Join our daily and weekly newsletters for the latest updates and exclusive content on industry-leading AI coverage. Learn More
SAN JOSE, Calif. — Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang took to the stage at the SAP Center on Tuesday morning, leather jacket intact and without a teleprompter, to deliver what has become one of the most anticipated keynotes in the technology industry. The GPU Technology Conference (GTC) 2025, self-described by Huang as the “Super Bowl of AI,” arrives at a critical juncture for Nvidia and the broader artificial intelligence sector.
“What an amazing year it was, and we have a lot of incredible things to talk about,” Huang told the packed arena, addressing an audience that has grown exponentially as AI has transformed from a niche technology into a fundamental force reshaping entire industries. The stakes were particularly high this year following market turbulence triggered by Chinese startup DeepSeek‘s release of its highly efficient R1 reasoning model, which sent Nvidia’s stock tumbling earlier this year amid concerns about potential reduced demand for its expensive GPUs.
Against this backdrop, Huang delivered a comprehensive vision of Nvidia’s future, emphasizing a clear roadmap for data center computing, advancements in AI reasoning capabilities, and bold moves into robotics and autonomous vehicles. The presentation painted a picture of a company working to maintain its dominant position in AI infrastructure while expanding into new territories where its technology can create value. Nvidia’s stock traded down throughout the presentation, closing more than 3% lower for the day, suggesting investors may have hoped for even more dramatic announcements.
But if Huang’s message was clear, it was this: AI isn’t slowing down, and neither is Nvidia. From groundbreaking chips to a push into physical AI, here are the five most important takeaways from GTC 2025.
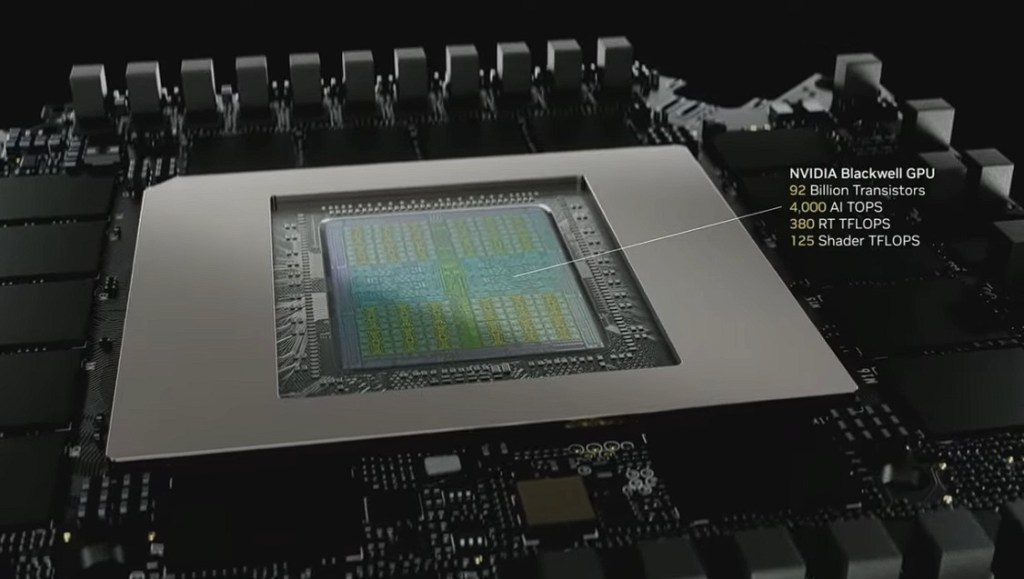
Blackwell platform ramps up production with 40x performance gain over Hopper
The centerpiece of Nvidia’s AI computing strategy, the Blackwell platform, is now in “full production,” according to Huang, who emphasized that “customer demand is incredible.” This is a significant milestone after what Huang had previously described as a “hiccup” in early production.
Huang made a striking comparison between Blackwell and its predecessor, Hopper: “Blackwell NVLink 72 with Dynamo is 40 times the AI factory performance of Hopper.” This performance leap is particularly crucial for inference workloads, which Huang positioned as “one of the most important workloads in the next decade as we scale out AI.”
