This article is part of VentureBeat’s special issue, “The cyber resilience playbook: Navigating the new era of threats.” Read more from this special issue here.
Procrastinating about patching has killed more networks and damaged more companies than any zero-day exploit or advanced cyberattack.
Complacency kills — and carries a high price. Down-rev (having old patches in place that are “down revision”) or no patching at all is how ransomware gets installed, data breaches occur and companies are fined for being out of compliance. It isn’t a matter of if a company will be breached but when — particularly if they don’t prioritize patch management.
Why so many security teams procrastinate – and pay a high price
Let’s be honest about how patching is perceived in many security teams and across IT organizations: It’s often delegated to staff members assigned with the department’s most rote, mundane tasks. Why? No one wants to spend their time on something that is often repetitive and at times manually intensive, yet requires complete focus to get done right.
Most security and IT teams tell VentureBeat in confidence that patching is too time-consuming and takes away from more interesting projects. That’s consistent with an Ivanti study that found that the majority (71%) of IT and security professionals think patching is overly complex, cumbersome and time-consuming.
Remote work and decentralized workspaces make patching even more complicated, 57% of security professionals reported. Also consistent with what VentureBeat is hearing from security teams, Ivanti found that 62% of IT and security leaders admit that patch management takes a backseat to other tasks.
The truth is that device inventory and manual approaches to patch management haven’t been keeping up for a while (years). In the meantime, adversaries are busy improving their tradecraft, creating weaponized large language models (LLMs) and attack apps.
Not patching? It’s like taking the lock off your front door
Crime waves are hitting affluent, gated communities as criminals use remote video cameras for 24/7 surveillance. Leaving a home unlocked without a security system is an open invitation for robbers.
Not patching endpoints is the same. And, let’s be honest: Any task that gets deprioritized and pushed down action item lists will most likely never be entirely completed. Adversaries are improving their tradecrafts all the time by studying common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVEs) and finding lists of companies that have those vulnerabilities — making them even more susceptible targets.
Gartner often weighs in on patching in their research and considers it part of their vulnerability management coverage. Their recent study, Top 5 Elements of Effective Vulnerability Management, emphasizes that “many organizations still mismanage patching exceptions, resulting in missing or ineffective mitigations and increased risk.”
Mismanagement starts when teams deprioritize patching and consider manual processes “good enough” to complete increasingly complex, challenging and mundane tasks. This is made worse with siloed teams. Such mismanagement creates exploitable gaps. The old mantra “scan, patch, rescan” isn’t scaling when adversaries are using AI and generative AI attacks to scan for endpoints to target at machine speed.
GigaOm’s Radar for Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) report further highlights how patching remains a significant challenge, with many vendors struggling to provide consistent application, device driver and firmware patching. The report urges organizations to consider how they can improve patch management as part of a broader effort to automate and scale vulnerability management.
Why traditional patch management fails in today’s threat landscape
Patch management in most organizations begins with scheduled monthly cycles that rely on static Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) severity scores to help prioritize vulnerabilities. Adversaries are moving faster and creating more complex threats than CVSS scores can keep up with.
As Karl Triebes, Ivanti’s CPO, explained: “Relying solely on severity ratings and a fixed monthly cycle exposes organizations to unaccounted risk. These ratings overlook unique business context, security gaps and evolving threats.” In today’s fast-moving environment, static scores cannot capture an organization’s nuanced risk profile.
Gartner’s framework underscores the need for “advanced prioritization techniques and automated workflows that integrate asset criticality and active threat data to direct limited resources toward vulnerabilities that truly matter.” The GigaOm report similarly notes that, while most UEM solutions support OS patching, fewer provide “patching for third-party applications, device drivers and firmware,” leaving gaps that adversaries exploit.
Risk-based and continuous patch management: A smarter approach
Chris Goettl, Ivanti’s VP of product management for endpoint security, explained to VentureBeat: “Risk-based patch prioritization goes beyond CVSS scores by considering active exploitation, threat intelligence and asset criticality.” Taking this more dynamic approach helps organizations anticipate and react to risks in real time, which is far more efficient than using CVSS scores.
Triebes expanded: “Relying solely on severity ratings and a fixed monthly cycle exposes organizations to unaccounted risk. These ratings overlook your unique business context, security gaps and evolving threats.” However, prioritization alone isn’t enough.
