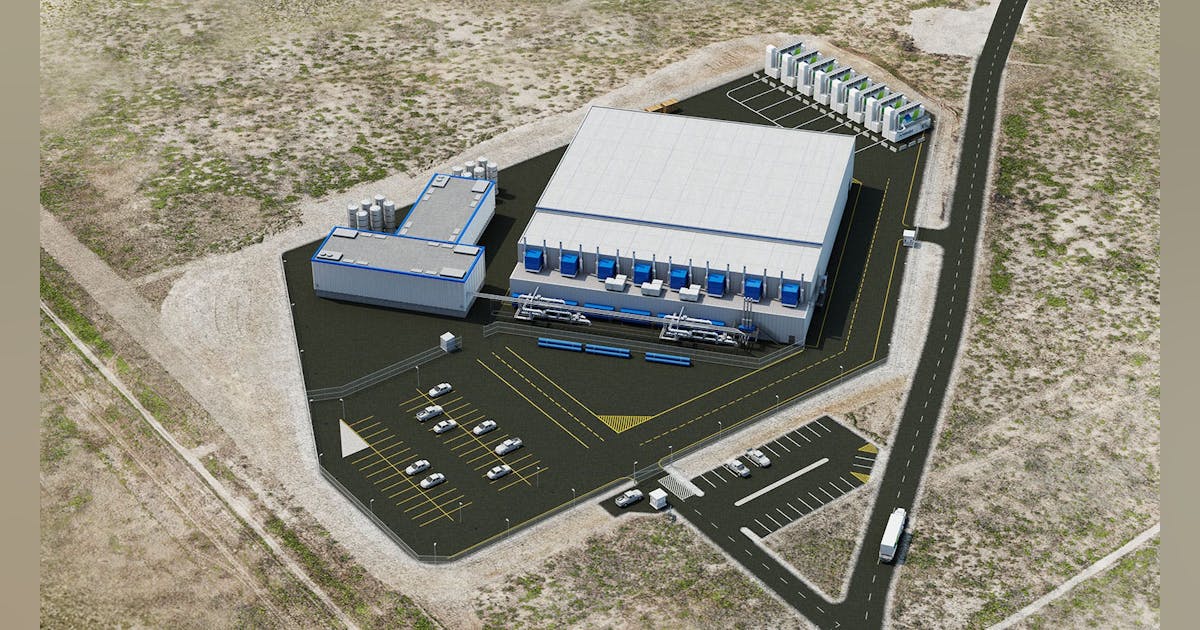
Access to power is now the defining factor for data center development, eclipsing traditional site selection considerations, such as proximity to fiber networks. As artificial intelligence drives explosive growth in compute demand, developers face a stark reality: without immediate, reliable power, schedules can stall, costs rise and relationships with both communities and customers are put at risk.
The scale of AI workloads magnifies the challenge. In major data center hubs, power demand is expected to more than double from 175 MW today to 375 MW by 2035. For technology companies, this shift has turned onsite generation from a backup measure into a primary source of power for operations and critical infrastructure.
Yet, onsite legacy technologies that have long supplied power are showing their limits. Gas turbines and reciprocating engines bring noise, carbon emissions, significant water consumption and slow permitting timelines – liabilities in an industry where speed, scale and sustainability now define competitiveness.
High-temperature solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), once overlooked as a niche solution, are changing the equation. With proven deployments across data centers and the ability to deliver power at the scale, speed and reliability AI demands, fuel cells have become the onsite power solution of choice for today’s digital infrastructure leaders.
Fuel Cells: A Solution Fit for the Digital Era
Fuel cells offer a strategic infrastructure choice for modern data centers, providing a fundamentally different approach to onsite power. Fuel cells convert natural gas directly into electricity without combustion, achieving 15% to 20% higher efficiency than most open-cycle gas turbines or reciprocating engines.
In their recent white paper, “Fuel Cells: A Technology Whose Time Has Come,” KR Sridhar and Peter Gross of Bloom Energy explained that this efficiency reduces fuel consumption. “The capital cost advantages over gas turbines and engines grow even stronger if customers require higher availability,” they said.
The technology is also firmly established in the market. With more than 1.5 GW of Bloom Energy fuel cells deployed across over 1,200 sites globally, including hundreds of megawatts powering data centers, fuel cells have moved beyond niche applications into mainstream, mission-critical use. Their proven reliability demonstrates that they can meet the uptime expectations of high-performance computing environments while providing operational resilience.
Speed, Scalability and AI Compatibility
In the digital era, speed to power is critical. Every delay in bringing data center infrastructure online means idle GPUs and lost revenue. Today, Bloom Energy can deliver 50 MW of fuel cells in as little as 90 and 100 MW in 120 days if gas supply and permits are in place. This rapid deployment enables operators to align power availability with aggressive project timelines.
Scalability is built into fuel cell design. Modular, “copy-and-paste” architecture allows capacity to grow incrementally with compute demand. Operators can expand power without risking stranded assets and can scale precisely as workloads increase.
Fuel cells are also suited to support volatile AI workloads, which can drive load swings between 20% and 150% in milliseconds, often multiple times per minute. Fuel cells follow the demand changes instantly, unlike turbines or engines, which require large battery arrays to manage variable loads.
“As solid state devices with no spinning components or mechanical lag, [fuel cells] respond at least twice as fast as rotating generators when stepping up, and instantly when stepping down. When combined with supercapacitors, they reach 100% in milliseconds,” Sridhar and Gross explained. This responsiveness ensures consistent performance without the complexity and cost of extensive energy storage.
Reliability and community alignment
Fuel cells provide a reliable source of power even during extreme conditions. By connecting directly to the resilient natural gas grid, they maintain uptime during outages on the electric grid and can support continuous operation through hurricanes, floods, wildfires and earthquakes. Millions of operating hours demonstrate their proven performance in diverse environments.
Reliability is further enhanced by a fuel cell system’s modular design and built-in redundancy, which eliminates the need for diesel backup.
“With no moving parts, fuel cells face fewer mechanical failures. When maintenance is needed, modules as small as 65 kW can be hot-swapped without shutting down the entire system,” ensuring stable operation over long periods, according to Sridhar and Gross.
Fuel cells also align with community priorities. They operate nearly silently, reduce emissions and preserve land compared with traditional onsite generation. By avoiding the need for costly grid upgrades, they protect ratepayers from price increases. In some cases, fuel cells can even make data centers grid-supporting assets, contributing positively to the local energy ecosystem.
Securing the Future of AI-Driven Data Centers
Power availability is the defining constraint for modern data centers, particularly those supporting AI workloads. Fuel cells remove that constraint by providing clean, scalable, fast-to-deploy and resilient onsite power. Operators who adopt fuel cells today can ensure uptime, reduce operational costs and position themselves to meet the evolving demands of the digital economy.
Bloom Energy’s SOFC Energy Server® power systems can be deployed behind or in front of the meter in multiple configurations and contracting models. For operators seeking a solution that aligns technical, economic and community objectives, fuel cells represent a strategic choice. To learn more, download “Fuel Cells: A Technology Whose Time Has Come.”