The performance gains come at a critical time for the industry, as reasoning AI models like DeepSeek‘s R1 require substantially more computation than traditional large language models. Huang illustrated this with a demonstration comparing a traditional LLM’s approach to a wedding seating arrangement (439 tokens, but wrong) versus a reasoning model’s approach (nearly 9,000 tokens, but correct).
“The amount of computation we have to do in AI is so much greater as a result of reasoning AI and the training of reasoning AI systems and agentic systems,” Huang explained, directly addressing the challenge posed by more efficient models like DeepSeek’s. Rather than positioning efficient models as a threat to Nvidia’s business model, Huang framed them as driving increased demand for computation — effectively turning a potential weakness into a strength.
Next-generation Rubin architecture unveiled with clear multi-year roadmap
In a move clearly designed to give enterprise customers and cloud providers confidence in Nvidia’s long-term trajectory, Huang laid out a detailed roadmap for AI computing infrastructure through 2027. This is an unusual level of transparency about future products for a hardware company, but reflects the long planning cycles required for AI infrastructure.
“We have an annual rhythm of roadmaps that has been laid out for you so that you could plan your AI infrastructure,” Huang stated, emphasizing the importance of predictability for customers making massive capital investments.
The roadmap includes Blackwell Ultra coming in the second half of 2025, offering 1.5 times more AI performance than the current Blackwell chips. This will be followed by Vera Rubin, named after the astronomer who discovered dark matter, in the second half of 2026. Rubin will feature a new CPU that’s twice as fast as the current Grace CPU, along with new networking architecture and memory systems.
“Basically everything is brand new, except for the chassis,” Huang explained about the Vera Rubin platform.
The roadmap extends even further to Rubin Ultra in the second half of 2027, which Huang described as an “extreme scale up” offering 14 times more computational power than current systems. “You can see that Rubin is going to drive the cost down tremendously,” he noted, addressing concerns about the economics of AI infrastructure.
This detailed roadmap serves as Nvidia’s answer to market concerns about competition and sustainability of AI investments, effectively telling customers and investors that the company has a clear path forward regardless of how AI model efficiency evolves.
Nvidia Dynamo emerges as the ‘operating system’ for AI factories
One of the most significant announcements was Nvidia Dynamo, an open-source software system designed to optimize AI inference. Huang described it as “essentially the operating system of an AI factory,” drawing a parallel to how traditional data centers rely on operating systems like VMware to orchestrate enterprise applications.
Dynamo addresses the complex challenge of managing AI workloads across distributed GPU systems, handling tasks like pipeline parallelism, tensor parallelism, expert parallelism, in-flight batching, disaggregated inferencing, and workload management. These technical challenges have become increasingly important as AI models grow more complex and reasoning-based approaches require more computation.
The system gets its name from the dynamo, which Huang noted was “the first instrument that started the last Industrial Revolution, the industrial revolution of energy.” The comparison positions Dynamo as a foundational technology for the AI revolution.
By making Dynamo open source, Nvidia is attempting to strengthen its ecosystem and ensure its hardware remains the preferred platform for AI workloads, even as software optimization becomes increasingly important for performance and efficiency. Partners including Perplexity are already working with Nvidia on Dynamo implementation.
“We’re so happy that so many of our partners are working with us on it,” Huang said, specifically highlighting Perplexity as “one of my favorite partners” due to “the revolutionary work that they do.”
The open-source approach is a strategic move to maintain Nvidia’s central position in the AI ecosystem while acknowledging the importance of software optimization in addition to raw hardware performance.
Physical AI and robotics take center stage with open-source Groot N1 model
In what may have been the most visually striking moment of the keynote, Huang unveiled a significant push into robotics and physical AI, culminating with the appearance of “Blue,” a Star Wars-inspired robot that walked onto the stage and interacted with Huang.
Meet Blue (Star Wars droid) after announcing NVIDIA partnership with DeepMind and Disney. pic.twitter.com/yLcdouF5XC
— Brian Roemmele (@BrianRoemmele) March 18, 2025
“By the end of this decade, the world is going to be at least 50 million workers short,” Huang explained, positioning robotics as a solution to global labor shortages and a massive market opportunity.
The company announced Nvidia Isaac Groot N1, described as “the world’s first open, fully customizable foundation model for generalized humanoid reasoning and skills.” Making this model open source represents a significant move to accelerate development in the robotics field, similar to how open-source LLMs have accelerated general AI development.
Alongside Groot N1, Nvidia announced a partnership with Google DeepMind and Disney Research to develop Newton, an open-source physics engine for robotics simulation. Huang explained the need for “a physics engine that is designed for very fine-grain, rigid and soft bodies, designed for being able to train tactile feedback and fine motor skills and actuator controls.”
The focus on simulation for robot training follows the same pattern that has proven successful in autonomous driving development, using synthetic data and reinforcement learning to train AI models without the limitations of physical data collection.
“Using Omniverse to condition Cosmos, and Cosmos to generate an infinite number of environments, allows us to create data that is grounded, controlled by us and yet systematically infinite at the same time,” Huang explained, describing how Nvidia’s simulation technologies enable robot training at scale.
These robotics announcements represent Nvidia’s expansion beyond traditional AI computing into the physical world, potentially opening up new markets and applications for its technology.
GM partnership signals major push into autonomous vehicles and industrial AI
Rounding out Nvidia’s strategy of extending AI from data centers into the physical world, Huang announced a significant partnership with General Motors to “build their future self-driving car fleet.”
“GM has selected Nvidia to partner with them to build their future self-driving car fleet,” Huang announced. “The time for autonomous vehicles has arrived, and we’re looking forward to building with GM AI in all three areas: AI for manufacturing, so they can revolutionize the way they manufacture; AI for enterprise, so they can revolutionize the way they work, design cars, and simulate cars; and then also AI for in the car.”
This partnership is a significant vote of confidence in Nvidia’s autonomous vehicle technology stack from America’s largest automaker. Huang noted that Nvidia has been working on self-driving cars for over a decade, inspired by the breakthrough performance of AlexNet in computer vision competitions.
“The moment I saw AlexNet was such an inspiring moment, such an exciting moment, it caused us to decide to go all in on building self-driving cars,” Huang recalled.
Alongside the GM partnership, Nvidia announced Halos, described as “a comprehensive safety system” for autonomous vehicles. Huang emphasized that safety is a priority that “rarely gets any attention” but requires technology “from silicon to systems, the system software, the algorithms, the methodologies.”
The automotive announcements extend Nvidia’s reach from data centers to factories and vehicles, positioning the company to capture value throughout the AI stack and across multiple industries.
The architect of AI’s second act: Nvidia’s strategic evolution beyond chips
GTC 2025 revealed Nvidia’s transformation from GPU manufacturer to end-to-end AI infrastructure company. Through the Blackwell-to-Rubin roadmap, Huang signaled Nvidia won’t surrender its computational dominance, while its pivot toward open-source software (Dynamo) and models (Groot N1) acknowledges hardware alone can’t secure its future.
Nvidia has cleverly reframed the DeepSeek efficiency challenge, arguing more efficient models will drive greater overall computation as AI reasoning expands—though investors remained skeptical, sending the stock lower despite the comprehensive roadmap.
What sets Nvidia apart is Huang’s vision beyond silicon. The robotics initiative isn’t just about selling chips; it’s about creating new computing paradigms that require massive computational resources. Similarly, the GM partnership positions Nvidia at the center of automotive AI transformation across manufacturing, design, and vehicles themselves.
Huang’s message was clear: Nvidia competes on vision, not just price. As computation extends from data centers into physical devices, Nvidia bets that controlling the full AI stack—from silicon to simulation—will define computing’s next frontier. In Huang’s world, the AI revolution is just beginning, and this time, it’s stepping out of the server room.
Daily insights on business use cases with VB Daily
If you want to impress your boss, VB Daily has you covered. We give you the inside scoop on what companies are doing with generative AI, from regulatory shifts to practical deployments, so you can share insights for maximum ROI.
Read our Privacy Policy
Thanks for subscribing. Check out more VB newsletters here.
An error occured.