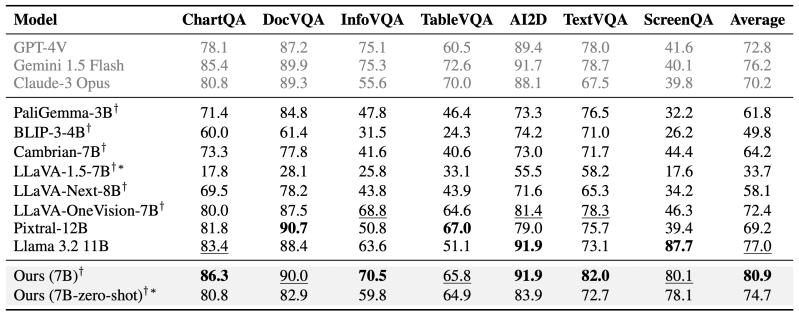
The report shows that AI is being deployed typically in high-volume, repetitive tasks. Troubleshooting and log analysis lead the way, with 41% and 35% of sysadmins, respectively, reporting use of AI in those areas—up significantly from 2024.
Respondents reported that the following tasks are most likely to be automated with AI in the next two years:
- Vulnerability prioritization: 67%
- Monitoring of server CPU and memory utilization: 67%
- Detecting and remediating incidents: 66%
- Patch management processes: 66%
- Security controls and compliance analysis: 65%
- Performing post-incident reviews: 57%
- Providing IT staff with guidance and training: 55%
- Troubleshooting: 55%
In contrast, sysadmins surveyed reported that the following tasks are less likely to be automated with AI in the next two years:
- Managing SSO and passwords: 48%
- Administering user permissions: 44%
- Managing files: 38%
- Defining system usage policies and procedures: 34%
- Providing end users with first-level IT support: 30%
- Installing and maintaining software: 29%
- Troubleshooting: 24%
- Performing post-incident reviews: 23% Providing IT staff with guidance and training: 23%
AI concerns persist
Sysadmins indicated they worry about falling behind peers. Some 40% expressed concern about being left behind by more AI-literate peers, a slight improvement from 45% in 2024. The top three reasons sysadmins are hesitant to embrace AI are:
- 79% worry about accuracy and reliability.
- 78% cite data privacy and security risks.
- 60% fear loss of control over automated actions.
As AI adoption increases, so does the visibility of its shortcomings. Troubleshooting, the most common use case, is also the topic where AI struggles the most—30% of sysadmins reported failures in this area, a figure that is nearly double from last year’s survey. Another 20% of sysadmins said AI implementations have caused operational disruptions.
Other areas that show AI isn’t yet performing up to expectations are: log analysis with 12% failure reports, and first-level IT support tasks also with 12% citing it as an area for AI failures. Even support for IT staff, such as training guidance, is falling short for some users as 10% cited this as an area in which AI has failed.