Anacortes, Washington-based Pacific Petroleum Operating LLC said it completed its acquisition of a portfolio of oil-producing assets located in Wyoming from a portfolio company of an undisclosed private equity group for a total purchase price of $9.65 million.
The acquisition was made alongside its business associate VCP Operating LLC, according to a news release from Pacific Petroleum, which is a fund of Pacific Bays Capital.
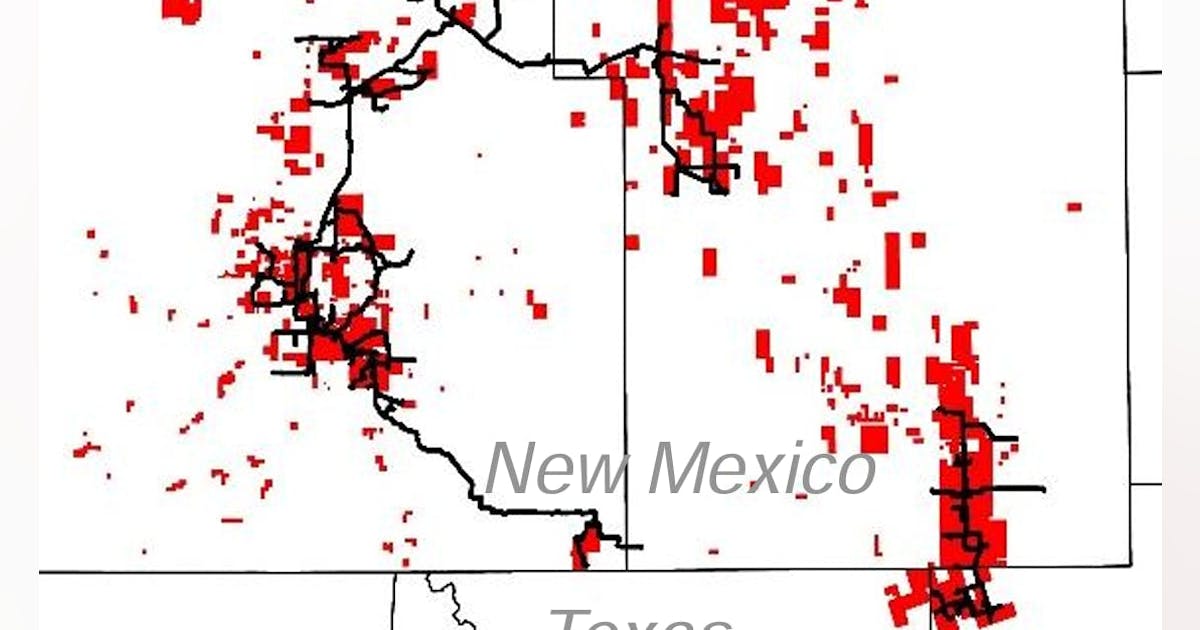
The acquired assets span multiple actively producing fields, including the Hunt, Rose Creek, Shoshone North, and West Oregon Basin fields. The properties are characterized by stable base production, low decline rates, and near-term optimization opportunities, the company said.
The acquisition was formally completed by Delaware-based investment vehicle Pacific Petroleum Holdings LP and was backed by institutional investors from Japan, according to the release.
The structure for Pacific Petroleum leverages a U.S. tax blocker, Pacific Petroleum Blocker LLC, to facilitate cross-border efficiency for its overseas investors, the release said.
Field operations will be managed by VCP Wyoming LLC, an affiliate of VCP Operating and a subsidiary of VCP Michigan, according to the release.
O-DE Capital, a firm specializing in Web3 and fintech-enabled asset management, is advising on the potential integration of next-generation technologies, including real-world asset tokenization, to enhance operational transparency and investor liquidity, the release stated.
Koji Muto, General Partner of Pacific Bays Capital and Director of O-DE Capital, said, “This fund represents the ‘stability’ component of Pacific Bays Capital’s core philosophy of ‘balancing innovation with stability.’ While oil & gas PDP (Proved Developed Producing) assets are legacy investments generating reliable cash flows, their tangible nature makes them exceptionally compatible with digital asset innovations like RWA tokenization. We believe technological advancement could transform these assets into [a] new financial infrastructure. O-DE Capital will fully support the implementation of Web3 technologies to enhance transparency and facilitate secondary market liquidity”.
“Furthermore, PDP investments have traditionally been a ‘closed’ market accessible only to seasoned operators and select private equity funds. Through the combination of technology and institutional framework design, we aim to lower barriers to entry and transform this exclusive domain into an open, accessible market,” Muto added.
Jason Nye, Managing Director of Pacific Petroleum Management LLC, which serves as the general partner for Pacific Petroleum, said, “We are proud to have completed this strategic acquisition that represents a major step forward in our U.S. energy investment strategy. Together with a strong and experienced business associate in VCP Operating, we aim to deliver sustainable value and dependable returns”.
“This acquisition in Wyoming’s prolific resource base comes at a strategically advantageous time. Given the current strength in WTI and the economic resilience of these mature Wyoming oil assets, we see this acquisition as a compelling opportunity to enhance operating margins and long-term project value. Added pressures to global markets from expanding international security risks, especially in the Middle East, could further increase pricing,” Nye added.
Toby Darden, Founder of VCP Operating LLC, said, “VCP brings over three decades of field-level operational experience. We are excited to collaborate with Pacific and leverage our on-the-ground capabilities to unlock further value from this portfolio”.
According to the release, VCP has developed and operated over 64,000 acres in the Michigan Basin, reaching production rates of over 10 million cubic feet per day within its first year of operation.
To contact the author, email [email protected]
WHAT DO YOU THINK?
Generated by readers, the comments included herein do not reflect the views and opinions of Rigzone. All comments are subject to editorial review. Off-topic, inappropriate or insulting comments will be removed.
MORE FROM THIS AUTHOR