Adversaries can quickly weaponize vulnerabilities within hours and have proven that genAI is making them even more efficient than in the past. Ransomware attackers find new ways to weaponize old vulnerabilities. Organizations following monthly or quarterly patching cycles can’t keep up with the pace of new tradecraft.
Machine learning (ML)-based patch management systems have long been able to prioritize patches based on current threats and business risks. Regular maintenance ensures compliance with PCI DSS, HIPAA and GDPR, while AI automation bridges the gap between detection and response, reducing exposure.
Gartner warns that relying on manual processes creates “bottlenecks, delays zero-day response and results in lower-priority patches being applied while actively exploited vulnerabilities remain unaddressed.” Organizations must shift to continuous, automated patching to keep pace with adversaries.
Choosing the right patch management solution
There are many advantages of integrating gen AI and improving long-standing ML algorithms that are at the core of automated patch management systems. All vendors who compete in the market have roadmaps incorporating these technologies.
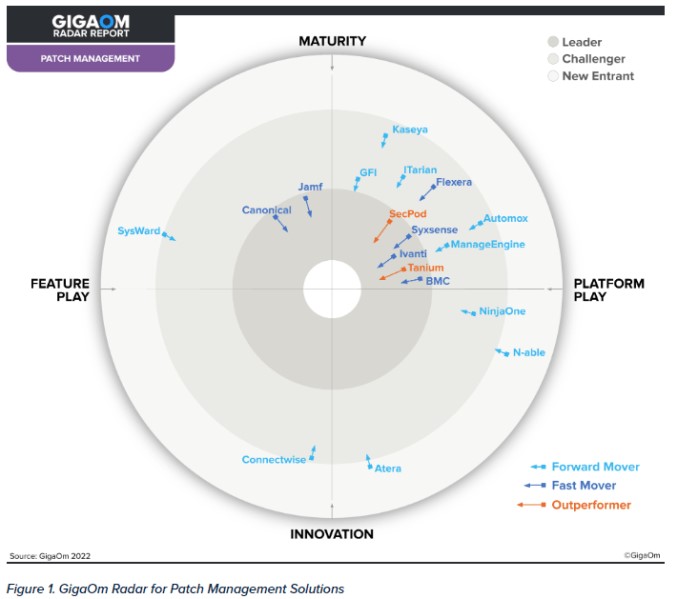
The GigaOm Radar for Patch Management Solutions Report highlights the technical strengths and weaknesses of top patch management providers. It compares vendors including Atera, Automox, BMC client management patch powered by Ivanti, Canonical, ConnectWise, Flexera, GFI, ITarian, Jamf, Kaseya, ManageEngine, N-able, NinjaOne, SecPod, SysWard, Syxsense and Tanium.
Gartner advises security teams to “leverage risk-based prioritization and automated workflow tools to reduce time-to-patch,” and every vendor in this market is reflecting that in their roadmaps. A strong patching strategy requires the following:
- Strategic deployment and automation: Mapping critical assets and reducing manual errors through AI-driven automation.
- Risk-based prioritization: Focusing on actively exploited threats.
- Centralized management and continuous monitoring: Consolidating patching efforts and maintaining real-time security visibility.
By aligning patching strategies with these principles, organizations can reduce their teams’ workloads and build stronger cyber resilience.
Automating patch management: Measuring success in real time
All vendors who compete in this market have attained a baseline level of performance and functionality by streamlining patch validation, testing and deployment. By correlating patch data with real-world exploit activity, vendors are reducing customers’ mean time to remediation (MTTR).
Measuring success is critical. Gartner recommends tracking the following (at a minimum):
- Mean-time-to-patch (MTTP): The average time to remediate vulnerabilities.
- Patch coverage percentage: The proportion of patched assets relative to vulnerable ones.
- Exploit window reduction: The time from vulnerability disclosure to remediation.
- Risk reduction impact: The number of actively exploited vulnerabilities patched before incidents occur.
Automate patch management — or fall behind
Patching isn’t the action item security teams should just get to after other higher-priority tasks are completed. It must be core to keeping a business alive and free of potential threats.
Simply put, patching is at the heart of cyber resilience. Yet, too many organizations deprioritize it, leaving known vulnerabilities wide open for attackers increasingly using AI to strike faster than ever. Static CVSS scores have proven they can’t keep up, and fixed cycles have turned into more of a liability than an asset.
The message is simple: When it comes to patching, complacency is dangerous — it’s time to make it a priority.