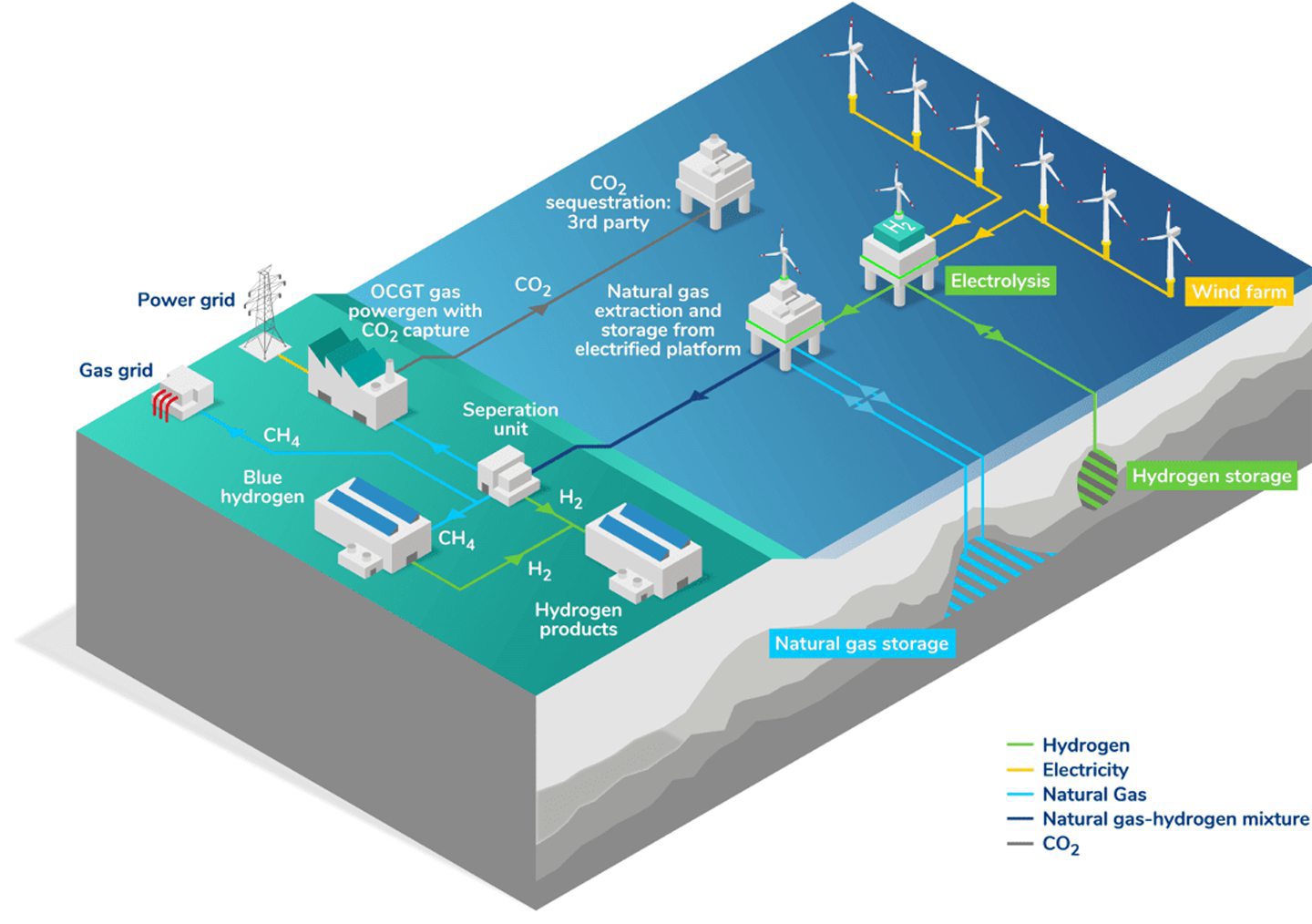
A Uganda-Tanzania petroleum pipeline project majority-owned by TotalEnergies SE has secured the first tranche of external syndicated financing.
The group of backers include regional banks African Export Import Bank, Standard Bank of South Africa Ltd., Stanbic Bank Uganda Ltd., KCB Bank Uganda and Islamic Corporation for the Development of the Private Sector (ICD), the project joint venture EACOP Ltd. said in an online statement. EACOP did not disclose any amount.
The East African Crude Oil Pipeline will transport up to 246,000 barrels a day from the Lake Albert oilfields in Uganda to the port of Tanga, Tanzania, for export to the global market, according to EACOP.
The funding “demonstrates the support of financial institutions on this transformative regional infrastructure”, it said.
Construction was more than 50 percent complete at the end of last year, EACOP said, noting over 8,000 Ugandan and Tanzanian citizens are employed for the project. Construction started last year and is expected to take 2 years to complete, according to EACOP.
Besides a 1,443-kilometer (896.63 miles), 24-inch buried pipeline, the project will also install 6 pumping stations, 2 pressure reduction stations and a marine export terminal with a 3-megawatt solar plant, according to EACOP.
Early last year TotalEnergies, which owns 62 percent of EACOP, said it had commissioned an assessment of its land acquisition process for the pipeline project and an associated oil development project, following allegations by an interfaith organization that the French energy giant failed to protect hundreds of graves.
“As the land acquisition process draws to a close, this mission will evaluate the land acquisition procedures implemented, the conditions for consultation, compensation and relocation of the populations concerned, and the grievance handling mechanism”, TotalEnergies said in a press release January 4, 2024.
“It will also assess the actions taken by TotalEnergies EP Uganda and EACOP to contribute to the improvement of the living conditions for the people affected by these land acquisitions and suggest additional measures to be implemented if needed”.
International environmental watchdog GreenFaith had documented cases of a lack of compensation for affected burial places; incomplete or poorly constructed relocation sites; risks of limited access to graves due to households having to relocate; and insufficient documentation to account for graves that would be affected.
New York City-based GreenFaith estimated over 2,000 graves in Uganda and Tanzania have been or would be affected by the pipeline designed to run from the town of Kabaale in Uganda to the port of Tanga in Tanzania. It said the figure was based on data from operator and 62-percent owner TotalEnergies itself.
It accused the company of failing to respect local traditions and follow international best practices and engineering standards in treating graves along the EACOP route.
The most common complaint was an inadequacy of compensation for affected graves, GreenFaith said.
TotalEnergies dismissed the GreenFaith report. It said that in accordance with World Bank project standards on cultural heritage, the project partners “developed a management plan for cultural and archaeological heritage” and conducted interviews “with key stakeholders, including communities”, as well as created an “inventory of sites of archaeological, historical, cultural, artistic and religious importance”.
“As much as possible, the project has adopted an avoidance protocol when choosing locations”, TotalEnergies said in a statement emailed to Rigzone at the time. “In the event that a cultural site cannot be avoided, precautions were taken to minimize the disruptions, inform and engage with stakeholders and ensure that cultural standards are strictly respected.
“Relocation of sacred sites involves strict adherence to the respective families/ clan’s traditional beliefs or customs, e.g. conducting relocation ceremonies to shift the spirits from sacred trees; sacred watercourses; springs and marshes; traditional religious cultural sites (clan sites and family shrines) to another place”.
On claims of a lack of compensation, TotalEnergies said affected residents “are compensated according to the values agreed with the Chief valuer”.
As of February 2025 over 99 percent of compensation agreements were paid, 100 percent of houses built and 97 percent of grievances resolved, according to information on TotalEnergies’ website.
The other owners are Uganda National Oil Co. Ltd. (15 percent), Tanzania Petroleum Development Corp. (15 percent) and China National Offshore Oil Corp. (8 percent).
To contact the author, email [email protected]