Popularity of RAG
Over the past two years while working with financial firms, I’ve observed firsthand how they identify and prioritize Generative AI use cases, balancing complexity with potential value.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) often stands out as a foundational capability across many LLM-driven solutions, striking a balance between ease of implementation and real-world impact. By combining a retriever that surfaces relevant documents with an LLM that synthesizes responses, RAG streamlines knowledge access, making it invaluable for applications like customer support, research, and internal knowledge management.
Defining clear evaluation criteria is key to ensuring LLM solutions meet performance standards, just as Test-Driven Development (TDD) ensures reliability in traditional software. Drawing from TDD principles, an evaluation-driven approach sets measurable benchmarks to validate and improve AI workflows. This becomes especially important for LLMs, where the complexity of open-ended responses demands consistent and thoughtful evaluation to deliver reliable results.
For RAG applications, a typical evaluation set includes representative input-output pairs that align with the intended use case. For example, in chatbot applications, this might involve Q&A pairs reflecting user inquiries. In other contexts, such as retrieving and summarizing relevant text, the evaluation set could include source documents alongside expected summaries or extracted key points. These pairs are often generated from a subset of documents, such as those that are most viewed or frequently accessed, ensuring the evaluation focuses on the most relevant content.
Key Challenges
Creating evaluation datasets for RAG systems has traditionally faced two major challenges.
- The process often relied on subject matter experts (SMEs) to manually review documents and generate Q&A pairs, making it time-intensive, inconsistent, and costly.
- Limitations preventing LLMs from processing visual elements within documents, such as tables or diagrams, as they are restricted to handling text. Standard OCR tools struggle to bridge this gap, often failing to extract meaningful information from non-textual content.
Multi-Modal Capabilities
The challenges of handling complex documents have evolved with the introduction of multimodal capabilities in foundation models. Commercial and open-source models can now process both text and visual content. This vision capability eliminates the need for separate text-extraction workflows, offering an integrated approach for handling mixed-media PDFs.
By leveraging these vision features, models can ingest entire pages at once, recognizing layout structures, chart labels, and table content. This not only reduces manual effort but also improves scalability and data quality, making it a powerful enabler for RAG workflows that rely on accurate information from a variety of sources.
Dataset Curation for Wealth Management Research Report
To demonstrate a solution to the problem of manual evaluation set generation, I tested my approach using a sample document — the 2023 Cerulli report. This type of document is typical in wealth management, where analyst-style reports often combine text with complex visuals. For a RAG-powered search assistant, a knowledge corpus like this would likely contain many such documents.
My goal was to demonstrate how a single document could be leveraged to generate Q&A pairs, incorporating both text and visual elements. While I didn’t define specific dimensions for the Q&A pairs in this test, a real-world implementation would involve providing details on types of questions (comparative, analysis, multiple choice), topics (investment strategies, account types), and many other aspects. The primary focus of this experiment was to ensure the LLM generated questions that incorporated visual elements and produced reliable answers.
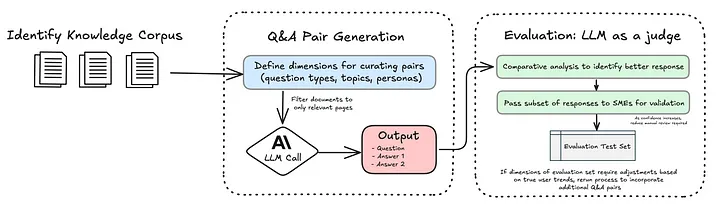
My workflow, illustrated in the diagram, leverages Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet 3.5 model, which simplifies the process of working with PDFs by handling the conversion of documents into images before passing them to the model. This built-in functionality eliminates the need for additional third-party dependencies, streamlining the workflow and reducing code complexity.
I excluded preliminary pages of the report like the table of contents and glossary, focusing on pages with relevant content and charts for generating Q&A pairs. Below is the prompt I used to generate the initial question-answer sets.
You are an expert at analyzing financial reports and generating question-answer pairs. For the provided PDF, the 2023 Cerulli report:1. Analyze pages {start_idx} to {end_idx} and for **each** of those 10 pages:
- Identify the **exact page title** as it appears on that page (e.g., "Exhibit 4.03 Core Market Databank, 2023").
- If the page includes a chart, graph, or diagram, create a question that references that visual element. Otherwise, create a question about the textual content.
- Generate two distinct answers to that question ("answer_1" and "answer_2"), both supported by the page’s content.
- Identify the correct page number as indicated in the bottom left corner of the page.
2. Return exactly 10 results as a valid JSON array (a list of dictionaries). Each dictionary should have the keys: “page” (int), “page_title” (str), “question” (str), “answer_1” (str), and “answer_2” (str). The page title typically includes the word "Exhibit" followed by a number.
Q&A Pair Generation
To refine the Q&A generation process, I implemented a comparative learning approach that generates two distinct answers for each question. During the evaluation phase, these answers are assessed across key dimensions such as accuracy and clarity, with the stronger response selected as the final answer.
This approach mirrors how humans often find it easier to make decisions when comparing alternatives rather than evaluating something in isolation. It’s like an eye examination: the optometrist doesn’t ask if your vision has improved or declined but instead, presents two lenses and asks, Which is clearer, option 1 or option 2? This comparative process eliminates the ambiguity of assessing absolute improvement and focuses on relative differences, making the choice simpler and more actionable. Similarly, by presenting two concrete answer options, the system can more effectively evaluate which response is stronger.
This methodology is also cited as a best practice in the article “What We Learned from a Year of Building with LLMs” by leaders in the AI space. They highlight the value of pairwise comparisons, stating: “Instead of asking the LLM to score a single output on a Likert scale, present it with two options and ask it to select the better one. This tends to lead to more stable results.” I highly recommend reading their three-part series, as it provides invaluable insights into building effective systems with LLMs!
LLM Evaluation
For evaluating the generated Q&A pairs, I used Claude Opus for its advanced reasoning capabilities. Acting as a “judge,” the LLM compared the two answers generated for each question and selected the better option based on criteria such as directness and clarity. This approach is supported by extensive research (Zheng et al., 2023) that showcases LLMs can perform evaluations on par with human reviewers.
This approach significantly reduces the amount of manual review required by SMEs, enabling a more scalable and efficient refinement process. While SMEs remain essential during the initial stages to spot-check questions and validate system outputs, this dependency diminishes over time. Once a sufficient level of confidence is established in the system’s performance, the need for frequent spot-checking is reduced, allowing SMEs to focus on higher-value tasks.
Lessons Learned
Claude’s PDF capability has a limit of 100 pages, so I broke the original document into four 50-page sections. When I tried processing each 50-page section in a single request — and explicitly instructed the model to generate one Q&A pair per page — it still missed some pages. The token limit wasn’t the real problem; the model tended to focus on whichever content it considered most relevant, leaving certain pages underrepresented.
To address this, I experimented with processing the document in smaller batches, testing 5, 10, and 20 pages at a time. Through these tests, I found that batches of 10 pages (e.g., pages 1–10, 11–20, etc.) provided the best balance between precision and efficiency. Processing 10 pages per batch ensured consistent results across all pages while optimizing performance.
Another challenge was linking Q&A pairs back to their source. Using tiny page numbers in a PDF’s footer alone didn’t consistently work. In contrast, page titles or clear headings at the top of each page served as reliable anchors. They were easier for the model to pick up and helped me accurately map each Q&A pair to the right section.
Example Output
Below is an example page from the report, featuring two tables with numerical data. The following question was generated for this page:
How has the distribution of AUM changed across different-sized Hybrid RIA firms?
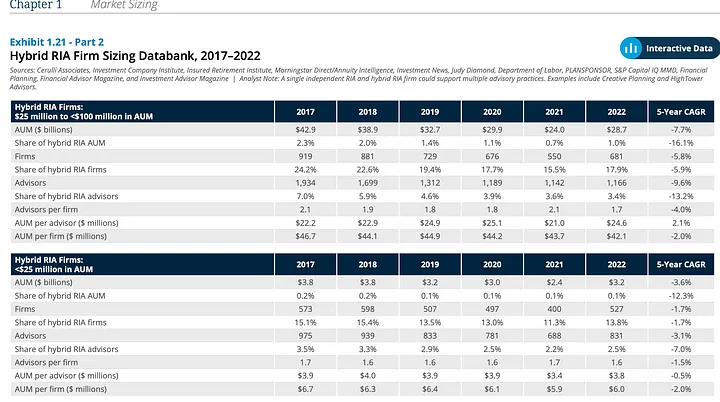
Answer: Mid-sized firms ($25m to <$100m) experienced a decline in AUM share from 2.3% to 1.0%.
In the first table, the 2017 column shows a 2.3% share of AUM for mid-sized firms, which decreases to 1.0% in 2022, thereby showcasing the LLM’s ability to synthesize visual and tabular content accurately.
Benefits
Combining caching, batching and a refined Q&A workflow led to three key advantages:
Caching
- In my experiment, processing a singular report without caching would have cost $9, but by leveraging caching, I reduced this cost to $3 — a 3x cost savings. Per Anthropic’s pricing model, creating a cache costs $3.75 / million tokens, however, reads from the cache are only $0.30 / million tokens. In contrast, input tokens cost $3 / million tokens when caching is not used.
- In a real-world scenario with more than one document, the savings become even more significant. For example, processing 10,000 research reports of similar length without caching would cost $90,000 in input costs alone. With caching, this cost drops to $30,000, achieving the same precision and quality while saving $60,000.
Discounted Batch Processing
- Using Anthropic’s Batches API cuts output costs in half, making it a much cheaper option for certain tasks. Once I had validated the prompts, I ran a single batch job to evaluate all the Q&A answer sets at once. This method proved far more cost-effective than processing each Q&A pair individually.
- For example, Claude 3 Opus typically costs $15 per million output tokens. By using batching, this drops to $7.50 per million tokens — a 50% reduction. In my experiment, each Q&A pair generated an average of 100 tokens, resulting in approximately 20,000 output tokens for the document. At the standard rate, this would have cost $0.30. With batch processing, the cost was reduced to $0.15, highlighitng how this approach optimizes costs for non-sequential tasks like evaluation runs.
Time Saved for SMEs
- With more accurate, context-rich Q&A pairs, Subject Matter Experts spent less time sifting through PDFs and clarifying details, and more time focusing on strategic insights. This approach also eliminates the need to hire additional staff or allocate internal resources for manually curating datasets, a process that can be time-consuming and expensive. By automating these tasks, companies save significantly on labor costs while streamlining SME workflows, making this a scalable and cost-effective solution.