.cst-large,
.cst-default {
width: 100%;
}
@media (max-width: 767px) {
.cst-block {
overflow-x: hidden;
}
}
@media (min-width: 630px) {
.cst-large {
margin-left: -25%;
width: 150%;
}
@media (min-width: 960px) {
.cst-large {
margin-left: -16.666666666666664%;
width: 140.26%;
}
}
@media (min-width: 1312px) {
.cst-large {
width: 145.13%;
}
}
}
.flourish-embed {
width: 60vw;
transform: translateX(-50%);
left: 50%;
position: relative;
}
}
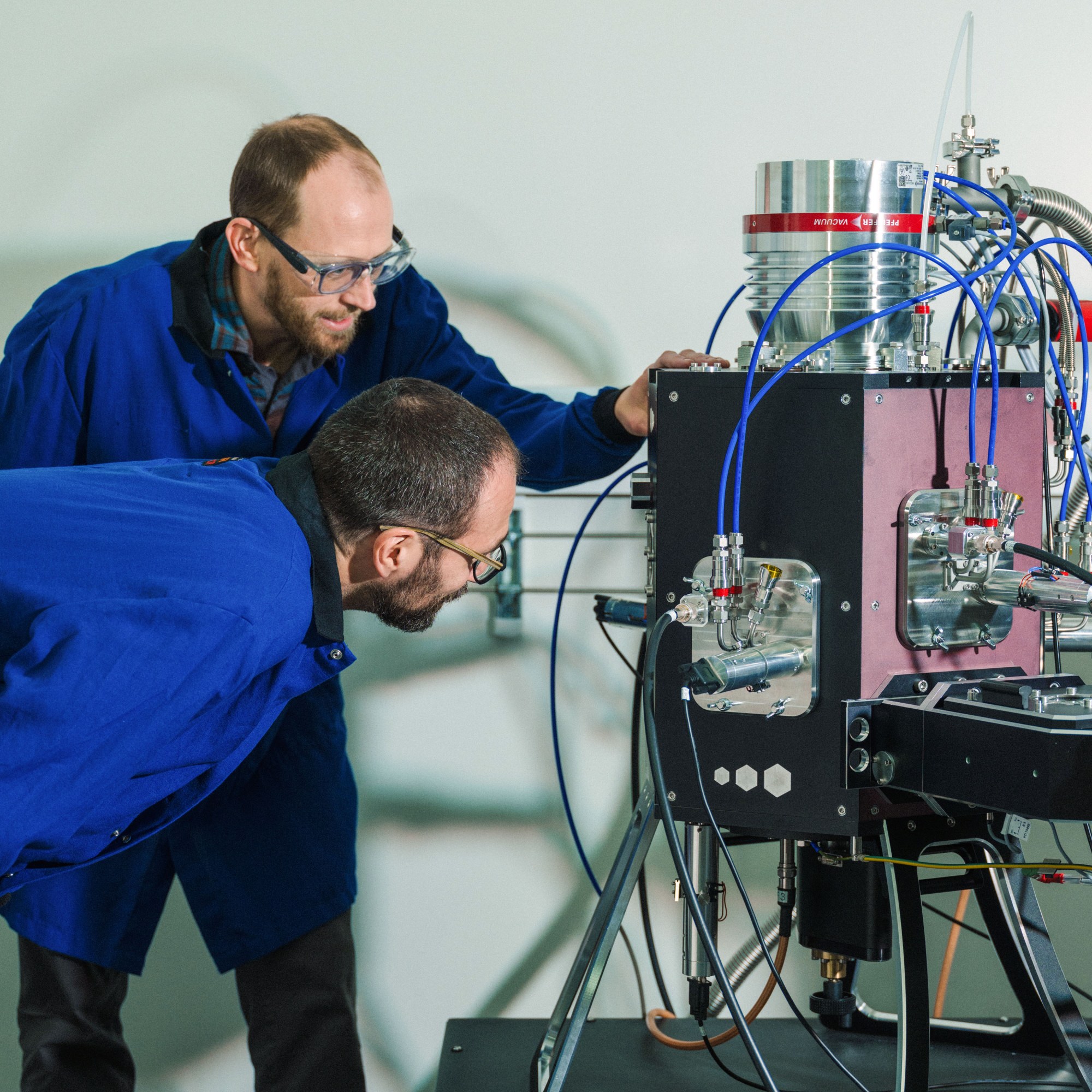
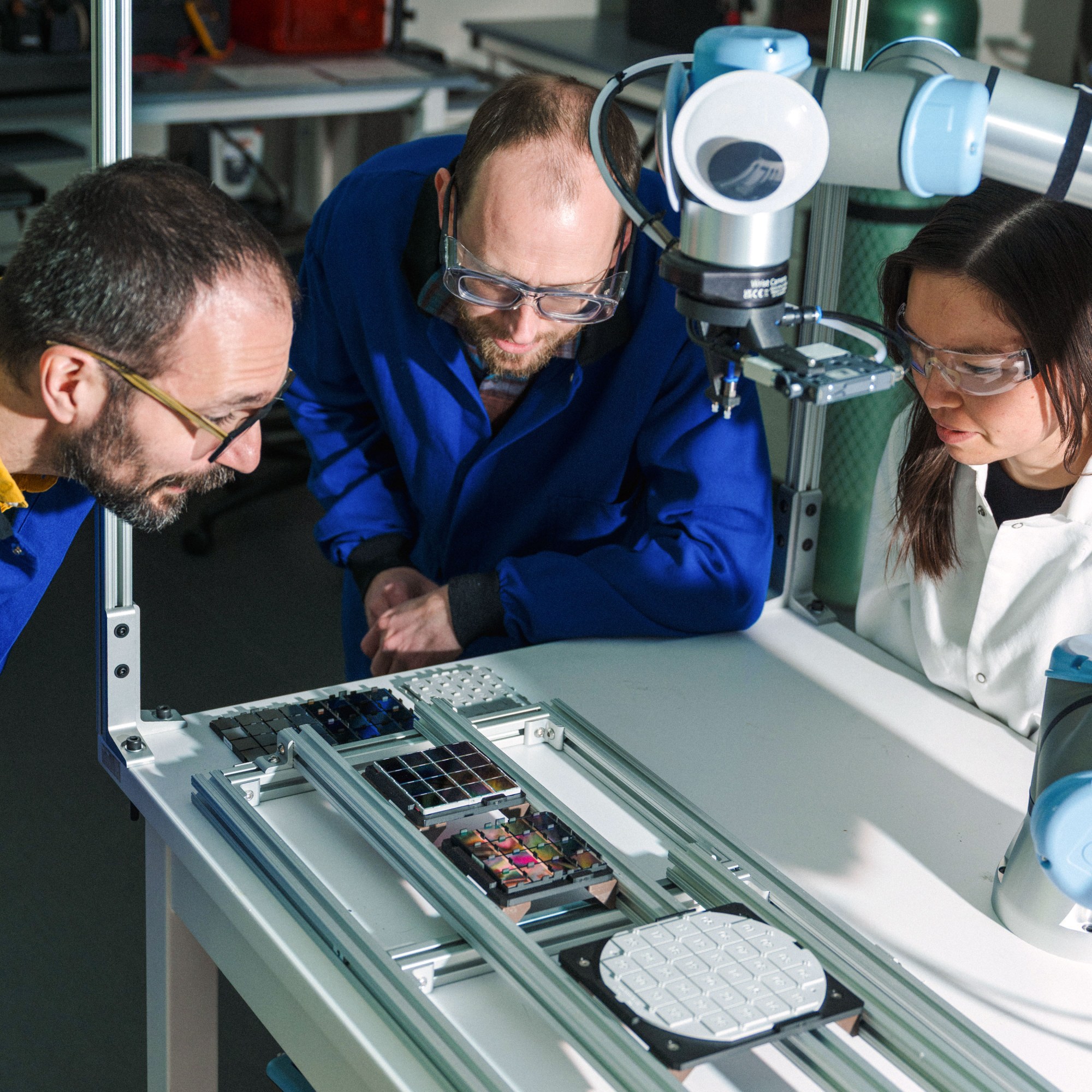
The microwave-size instrument at Lila Sciences in Cambridge, Massachusetts, doesn’t look all that different from others that I’ve seen in state-of-the-art materials labs. Inside its vacuum chamber, the machine zaps a palette of different elements to create vaporized particles, which then fly through the chamber and land to create a thin film, using a technique called sputtering. What sets this instrument apart is that artificial intelligence is running the experiment; an AI agent, trained on vast amounts of scientific literature and data, has determined the recipe and is varying the combination of elements.
Later, a person will walk the samples, each containing multiple potential catalysts, over to a different part of the lab for testing. Another AI agent will scan and interpret the data, using it to suggest another round of experiments to try to optimize the materials’ performance.
This story is part of MIT Technology Review’s Hype Correction package, a series that resets expectations about what AI is, what it makes possible, and where we go next.
For now, a human scientist keeps a close eye on the experiments and will approve the next steps on the basis of the AI’s suggestions and the test results. But the startup is convinced this AI-controlled machine is a peek into the future of materials discovery—one in which autonomous labs could make it far cheaper and faster to come up with novel and useful compounds.
Flush with hundreds of millions of dollars in new funding, Lila Sciences is one of AI’s latest unicorns. The company is on a larger mission to use AI-run autonomous labs for scientific discovery—the goal is to achieve what it calls scientific superintelligence. But I’m here this morning to learn specifically about the discovery of new materials.
We desperately need better materials to solve our problems. We’ll need improved electrodes and other parts for more powerful batteries; compounds to more cheaply suck carbon dioxide out of the air; and better catalysts to make green hydrogen and other clean fuels and chemicals. And we will likely need novel materials like higher-temperature superconductors, improved magnets, and different types of semiconductors for a next generation of breakthroughs in everything from quantum computing to fusion power to AI hardware.
But materials science has not had many commercial wins in the last few decades. In part because of its complexity and the lack of successes, the field has become something of an innovation backwater, overshadowed by the more glamorous—and lucrative—search for new drugs and insights into biology.
The idea of using AI for materials discovery is not exactly new, but it got a huge boost in 2020 when DeepMind showed that its AlphaFold2 model could accurately predict the three-dimensional structure of proteins. Then, in 2022, came the success and popularity of ChatGPT. The hope that similar AI models using deep learning could aid in doing science captivated tech insiders. Why not use our new generative AI capabilities to search the vast chemical landscape and help simulate atomic structures, pointing the way to new substances with amazing properties?
“Simulations can be super powerful for framing problems and understanding what is worth testing in the lab. But there’s zero problems we can ever solve in the real world with simulation alone.”
John Gregoire, Lila Sciences, chief autonomous science officer
Researchers touted an AI model that had reportedly discovered “millions of new materials.” The money began pouring in, funding a host of startups. But so far there has been no “eureka” moment, no ChatGPT-like breakthrough—no discovery of new miracle materials or even slightly better ones.
The startups that want to find useful new compounds face a common bottleneck: By far the most time-consuming and expensive step in materials discovery is not imagining new structures but making them in the real world. Before trying to synthesize a material, you don’t know if, in fact, it can be made and is stable, and many of its properties remain unknown until you test it in the lab.
“Simulations can be super powerful for kind of framing problems and understanding what is worth testing in the lab,” says John Gregoire, Lila Sciences’ chief autonomous science officer. “But there’s zero problems we can ever solve in the real world with simulation alone.”
Startups like Lila Sciences have staked their strategies on using AI to transform experimentation and are building labs that use agents to plan, run, and interpret the results of experiments to synthesize new materials. Automation in laboratories already exists. But the idea is to have AI agents take it to the next level by directing autonomous labs, where their tasks could include designing experiments and controlling the robotics used to shuffle samples around. And, most important, companies want to use AI to vacuum up and analyze the vast amount of data produced by such experiments in the search for clues to better materials.
If they succeed, these companies could shorten the discovery process from decades to a few years or less, helping uncover new materials and optimize existing ones. But it’s a gamble. Even though AI is already taking over many laboratory chores and tasks, finding new—and useful—materials on its own is another matter entirely.
Innovation backwater
I have been reporting about materials discovery for nearly 40 years, and to be honest, there have been only a few memorable commercial breakthroughs, such as lithium-ion batteries, over that time. There have been plenty of scientific advances to write about, from perovskite solar cells to graphene transistors to metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), materials based on an intriguing type of molecular architecture that recently won its inventors a Nobel Prize. But few of those advances—including MOFs—have made it far out of the lab. Others, like quantum dots, have found some commercial uses, but in general, the kinds of life-changing inventions created in earlier decades have been lacking.
Blame the amount of time (typically 20 years or more) and the hundreds of millions of dollars it takes to make, test, optimize, and manufacture a new material—and the industry’s lack of interest in spending that kind of time and money in low-margin commodity markets. Or maybe we’ve just run out of ideas for making stuff.
The need to both speed up that process and find new ideas is the reason researchers have turned to AI. For decades, scientists have used computers to design potential materials, calculating where to place atoms to form structures that are stable and have predictable characteristics. It’s worked—but only kind of. Advances in AI have made that computational modeling far faster and have promised the ability to quickly explore a vast number of possible structures. Google DeepMind, Meta, and Microsoft have all launched efforts to bring AI tools to the problem of designing new materials.
But the limitations that have always plagued computational modeling of new materials remain. With many types of materials, such as crystals, useful characteristics often can’t be predicted solely by calculating atomic structures.
To uncover and optimize those properties, you need to make something real. Or as Rafael Gómez-Bombarelli, one of Lila’s cofounders and an MIT professor of materials science, puts it: “Structure helps us think about the problem, but it’s neither necessary nor sufficient for real materials problems.”
Perhaps no advance exemplified the gap between the virtual and physical worlds more than DeepMind’s announcement in late 2023 that it had used deep learning to discover “millions of new materials,” including 380,000 crystals that it declared “the most stable, making them promising candidates for experimental synthesis.” In technical terms, the arrangement of atoms represented a minimum energy state where they were content to stay put. This was “an order-of-magnitude expansion in stable materials known to humanity,” the DeepMind researchers proclaimed.
To the AI community, it appeared to be the breakthrough everyone had been waiting for. The DeepMind research not only offered a gold mine of possible new materials, it also created powerful new computational methods for predicting a large number of structures.
But some materials scientists had a far different reaction. After closer scrutiny, researchers at the University of California, Santa Barbara, said they’d found “scant evidence for compounds that fulfill the trifecta of novelty, credibility, and utility.” In fact, the scientists reported, they didn’t find any truly novel compounds among the ones they looked at; some were merely “trivial” variations of known ones. The scientists appeared particularly peeved that the potential compounds were labeled materials. They wrote: “We would respectfully suggest that the work does not report any new materials but reports a list of proposed compounds. In our view, a compound can be called a material when it exhibits some functionality and, therefore, has potential utility.”
Some of the imagined crystals simply defied the conditions of the real world. To do computations on so many possible structures, DeepMind researchers simulated them at absolute zero, where atoms are well ordered; they vibrate a bit but don’t move around. At higher temperatures—the kind that would exist in the lab or anywhere in the world—the atoms fly about in complex ways, often creating more disorderly crystal structures. A number of the so-called novel materials predicted by DeepMind appeared to be well-ordered versions of disordered ones that were already known.
More generally, the DeepMind paper was simply another reminder of how challenging it is to capture physical realities in virtual simulations—at least for now. Because of the limitations of computational power, researchers typically perform calculations on relatively few atoms. Yet many desirable properties are determined by the microstructure of the materials—at a scale much larger than the atomic world. And some effects, like high-temperature superconductivity or even the catalysis that is key to many common industrial processes, are far too complex or poorly understood to be explained by atomic simulations alone.
A common language
Even so, there are signs that the divide between simulations and experimental work is beginning to narrow. DeepMind, for one, says that since the release of the 2023 paper it has been working with scientists in labs around the world to synthesize AI-identified compounds and has achieved some success. Meanwhile, a number of the startups entering the space are looking to combine computational and experimental expertise in one organization.
One such startup is Periodic Labs, cofounded by Ekin Dogus Cubuk, a physicist who led the scientific team that generated the 2023 DeepMind headlines, and by Liam Fedus, a co-creator of ChatGPT at OpenAI. Despite its founders’ background in computational modeling and AI software, the company is building much of its materials discovery strategy around synthesis done in automated labs.
The vision behind the startup is to link these different fields of expertise by using large language models that are trained on scientific literature and able to learn from ongoing experiments. An LLM might suggest the recipe and conditions to make a compound; it can also interpret test data and feed additional suggestions to the startup’s chemists and physicists. In this strategy, simulations might suggest possible material candidates, but they are also used to help explain the experimental results and suggest possible structural tweaks.
The grand prize would be a room-temperature superconductor, a material that could transform computing and electricity but that has eluded scientists for decades.
Periodic Labs, like Lila Sciences, has ambitions beyond designing and making new materials. It wants to “create an AI scientist”—specifically, one adept at the physical sciences. “LLMs have gotten quite good at distilling chemistry information, physics information,” says Cubuk, “and now we’re trying to make it more advanced by teaching it how to do science—for example, doing simulations, doing experiments, doing theoretical modeling.”
The approach, like that of Lila Sciences, is based on the expectation that a better understanding of the science behind materials and their synthesis will lead to clues that could help researchers find a broad range of new ones. One target for Periodic Labs is materials whose properties are defined by quantum effects, such as new types of magnets. The grand prize would be a room-temperature superconductor, a material that could transform computing and electricity but that has eluded scientists for decades.
Superconductors are materials in which electricity flows without any resistance and, thus, without producing heat. So far, the best of these materials become superconducting only at relatively low temperatures and require significant cooling. If they can be made to work at or close to room temperature, they could lead to far more efficient power grids, new types of quantum computers, and even more practical high-speed magnetic-levitation trains.

The failure to find a room-temperature superconductor is one of the great disappointments in materials science over the last few decades. I was there when President Reagan spoke about the technology in 1987, during the peak hype over newly made ceramics that became superconducting at the relatively balmy temperature of 93 Kelvin (that’s −292 °F), enthusing that they “bring us to the threshold of a new age.” There was a sense of optimism among the scientists and businesspeople in that packed ballroom at the Washington Hilton as Reagan anticipated “a host of benefits, not least among them a reduced dependence on foreign oil, a cleaner environment, and a stronger national economy.” In retrospect, it might have been one of the last times that we pinned our economic and technical aspirations on a breakthrough in materials.
The promised new age never came. Scientists still have not found a material that becomes superconducting at room temperatures, or anywhere close, under normal conditions. The best existing superconductors are brittle and tend to make lousy wires.
One of the reasons that finding higher-temperature superconductors has been so difficult is that no theory explains the effect at relatively high temperatures—or can predict it simply from the placement of atoms in the structure. It will ultimately fall to lab scientists to synthesize any interesting candidates, test them, and search the resulting data for clues to understanding the still puzzling phenomenon. Doing so, says Cubuk, is one of the top priorities of Periodic Labs.
AI in charge
It can take a researcher a year or more to make a crystal structure for the first time. Then there are typically years of further work to test its properties and figure out how to make the larger quantities needed for a commercial product.
Startups like Lila Sciences and Periodic Labs are pinning their hopes largely on the prospect that AI-directed experiments can slash those times. One reason for the optimism is that many labs have already incorporated a lot of automation, for everything from preparing samples to shuttling test items around. Researchers routinely use robotic arms, software, automated versions of microscopes and other analytical instruments, and mechanized tools for manipulating lab equipment.
The automation allows, among other things, for high-throughput synthesis, in which multiple samples with various combinations of ingredients are rapidly created and screened in large batches, greatly speeding up the experiments.
The idea is that using AI to plan and run such automated synthesis can make it far more systematic and efficient. AI agents, which can collect and analyze far more data than any human possibly could, can use real-time information to vary the ingredients and synthesis conditions until they get a sample with the optimal properties. Such AI-directed labs could do far more experiments than a person and could be far smarter than existing systems for high-throughput synthesis.
But so-called self-driving labs for materials are still a work in progress.
Many types of materials require solid-state synthesis, a set of processes that are far more difficult to automate than the liquid-handling activities that are commonplace in making drugs. You need to prepare and mix powders of multiple inorganic ingredients in the right combination for making, say, a catalyst and then decide how to process the sample to create the desired structure—for example, identifying the right temperature and pressure at which to carry out the synthesis. Even determining what you’ve made can be tricky.
In 2023, the A-Lab at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory claimed to be the first fully automated lab to use inorganic powders as starting ingredients. Subsequently, scientists reported that the autonomous lab had used robotics and AI to synthesize and test 41 novel materials, including some predicted in the DeepMind database. Some critics questioned the novelty of what was produced and complained that the automated analysis of the materials was not up to experimental standards, but the Berkeley researchers defended the effort as simply a demonstration of the autonomous system’s potential.
“How it works today and how we envision it are still somewhat different. There’s just a lot of tool building that needs to be done,” says Gerbrand Ceder, the principal scientist behind the A-Lab.
AI agents are already getting good at doing many laboratory chores, from preparing recipes to interpreting some kinds of test data—finding, for example, patterns in a micrograph that might be hidden to the human eye. But Ceder is hoping the technology could soon “capture human decision-making,” analyzing ongoing experiments to make strategic choices on what to do next. For example, his group is working on an improved synthesis agent that would better incorporate what he calls scientists’ “diffused” knowledge—the kind gained from extensive training and experience. “I imagine a world where people build agents around their expertise, and then there’s sort of an uber-model that puts it together,” he says. “The uber-model essentially needs to know what agents it can call on and what they know, or what their expertise is.”
“In one field that I work in, solid-state batteries, there are 50 papers published every day. And that is just one field that I work in. The A I revolution is about finally gathering all the scientific data we have.”
Gerbrand Ceder, principal scientist, A-Lab
One of the strengths of AI agents is their ability to devour vast amounts of scientific literature. “In one field that I work in, solid-state batteries, there are 50 papers published every day. And that is just one field that I work in,” says Ceder. It’s impossible for anyone to keep up. “The AI revolution is about finally gathering all the scientific data we have,” he says.
Last summer, Ceder became the chief science officer at an AI materials discovery startup called Radical AI and took a sabbatical from the University of California, Berkeley, to help set up its self-driving labs in New York City. A slide deck shows the portfolio of different AI agents and generative models meant to help realize Ceder’s vision. If you look closely, you can spot an LLM called the “orchestrator”—it’s what CEO Joseph Krause calls the “head honcho.”
New hope
So far, despite the hype around the use of AI to discover new materials and the growing momentum—and money—behind the field, there still has not been a convincing big win. There is no example like the 2016 victory of DeepMind’s AlphaGo over a Go world champion. Or like AlphaFold’s achievement in mastering one of biomedicine’s hardest and most time-consuming chores, predicting 3D structures of proteins.
The field of materials discovery is still waiting for its moment. It could come if AI agents can dramatically speed the design or synthesis of practical materials, similar to but better than what we have today. Or maybe the moment will be the discovery of a truly novel one, such as a room-temperature superconductor.

With or without such a breakthrough moment, startups face the challenge of trying to turn their scientific achievements into useful materials. The task is particularly difficult because any new materials would likely have to be commercialized in an industry dominated by large incumbents that are not particularly prone to risk-taking.
Susan Schofer, a tech investor and partner at the venture capital firm SOSV, is cautiously optimistic about the field. But Schofer, who spent several years in the mid-2000s as a catalyst researcher at one of the first startups using automation and high-throughput screening for materials discovery (it didn’t survive), wants to see some evidence that the technology can translate into commercial successes when she evaluates startups to invest in.
In particular, she wants to see evidence that the AI startups are already “finding something new, that’s different, and know how they are going to iterate from there.” And she wants to see a business model that captures the value of new materials. She says, “I think the ideal would be: I got a spec from the industry. I know what their problem is. We’ve defined it. Now we’re going to go build it. Now we have a new material that we can sell, that we have scaled up enough that we’ve proven it. And then we partner somehow to manufacture it, but we get revenue off selling the material.”
Schofer says that while she gets the vision of trying to redefine science, she’d advise startups to “show us how you’re going to get there.” She adds, “Let’s see the first steps.”
Demonstrating those first steps could be essential in enticing large existing materials companies to embrace AI technologies more fully. Corporate researchers in the industry have been burned before—by the promise over the decades that increasingly powerful computers will magically design new materials; by combinatorial chemistry, a fad that raced through materials R&D labs in the early 2000s with little tangible result; and by the promise that synthetic biology would make our next generation of chemicals and materials.
More recently, the materials community has been blanketed by a new hype cycle around AI. Some of that hype was fueled by the 2023 DeepMind announcement of the discovery of “millions of new materials,” a claim that, in retrospect, clearly overpromised. And it was further fueled when an MIT economics student posted a paper in late 2024 claiming that a large, unnamed corporate R&D lab had used AI to efficiently invent a slew of new materials. AI, it seemed, was already revolutionizing the industry.
A few months later, the MIT economics department concluded that “the paper should be withdrawn from public discourse.” Two prominent MIT economists who are acknowledged in a footnote in the paper added that they had “no confidence in the provenance, reliability or validity of the data and the veracity of the research.”
Can AI move beyond the hype and false hopes and truly transform materials discovery? Maybe. There is ample evidence that it’s changing how materials scientists work, providing them—if nothing else—with useful lab tools. Researchers are increasingly using LLMs to query the scientific literature and spot patterns in experimental data.
But it’s still early days in turning those AI tools into actual materials discoveries. The use of AI to run autonomous labs, in particular, is just getting underway; making and testing stuff takes time and lots of money. The morning I visited Lila Sciences, its labs were largely empty, and it’s now preparing to move into a much larger space a few miles away. Periodic Labs is just beginning to set up its lab in San Francisco. It’s starting with manual synthesis guided by AI predictions; its robotic high-throughput lab will come soon. Radical AI reports that its lab is almost fully autonomous but plans to soon move to a larger space.

When I talk to the scientific founders of these startups, I hear a renewed excitement about a field that long operated in the shadows of drug discovery and genomic medicine. For one thing, there is the money. “You see this enormous enthusiasm to put AI and materials together,” says Ceder. “I’ve never seen this much money flow into materials.”
Reviving the materials industry is a challenge that goes beyond scientific advances, however. It means selling companies on a whole new way of doing R&D.
But the startups benefit from a huge dose of confidence borrowed from the rest of the AI industry. And maybe that, after years of playing it safe, is just what the materials business needs.
This story is part of an online package on resetting expectations around AI. For more see technologyreview.com/hypecorrection.