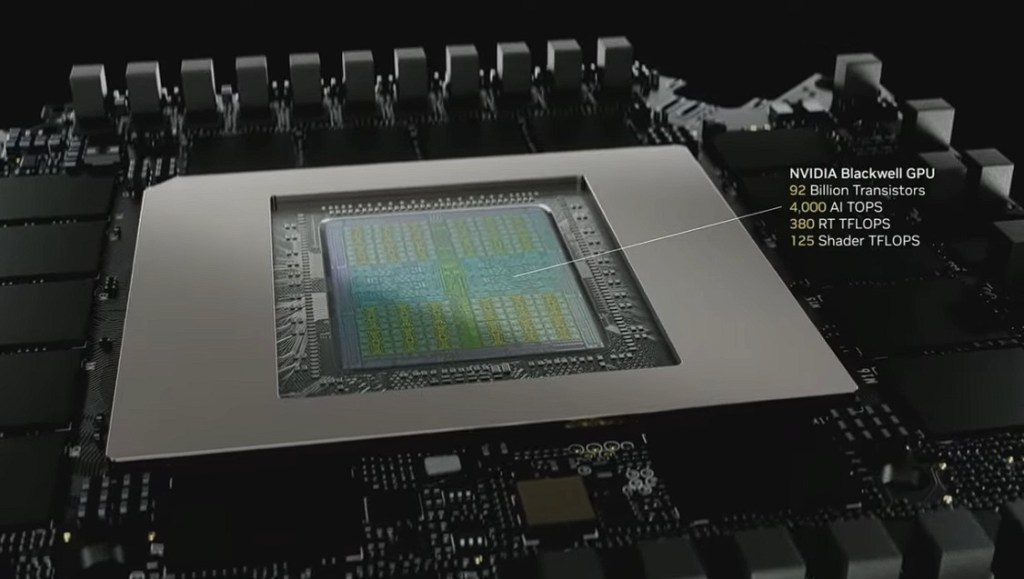
Schneider Electric, a global leader in energy management and automation, has established its Global Innovation Hubs as key centers for technological advancement, collaboration, and sustainable development.
These hub facilities serve as ecosystems where cutting-edge solutions in energy efficiency, industrial automation, and digital transformation are designed, tested, and deployed to address the world’s most pressing energy and sustainability challenges.
Energy Management and Industrial Automation Focus
Strategically located around the world, Schneider Electric’s Global Innovation Hubs are positioned to drive regional and global innovation in energy management and industrial automation.
The hubs focus on developing smart, connected, and sustainable solutions across various sectors, including data centers, smart buildings, industrial automation, and renewable energy.
Key aspects of the Schneider Global Innovation Hubs include:
Collaboration and Co-Innovation: Partnering with startups, industry leaders, and research institutions to accelerate innovation. Fostering an open ecosystem where ideas can be rapidly developed and tested.
Digital Transformation and Automation: Leveraging IoT, AI, and cloud technologies to enhance energy efficiency. Implementing digital twin technology for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency: Developing solutions that contribute to decarbonization and net-zero emissions. Creating energy-efficient systems for buildings, industries, and critical infrastructure.
Customer-focused Innovation: Offering live demonstrations, simulation environments, and test labs for customers. Customizing solutions to meet specific industry challenges and regulatory requirements.
Schneider’s Andover R&D Lab Highlights
While there are 11 hubs worldwide to give the global customer base more convenient locations where they can evaluate Schneider product, the new lab facilities have also been added to one of the company’s five global R&D locations.
The selected location is co-located with Schneider’s US research labs in Andover, Massachusetts. With the addition of these two new labs there are now 41 labs located in Andover. Over the last year, Schneider Electric has invested approximately $2.4 billion in R&D.
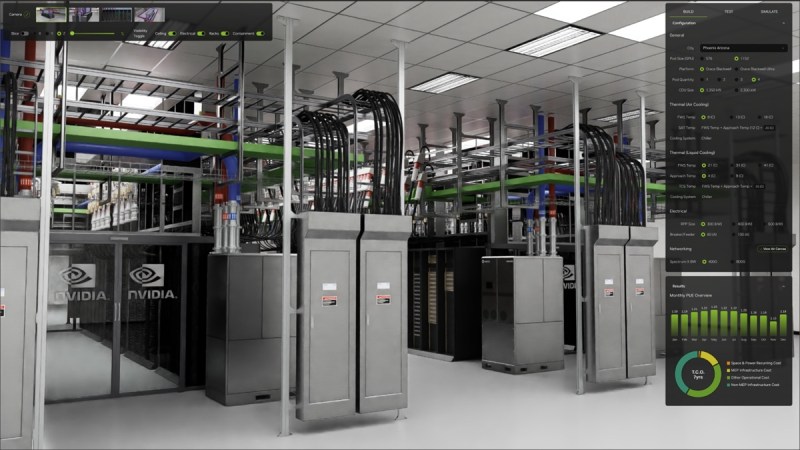
The 53,000 sq ft Innovation Hub Andover sees more than 18,000 annual visitors, and the labs on-site give researchers and customers the opportunity for real world evaluations of the Schneider product line.
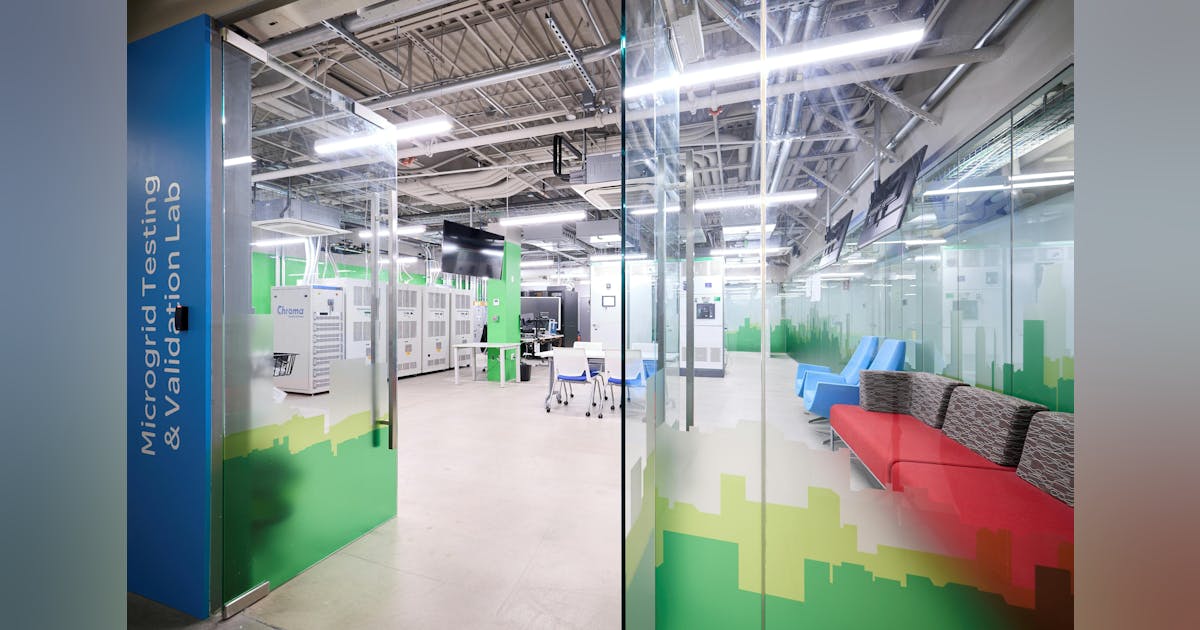
PDU and Microgrid Labs
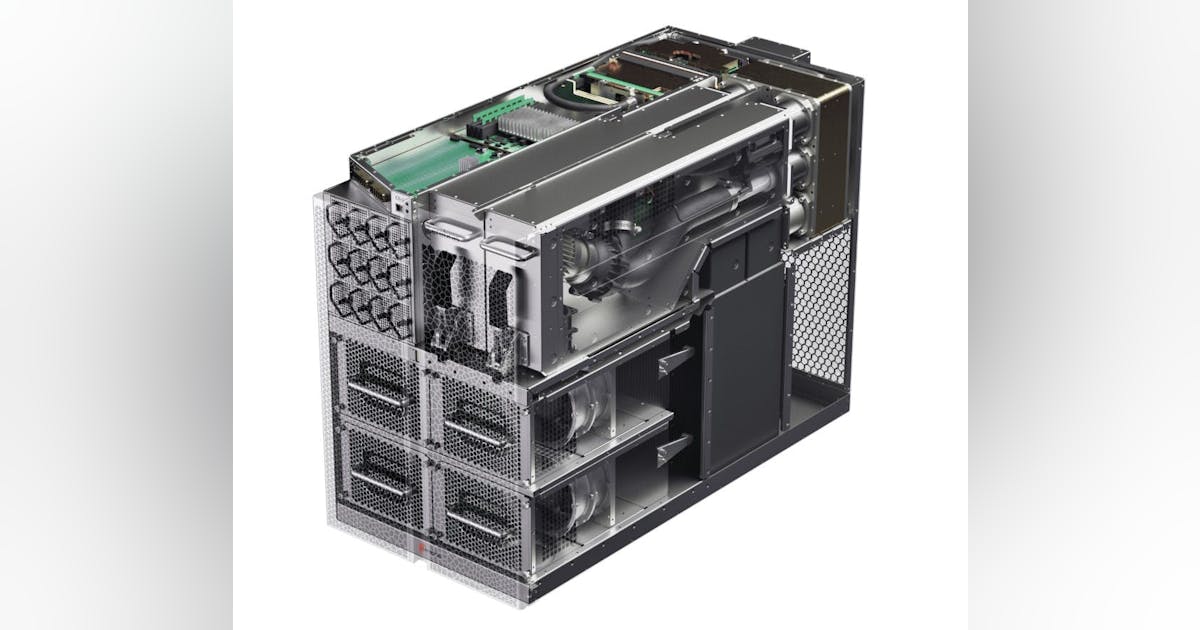
The new Power Distribution Unit laboratory is designed to allow customers and researchers to test the high-powered voltage systems designed for implementing and deploying AI data centers. With 6,000 sq ft of available space divided into three testing bays multiple configurations can be configured and tested to meet the customer requirements.
The Microgrid laboratory is a 1500 sq ft space that includes four 90 kW grid simulators and three 45 kW solar simulators. The four grid simulators are the equivalent of 300 homes using the provided power, while the solar simulators represent the energy demand of 110 homes.
The Andover facility also includes testing capabilities for the Schneider Electric behind-the-meter energy storage system, known as BESS. BESS, a fully self-contained, containerized battery system, is in this case used to simulate energy storage systems to work in conjunction with other services in the hub.
Schneider has significant experience in the microgrid space, having designed, built, and maintained more than 350 microgrid projects. Microgrid projects in the United States have been managing more than 100 GW of power.
About these labs, Pankaj Sharma, Executive Vice President, Data Centers & Networks at Schneider Electric, said: