Addressing the challenge
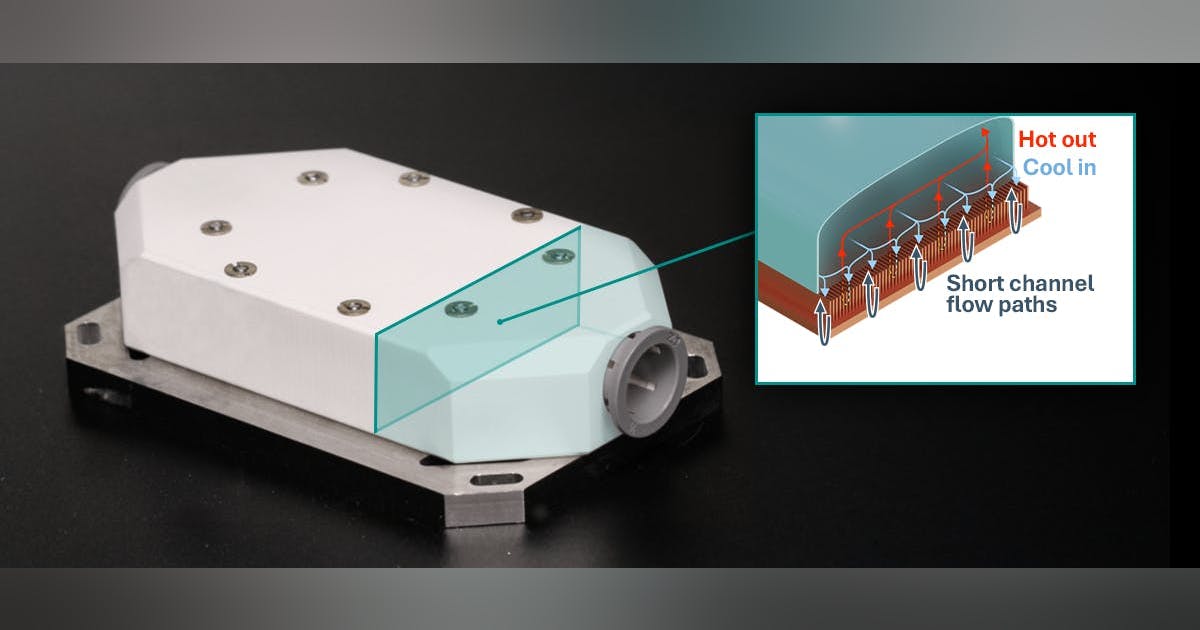
Modern AI accelerators now draw more than 700W per GPU, and multi-GPU nodes can reach 6kW, creating concentrated heat zones, rapid power swings, and a higher risk of interconnect degradation in dense racks, according to Manish Rawat, semiconductor analyst at TechInsights.
Traditional cooling methods and static power planning increasingly struggle to keep pace with these loads.
“Rich vendor telemetry covering real-time power draw, bandwidth behavior, interconnect health, and airflow patterns shifts operators from reactive monitoring to proactive design,” Rawat said. “It enables thermally aware workload placement, faster adoption of liquid or hybrid cooling, and smarter network layouts that reduce heat-dense traffic clusters.”
Rawat added that the software’s fleet-level configuration insights can also help operators catch silent errors caused by mismatched firmware or driver versions. This can improve training reproducibility and strengthen overall fleet stability.
“Real-time error and interconnect health data also significantly accelerates root-cause analysis, reducing MTTR and minimizing cluster fragmentation,” Rawat said.
These operational pressures can shape budget decisions and infrastructure strategy at the enterprise level.