AI Factories Redefine Infrastructure
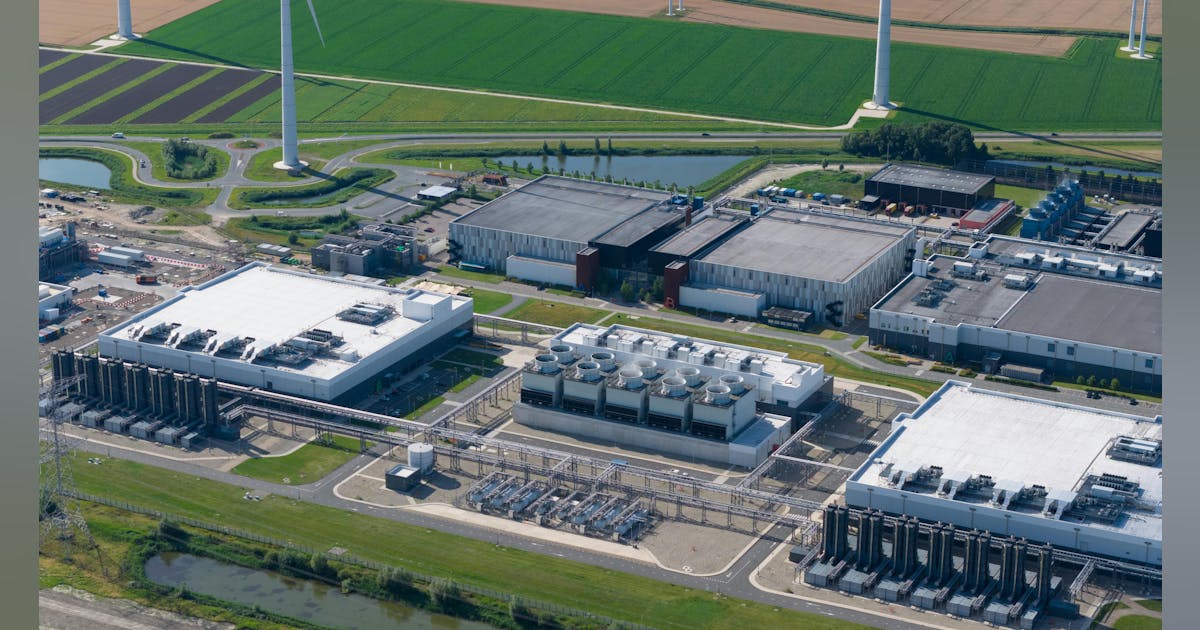
The architecture of AI factories reflects a paradigm shift that mirrors the evolution of the industrial age itself—from manual processes to automation, and now to autonomous intelligence. Nvidia’s framing of these systems as “factories” isn’t just branding; it’s a conceptual leap that positions AI infrastructure as the new production line. GPUs are the engines, data is the raw material, and the output isn’t a physical product, but predictive power at unprecedented scale. In this vision, compute capacity becomes a strategic asset, and the ability to iterate faster on AI models becomes a competitive differentiator, not just a technical milestone.
This evolution also introduces a new calculus for data center investment. The cost-per-token of inference—how efficiently a system can produce usable AI output—emerges as a critical KPI, replacing traditional metrics like PUE or rack density as primary indicators of performance. That changes the game for developers, operators, and regulators alike. Just as cloud computing shifted the industry’s center of gravity over the past decade, the rise of AI factories is likely to redraw the map again—favoring locations with not only robust power and cooling, but with access to clean energy, proximity to data-rich ecosystems, and incentives that align with national digital strategies.
The Economics of AI: Scaling Laws and Compute Demand
At the heart of the AI factory model is a requirement for a deep understanding of the scaling laws that govern AI economics.
Initially, the emphasis in AI revolved around pretraining large models, requiring massive amounts of compute, expert labor, and curated data. Over five years, pretraining compute needs have increased by a factor of 50 million. However, once a foundational model is trained, the downstream potential multiplies exponentially, while the compute required to utilize a fully trained model for standard inference is significantly less than that required for training and fine-tuning models for use.
The challenge shifts to post-training scaling and test-time scaling. Fine-tuning models to suit specific applications demands 30x more compute than the original pretraining. Meanwhile, the latest advanced inference tasks like agentic AI, where models reason iteratively before responding, can require 100x more compute than standard inference. These compute-intensive needs simply exceed the capacity of general-purpose data centers.
AI factories are designed with this exponential growth in mind. From the ground up, they are built to support massive inference demands, iterative reasoning, and adaptive model deployment.
AI’s New Cost Curve
This shift in workload dynamics rewrites the economic blueprint for infrastructure investment. Where once the ROI of data center capacity was measured against steady-state cloud or enterprise workloads, AI factories demand a forward-looking calculus based on scaling behavior and future inference velocity.
The cost per token or decision point becomes a more meaningful financial metric than simple cost per kWh or per-core performance. Operators must not only provision for peak demand but architect systems flexible enough to evolve with model complexity—supporting seamless upgrades in compute density, interconnect bandwidth, and software orchestration.
Moreover, these economics aren’t confined to hyperscale players alone. Enterprises deploying vertical-specific models—whether for fraud detection, supply chain optimization, or autonomous control systems—are increasingly recognizing that the benefits of faster, smarter AI decisions justify the infrastructure premium.
This drives demand for regional and modular AI factories tailored to industry use cases, where latency, data locality, and compliance matter as much as raw compute. As with previous inflections in the digital economy, those who internalize and invest early in the new cost curves will be best positioned to lead in a world where intelligence itself is the product.
AI Factory Development Around the World
Nvidia is not alone in recognizing the strategic importance of AI factories. Governments and enterprises across the globe are racing to deploy them:
India: Through a high-profile partnership with NVIDIA, Yotta Data Services has launched the Shakti Cloud Platform—one of the country’s first AI supercomputing infrastructures. Positioned as a national resource, Shakti aims to democratize access to high-performance GPU resources for startups, research institutions, and public sector innovation, reflecting India’s broader ambition to become a global AI hub.
Japan: Cloud providers like GMO Internet and KDDI are rapidly scaling NVIDIA-powered AI infrastructure to accelerate advancements in robotics, precision medicine, and smart cities. These efforts align with Japan’s Society 5.0 vision, which emphasizes the fusion of cyber and physical systems to tackle demographic and economic challenges through AI and automation.
Europe: The European Union is taking a coordinated, multi-national approach to AI factory development, investing in seven advanced computing centers across 17 member states via the High Performance Computing Joint Undertaking (EuroHPC JU). These sites are being positioned not just as data centers but as digital sovereignty assets—powering AI research, public sector applications, and secure industrial innovation.
Norway: Telenor’s NVIDIA-powered AI factory exemplifies how Nordic countries are integrating sustainability into digital transformation. With a strong emphasis on green energy, regional talent development, and cross-border collaboration, the initiative is laying a foundation for climate-conscious AI infrastructure that aligns with European ESG priorities.
United States: AI factory development is taking a dual-track approach. Public-private initiatives like the Stargate project—focused on frontier-scale computing—and executive directives from the White House underscore Washington’s intent to lead in both commercial and governmental AI capabilities. The U.S. sees AI infrastructure not just as a competitive edge but as a strategic imperative for national resilience.
Saudi Arabia: Through its Vision 2030 strategy, the Kingdom is investing heavily in AI infrastructure, including a partnership between the Saudi Data and Artificial Intelligence Authority (SDAIA) and global hyperscalers. Recent announcements include the creation of sovereign AI compute clusters designed to support Arabic-language models and AI-driven public services.
Singapore: Known for its methodical approach to digital infrastructure, Singapore is building out AI factories as part of its National AI Strategy 2.0. With investments in sovereign compute capabilities and robust data governance, the city-state is positioning itself as Southeast Asia’s AI nerve center—balancing innovation with regulatory foresight.
These projects highlight how AI factories are quickly becoming essential national infrastructure, akin to telecommunications and energy grids. More than just data centers, they represent strategic bets on where intelligence will be created, who controls its production, and how nations will compete in an AI-first global economy.
Inside the AI Factory: A Full-Stack Approach to Intelligence Production
Nvidia’s AI factory model isn’t just a high-powered compute stack—it’s a vertically integrated platform purpose-built to accelerate every stage of the AI lifecycle. From training foundational models to deploying them at scale in real-time applications, the architecture spans compute, networking, software, data pipelines, and digital twin simulation. Each layer is engineered for high-efficiency throughput, reflecting Nvidia’s belief that intelligence production requires the same rigor and precision as modern manufacturing.
1. Compute Performance: The Engine Room of Intelligence
At the core of the AI factory is GPU horsepower. Nvidia’s Hopper, Blackwell, and the forthcoming Blackwell Ultra architectures offer exponential leaps in performance. The flagship GB200 NVL72 system—a rack-scale unit with dual Blackwell GPUs connected by NVLink Switch—delivers 50x more AI inference throughput compared to the A100 generation. Integrated into DGX SuperPOD clusters, these systems can scale to tens of thousands of nodes, forming the compute backbone for hyperscale AI development.
DGX Cloud extends these capabilities into a managed, consumption-based model, allowing enterprises to access AI factory-grade infrastructure through major cloud platforms like Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, and Oracle. It’s an operating model built for rapid deployment and elastic growth.
2. High-Performance Networking: Compute Without Bottlenecks
Scaling AI requires more than raw compute—it demands precision networking. Nvidia’s NVLink, Quantum-2 InfiniBand, and Spectrum-X Ethernet fabrics are designed to minimize latency and ensure lossless, high-bandwidth data movement between tens of thousands of GPUs. ConnectX-8 SmartNICs and BlueField-3 DPUs enable secure, multi-tenant environments while offloading network and storage tasks to free up GPU cycles. The result is a tightly-coupled infrastructure where compute and data flow at AI-native speeds.
3. Orchestration and Operational Intelligence
Orchestrating AI workloads at scale is non-trivial. Tools like Nvidia Run:ai, Base Command, and Mission Control provide full-stack visibility and GPU-aware scheduling, ensuring optimal utilization across heterogeneous environments. These platforms support multi-tenant operations, dynamic scaling, and fine-grained workload isolation—critical in enterprise and sovereign AI environments where uptime and performance cannot be compromised.
4. Inference Stack: From Model to Real-Time Decisions
The Nvidia inference stack—including TensorRT for optimized execution, NVIDIA Inference Microservices (NIMs) for containerized deployment, and NVIDIA Triton for scalable serving—enables low-latency, high-throughput AI services. These tools are optimized for transformer architectures and multimodal models, addressing the growing demand for agentic inference, edge reasoning, and continuous learning in production.
5. Data Infrastructure: Feeding the Intelligence Pipeline
AI performance is bound by the quality and availability of data. The Nvidia AI Data Platform enables seamless integration with modern data lakes, object stores, and streaming platforms. It provides end-to-end support for preprocessing, labeling, and versioning at scale—turning chaotic data pipelines into repeatable, high-performance processes. Certified storage partners (like NetApp, Dell, and VAST Data) ensure that storage throughput can keep pace with real-time inference and training demands.
6. Omniverse Blueprint: Digital Twin-Driven Infrastructure Planning
Designing an AI factory involves massive complexity—up to 5 billion components, 210,000 miles of cabling, and megawatt-scale power demands. Nvidia’s Omniverse Blueprint introduces a systems-level digital twin to simulate, validate, and optimize AI factory builds before breaking ground. This includes everything from airflow and thermals to rack placement and interconnect design.
By enabling real-time collaboration across electrical, mechanical, and IT disciplines, Omniverse reduces time-to-deployment and mitigates critical risk. In environments where an hour of downtime can equate to tens of millions in lost inference capacity, this level of planning precision is no longer optional—it’s a necessity.
AI factories represent more than just technical innovation—they are a new class of infrastructure, purpose-built for the intelligence economy. Nvidia’s full-stack platform provides the modularity, scalability, and performance required to manufacture intelligence at scale, redefining how enterprises and nations deploy AI as a core strategic asset.
Deep Dive on Omniverse Developments: Advancing AI Factory Design and Simulation
As AI continues to drive unprecedented demand for specialized infrastructure, NVIDIA is taking bold steps to help design and optimize the next generation of AI factories with its new Omniverse Blueprint for AI factory design and operations. Unveiled during NVIDIA’s GTC keynote, this innovative blueprint is designed to help engineers simulate, plan, and optimize the development of gigawatt-scale AI factories, which require the seamless integration of billions of components and complex systems.
In collaboration with leading simulation and infrastructure partners, including Cadence, ETAP, Schneider Electric, and Vertiv, the Omniverse Blueprint enables digital twin technology to support the design, testing, and optimization of AI factory components such as power, cooling, and networking systems long before physical construction begins.
Engineering AI Factories: A Simulation-First Approach
Using OpenUSD libraries, NVIDIA’s Omniverse Blueprint aggregates 3D data from multiple sources, including building layouts, accelerated computing systems like NVIDIA DGX SuperPODs, and power/cooling units from partners such as Schneider Electric and Vertiv. This unified approach allows engineers to address key challenges in AI factory development, such as:
-
Component Integration and Space Optimization: Seamlessly integrating NVIDIA systems with billions of components for optimal layouts.
-
Cooling Efficiency: Using the Cadence Reality Digital Twin Platform to simulate and evaluate cooling solutions, from hybrid air to liquid cooling.
-
Power Distribution: Designing scalable, redundant systems to simulate and optimize power reliability using ETAP.
-
Networking Topology: Fine-tuning high-bandwidth networking infrastructure with NVIDIA Spectrum-X and NVIDIA Air.
The blueprint empowers engineers to collaborate in real-time across disciplines, reducing inefficiencies and enabling parallel workflows. Real-time simulations allow for faster decision-making and optimization, with teams able to adjust configurations and immediately see the impact — drastically reducing design time and avoiding costly mistakes during construction.
Building Resilience Into the AI Frontier
As AI workloads continue to evolve, the blueprint offers advanced features such as workload-aware simulations and failure scenario testing to ensure AI factories can scale and adapt to future demands. With the growing importance of minimizing downtime (which can cost millions per day in gigawatt-scale AI factories), the Omniverse Blueprint reduces risk, improves efficiency, and helps AI factory operators stay ahead of infrastructure needs.
NVIDIA’s ongoing efforts with partners like Vertech and Phaidra will bring AI-enabled operations into the fold, including reinforcement-learning agents that optimize energy efficiency and system stability. These advancements ensure that AI factories can adapt to changing hardware and environmental conditions in real-time, contributing to ongoing operational resilience.
The integration of digital twin technology into AI factory design is not just a theoretical enhancement—it’s essential for the future of AI-driven data centers. With over $1 trillion projected for AI-related upgrades, NVIDIA’s Omniverse Blueprint stands poised to lead this transformation, helping AI factory operators navigate the complexities of AI workloads while minimizing risk and maximizing efficiency.
To explore these developments further, watch the GTC keynote, and discover how NVIDIA and its partners are shaping the future of AI factory infrastructure.
The Age of Reasoning and Agentic AI
Nvidia defines its Blackwell Ultra platform not just as another leap in GPU performance, but as the gateway to a new phase in AI development—what it calls the age of reasoning. As workloads transition from static inference to dynamic decision-making, AI systems must increasingly mimic human-like cognition: analyzing context, planning multistep actions, and adapting behavior in real time. This shift is giving rise to two transformative paradigms—agentic AI and physical AI—both of which are redefining the infrastructure requirements for scalable intelligence.
-
Agentic AI involves AI models that operate autonomously to solve complex, multistep problems. These models reason iteratively, self-correct, and manage workflows across multiple domains. They’re already emerging in tools like AutoGPT, Devin, and AI copilots that can write code, generate research plans, or manage enterprise workflows. Unlike traditional inference, agentic AI requires continual interaction with large-scale memory, context retrieval, and recursive reasoning—all of which drive up compute needs by orders of magnitude.
-
Physical AI focuses on embodied intelligence—where simulation, sensor fusion, and real-world control intersect. Applications include real-time photorealistic simulation for digital twins, robotics, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation. These workloads demand ultra-low latency and tight coupling between simulation and inference engines.
Blackwell Ultra is engineered for this new class of demands. It enables AI factories to scale compute across the full lifecycle—from massive pretraining runs to highly variable post-training tasks, including fine-tuning, retraining, and real-time inference. Crucially, Nvidia’s Dynamo software stack coordinates these large-scale operations, orchestrating token generation and communication across thousands of GPUs with efficiency that keeps latency low and throughput high.
In this new era, compute isn’t just about speed—it’s about intelligence per watt, adaptability per dollar, and the ability to support inference that behaves less like static prediction and more like dynamic reasoning. Blackwell Ultra and its supporting ecosystem are designed to meet that challenge head-on, reshaping not only how AI runs, but what it can become.
Oracle and NVIDIA Team Up to Accelerate the AI Factory Model with Agentic AI Integration
At NVIDIA’s 2025 GTC conference, Oracle and NVIDIA unveiled a major step forward in the buildout of enterprise-scale AI infrastructure — a key component of the emerging “AI Factory” model. The companies announced a deep integration between Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) and the NVIDIA AI Enterprise software platform, aimed at accelerating the deployment of agentic AI — autonomous AI systems capable of reasoning, planning, and executing complex tasks.
This collaboration brings NVIDIA’s inference stack — including 160+ AI tools and more than 100 NIM™ (NVIDIA Inference Microservices) — natively into the OCI Console. Oracle customers can now tap into a fully integrated AI stack, available in Oracle’s cloud regions, sovereign clouds, on-premises via OCI Dedicated Region, and even at the edge.
“Oracle has become the platform of choice for both AI training and inferencing,” said Oracle CEO Safra Catz. “This partnership enhances our ability to help customers achieve greater innovation and business results.”
NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang underscored the significance of the integration for enterprise AI: “Together, we help enterprises innovate with agentic AI to deliver amazing things for their customers and partners.”
No-Code Blueprints and Turnkey Inference
A key element of the Oracle-NVIDIA collaboration is the launch of no-code OCI AI Blueprints, which allow enterprises to deploy multimodal large language models, inference pipelines, and observability tools without managing infrastructure. These blueprints are optimized for NVIDIA GPUs and microservices, and can reduce the time-to-deployment from weeks to minutes.
NVIDIA is also contributing its own Blueprints to the OCI Marketplace, preloaded with workflows for enterprise use cases in customer service, simulation, and robotics. For example, Oracle plans to offer NVIDIA Omniverse and Isaac Sim tools on OCI, bundled with preconfigured NVIDIA L40S GPU instances for simulation and physical AI development.
Pipefy, a business process automation platform, is already deploying multimodal LLMs on OCI using these AI Blueprints. “Using these prepackaged and verified blueprints, deploying our AI models on OCI is now fully automated and significantly faster,” said Gabriel Custódio, principal software engineer at Pipefy.
Enabling Real-Time Inference and Vector Search
Oracle is also integrating NVIDIA NIM microservices into OCI Data Science, enabling real-time inference with a pay-as-you-go model. These microservices can be deployed within a customer’s OCI tenancy for AI use cases ranging from copilots to recommendation engines, delivering rapid time-to-value while maintaining data security and compliance.
In the AI data stack, Oracle Database 23ai now supports accelerated vector search powered by NVIDIA GPUs and the cuVS library — enabling fast creation of vector embeddings and indexes for massive datasets. Companies like DeweyVision, which provides AI-driven media cataloging and search tools, are using this integration to ingest, search, and manage high volumes of video content efficiently.
“Oracle Database 23ai with AI Vector Search can significantly increase Dewey’s search performance while increasing the scalability of the DeweyVision platform,” said CEO Majid Bemanian.
Blackwell-Powered Superclusters Signal the AI Factory Future
Perhaps most notably, Oracle is among the first cloud providers to roll out NVIDIA’s latest generation Blackwell Ultra GPUs across its AI Supercluster. The NVIDIA GB300 NVL72 and HGX B300 NVL16 platforms — successors to last year’s GB200 — promise up to 1.5x performance gains and are designed for large-scale AI factories spanning tens of thousands of GPUs. Oracle’s Supercluster deployments will soon support up to 131,072 GPUs, connected by NVIDIA’s Quantum-2 InfiniBand and NVLink fabrics.
Companies like Soley Therapeutics and SoundHound AI are already leveraging this full-stack Oracle-NVIDIA platform to train next-generation models for drug discovery and voice AI, respectively. “The combination of OCI and NVIDIA delivers a full-stack AI solution,” said Yerem Yeghiazarians, CEO of Soley Therapeutics. “It provides us the storage, compute, software tools, and support necessary to innovate faster with petabytes of data.”
As AI workloads continue to demand ever-larger compute clusters and sophisticated software integration, partnerships like Oracle and NVIDIA’s are laying the foundation for scalable, enterprise-ready AI factories — designed to push the limits of reasoning, automation, and insight.
Secure AI Factories: The Cisco-NVIDIA Collaboration
As AI infrastructure becomes a foundational layer of national and enterprise strategy, its security posture can no longer be an afterthought—it must be embedded from the silicon up. Cisco and NVIDIA have partnered to deliver exactly that with the Secure AI Factory: a full-stack architecture that merges scalable compute and high-performance networking with zero-trust security principles and AI-native threat protection.
The collaboration tightly integrates Cisco’s security and networking stack—including Hypershield, AI Defense, and hybrid mesh firewalls—with NVIDIA’s BlueField-3 DPUs and AI Enterprise platform. The result is a unified framework that provides policy enforcement, observability, and real-time threat detection across every layer of the AI stack.
-
Hypershield applies adaptive segmentation and micro-isolation, using AI to identify and quarantine threats across east-west traffic inside data centers.
-
AI Defense leverages behavior-based analysis to protect against AI-specific risks such as prompt injection, model hijacking, adversarial inputs, and data leakage during runtime.
-
BlueField-3 DPUs offload security and network processing from host CPUs, enabling wire-speed telemetry, access control, and cryptographic operations without impacting AI performance.
This joint platform supports on-premises deployments through Cisco UCS AI servers and Nexus switches, or cloud and hybrid deployments using validated reference architectures optimized for AI factories. Security scales automatically with workload changes—eliminating blind spots in dynamic, multi-tenant environments where AI models evolve in real time.
By embedding security into every node, packet, and process, Cisco and NVIDIA are enabling enterprises to move fast without sacrificing control. In an era where AI models make mission-critical decisions and process sensitive data, the Secure AI Factory ensures that trust is not just assumed—it’s architected.
Chuck Robbins, Chair and CEO, Cisco, said: