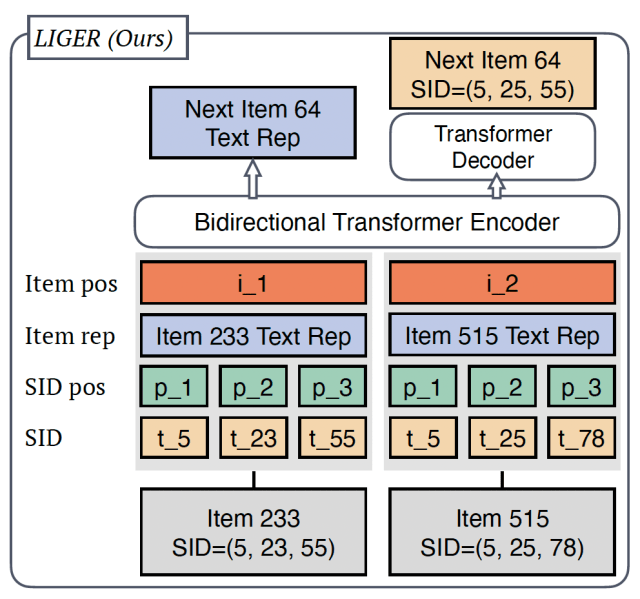
The key to making generative retrieval work is to compute “semantic IDs” (SIDs) which contain the contextual information about each item. Generative retrieval systems like TIGER work in two phases. First, an encoder model is trained to create a unique embedding value for each item based on its description and properties. These embedding values become the SIDs and are stored along with the item.
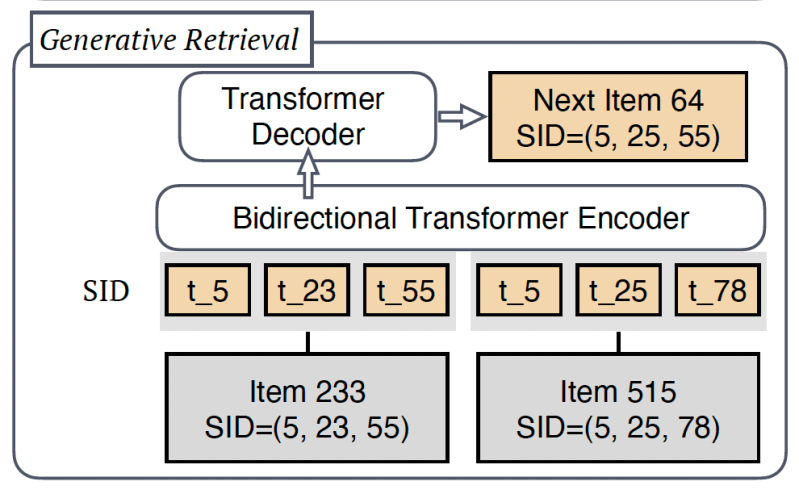
In the second stage, a Transformer model is trained to predict the next SID in an input sequence. The list of input SIDs represents the user’s interactions with past items and the model’s prediction is the SID of the item to recommend. Generative retrieval reduces the need for storing and searching across individual item embeddings. It also enhances the ability to capture deeper semantic relationships within the data and provides other benefits of generative models, such as modifying the temperature to adjust the diversity of recommendations.
Advanced generative retrieval
Despite its lower storage and inference costs, generative retrieval suffers from some limitations. For example, it tends to overfit to the items it has seen during training, which means it has trouble dealing with items that were added to the catalog after the model was trained. In recommendation systems, this is often referred to as “the cold start problem,” which pertains to users and items that are new and have no interaction history.
To address these shortcomings, Meta has developed a hybrid recommendation system called LIGER, which combines the computational and storage efficiencies of generative retrieval with the robust embedding quality and ranking capabilities of dense retrieval.
During training, LIGER uses both similarity score and next-token goals to improve the model’s recommendations. During inference, LIGER selects several candidates based on the generative mechanism and supplements them with a few cold-start items, which are then ranked based on the embeddings of the generated candidates.
The researchers note that “the fusion of dense and generative retrieval methods holds tremendous potential for advancing recommendation systems” and as the models evolve, “they will become increasingly practical for real-world applications, enabling more personalized and responsive user experiences.”
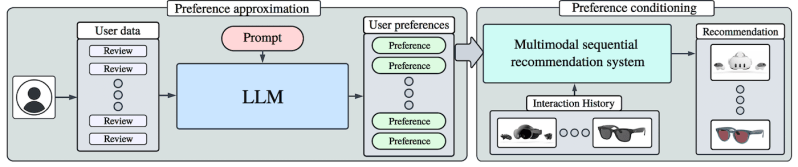
In a separate paper, the researchers introduce a novel multimodal generative retrieval method named Multimodal preference discerner (Mender), a technique that can enable generative models to pick up implicit preferences from user’s interactions with different items. Mender builds on top of the generative retrieval methods based on SIDs and adds a few components that can enrich recommendations with user preferences.
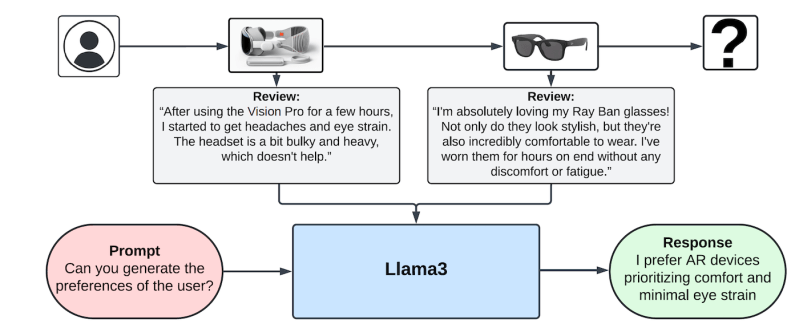
Mender uses a large language model (LLM) to translate user interactions into specific preferences. For example, if the user has praised or complained about a specific item in a review, the model will summarize it into a preference about that product category.
The main recommender model is trained to be conditioned both on the sequence of user interactions and the user preferences when predicting the next semantic ID in the input sequence. This gives the recommender model the ability to generalize and perform in-context learning and adapt to user preferences without being explicitly trained on them.
“Our contributions pave the way for a new class of generative retrieval models that unlock the ability to utilize organic data for steering recommendation via textual user preferences,” the researchers write.
Implications for enterprise applications
The efficiency provided by generative retrieval systems can have important implications for enterprise applications. These advancements translate into immediate practical benefits, including reduced infrastructure costs and faster inference. The technology’s ability to maintain constant storage and inference costs regardless of catalog size makes it particularly valuable for growing businesses.
The benefits extend across industries, from e-commerce to enterprise search. Generative retrieval is still in its early stages and we can expect applications and frameworks to emerge as it matures.
Daily insights on business use cases with VB Daily
If you want to impress your boss, VB Daily has you covered. We give you the inside scoop on what companies are doing with generative AI, from regulatory shifts to practical deployments, so you can share insights for maximum ROI.
Read our Privacy Policy
Thanks for subscribing. Check out more VB newsletters here.
An error occured.