Dive Brief:
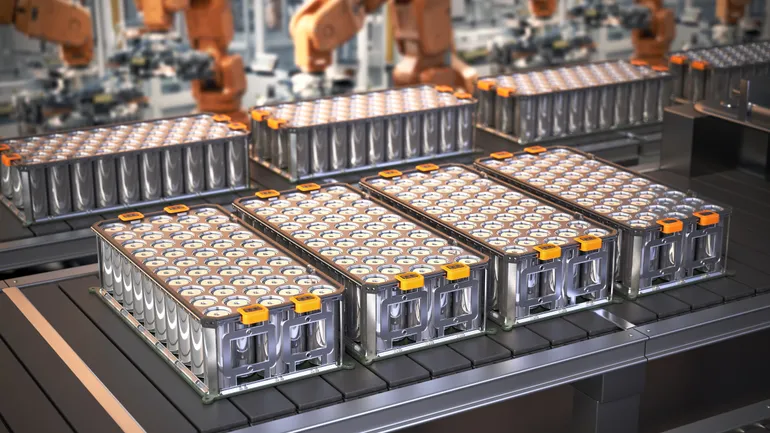
- Toyota Motor North America scored a $4.5 million Department of Energy grant to help advance electric vehicle battery recycling initiatives, the company announced last month.
- The funding will support a project led by the Toyota Research Institute of North America, whose goal is to develop an industry template for a reduce, reuse, recycle battery facility of the future.
- “As it stands, this project and program will highlight avenues for everyone to rethink their approach to battery circularity, and help prioritize the extension of battery life, facilitate battery reuse, and reduce battery waste while unveiling the appropriate pathways to achieve such priorities,” Nik Singh, project leader and principal scientist at TRINA, said in the release.
Dive Insight:
The DOE’s Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy initiative provided funding to Toyota to support a circular domestic supply chain for EV batteries.
Singh and his team are leading the development of a robotic disassembly process for batteries in collaboration with Oak Ridge National Laboratory, the National Renewable Energy Laboratory and energy technology firm Baker Hughes’ inspection technology product line, Waygate Technologies.
The project’s goal is to resolve bottlenecks in the current battery supply chain circularity, according to the release. This includes the automation of battery pack disassembly, data-driven battery classification and addressing cell degradation.
The DOE effort is driven by the growing need for EV battery recycling as electric vehicle usage becomes more widespread. Automakers and suppliers have committed billions of dollars in private investment to take advantage of government aid to transition to the technology and foster its adoption.
Researchers will also develop advanced diagnostic tools and a refabrication method for the recycling of battery cells into new energy systems.
As end-of-life and battery scrap volumes increase from rising global EV adoption, a new approach is needed to extend the useful life of many standard battery pack components, researchers said.
“We will generate processes to streamline reusing and refurbishing valuable battery cells and modules from end-of-life packs, without having to scan every single battery pack every single time,” said Marm Dixit, who is co-leading Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s contributions to the project. “By extending the life of the battery components, we reduce their total emissions per mile.