Britain could be in line for a swathe of new “super-batteries” in the coming years, under plans to boost investment into renewable energy storage.
Regulator Ofgem is launching a new funding scheme to make it less risky to develop and invest in large-scale storage projects, including so-called “water batteries”.
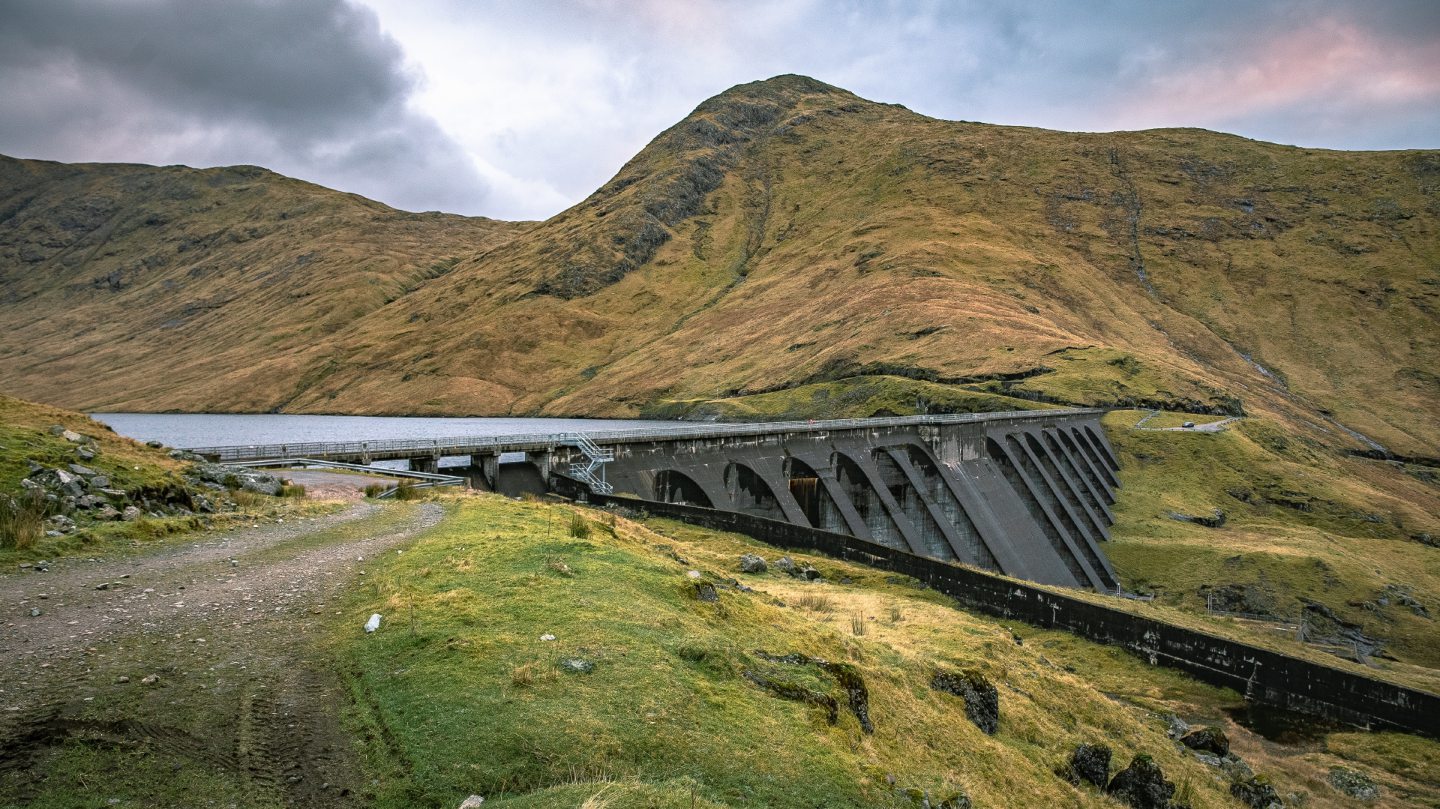
The projects, officially called pumped storage hydropower, are a way of storing energy using reservoirs.
The sites work by buying electricity when it is cheap – for example, when wind turbines are spinning – to pump water uphill from a river or lake, where it is then held at the top.
When electricity is more expensive or at times of higher demand, the hydropower sites release the water back downhill to generate more power for the grid.
The technology is not new and Britain has four such sites already in Scotland and Wales. One at Dinorwig in Snowdonia is nicknamed Electric Mountain.
But no new sites have been built for 40 years because they are expensive to develop, even though operating costs are comparatively low.
Several are in the works, including one at Loch Ness in the Highlands, but officials estimate Britain needs about five times more long duration energy storage capacity to hit net zero by 2050.
Akshay Kaul, director-general for infrastructure at Ofgem, said: “Renewable energy is the key to securing Britain’s energy independence and driving down customer bills in the long term – so it’s vital that none of this precious resource goes to waste.
“By creating the confidence for investors to support new projects such as super-batteries capable of storing the extra electricity created when the wind blows hard and the sun shines strong, we can reduce the need to turn to fossil-fuelled power as back-up when the weather changes.”
Officials hope to make it easier to attract investment with the so-called cap-and-floor financing scheme.
The model guarantees a minimum income for companies that want to develop the projects – the floor – in return for a cap on how much revenue they can generate from the sites.
Now the first window for developers to apply for the scheme is open, and Ofgem expects the first batch of projects to be agreed in the first half of 2026.
Energy minister Michael Shanks said: “Storing renewable electricity is the key to unlocking a clean power system, but it’s been over four decades since a major long duration storage project was built in Britain.”
He said: “This will benefit billpayers and reduce our reliance on dictator-driven fossil fuel markets, as well as creating jobs across the country.”