At customer locations, only a lightweight demarcation device is required. This equipment creates a clean handoff point but contains no processing logic or intelligence. All routing, security, traffic management and network services run on the pre-deployed hardware in Zayo’s facilities.
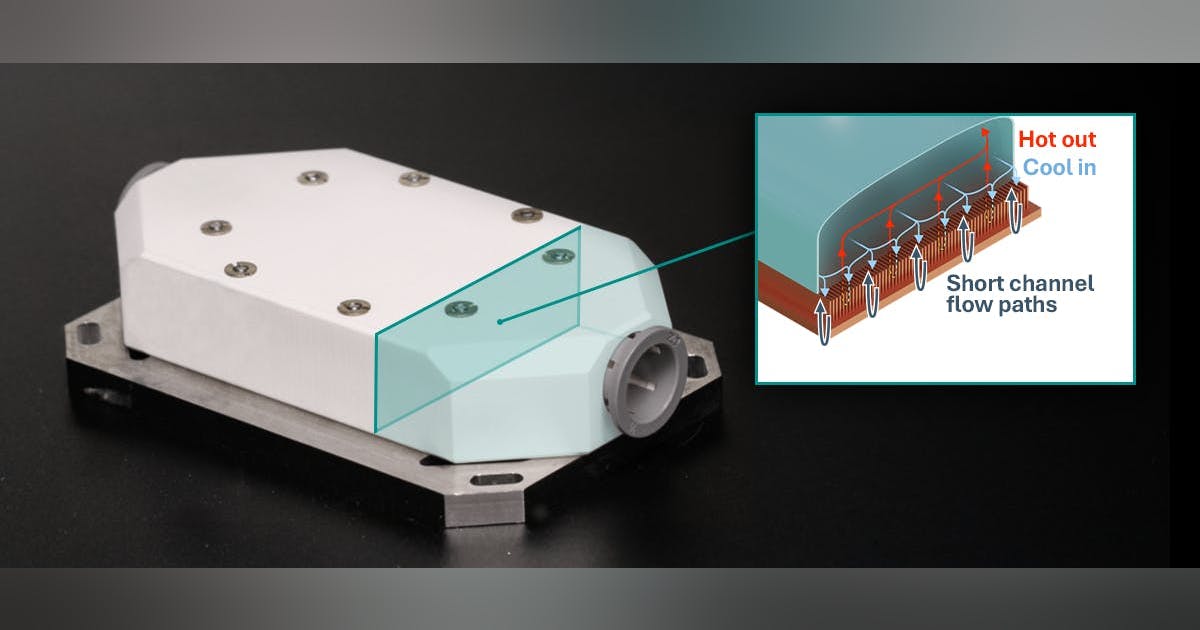
“We’ve basically taken the logic out of those boxes that used to sit on premise, sucked that into the core of the network, and then put it on hardware that can do extremely fast multi-terabyte level, single-packet processing. You know, line rate, speed performance,” Long explained.
Service model: One port, multiple functions
DynamicLink’s commercial model centers on port-based pricing. Organizations purchase ports at locations where they need connectivity. This includes headquarters, branch offices, colocation facilities, cloud on-ramps or any location Zayo’s network reaches.
Each port provides flexible capacity that can be allocated across different services. A single 10 Gbps port might simultaneously support point-to-point Ethernet between facilities, dedicated internet access and cloud connectivity. Customers reconfigure these allocations through a self-service portal.
“If you have a dynamic link port, that, if you have, like, a dynamic link in three different locations, let’s say it’s at a headquarters location and two of your data centers, you can use that to have a point to point Ethernet,” Long said. “If you want to use those 10 gigs at one location to go out to the internet, you can use it to go out to the internet.”
Previously, each of these functions required ordering a separate service. An organization wanting dedicated internet access ordered a DIA port. Point-to-point Ethernet between data centers required two separate ports. Each service involved manual provisioning and fixed configuration.