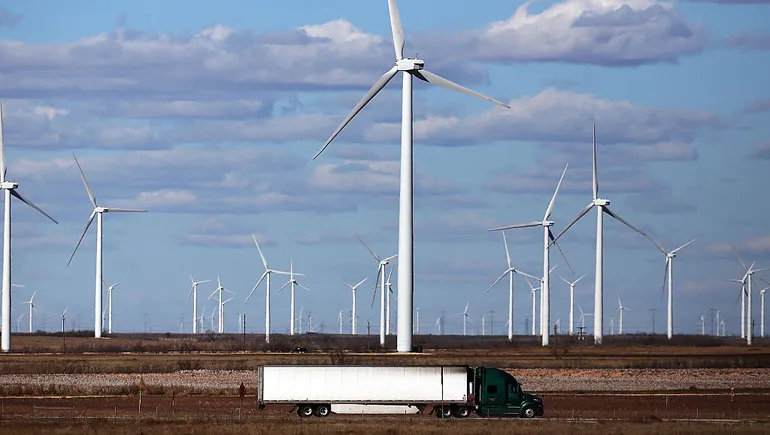
The Texas Legislature is considering bills that would increase requirements for renewable energy facility siting and generation reliability, raising concerns from the sector about how this legislation could reduce deployment during a time of increasing energy demand.
“With energy demand rising fast, Texas needs every megawatt it can generate to keep the lights on and our economy strong,” said Daniel Giese, the Solar Energy Industries Association’s Texas director of state affairs, in an April 15 press release following the Texas Senate passing one such bill, SB 819.
SB 819 would “represent a significant change to renewables development,” even after the Senate “scaled back some of the more rigorous requirements,” law firm Vinson & Elkins said in an April 21 blog post.
The bill would require “create a siting regime for most new or expanded solar and wind projects,” Vinson & Elkins said, requiring developers to “apply for and receive a permit before interconnection to the ERCOT transmission grid of a renewable generation facility with a capacity of 10 MW or greater,” the firm said.
SEIA said the bill “adds onerous requirements to new solar projects that would not apply to other energy sources except wind,” which would risk grid reliability, raise utility bills and infringe on property rights.
“Property rights are a core Texas value, but this bill would claw back landowners’ rights to make land use decisions that are best for themselves and their families,” SEIA said. “The state telling landowners that they can’t use their land in the way they see fit is antithetical to the Texas identity.”
Stewards of Texas, a policy group lobbying for the bill, argues the opposite. It says in a Jan. 17 release that the bill “will ensure responsible siting of wind and solar projects to minimize environmental damage while safeguarding landowner rights and natural resources.”
Sen. Lois Kolkhorst, the bill’s sponsor, said in the Stewards of Texas release that “this bipartisan legislation offers a common-sense approach to the encroachment of wind and solar facilities being scattered across our great state with no consideration or safeguards for landowners.”
Texas is one of the top solar energy-producing states in the U.S., ranking first in installed solar capacity in 2023 and first in total utility-scale solar and new solar added in 2024, according to SEIA. The state is also consistently the top wind energy producer in the U.S., producing 28% of all U.S. wind-sourced electricity in 2023, according to the Energy Information Administration.
After passing the Senate, SB 819 was referred to the House Committee on State Affairs on Tuesday.
Retroactive reliability standards
The legislature is also considering SB 715 and the identical House companion bill, HB 3356, which would alter existing legislation that sets reliability standards for generators coming into service on or after Jan. 1, 2028. SB 715 moves the deadline back a year, and stipulates that the requirement apply to all generators retroactively.
“This would be wildly expensive, creating thousands of mini-ERCOTs who each must procure their own reserves,” said Doug Lewin, founder of Stoic Energy Consulting, in an April 15 blog post. “This is almost certainly illegal as hundreds of billions of dollars were invested based on the rules that were in place at the time.”
The Texas Public Policy Foundation, a think tank which provided testimony in support of HB 3356, said in a release that “a uniform standard for all generators — not just new generators — is essential to ensure that new generators are not advantaged or disadvantaged relative to existing generators.”
Brent Bennett, policy director of TPPF’s Life:Powered project, testified to the House State Affairs Committee on April 14 that “wind and solar volatility imposes such a steep cost because it creates more uncertainty in how much dispatchable capacity is needed to keep the system running and when that capacity must be dispatched.”
Bennett said this volatility “will lead to spiraling costs as dispatchable power will need to be paid more and more to close a growing reliability deficit.”
Lewin noted in his blog post that the Public Utility Commission of Texas filed a report “on costs associated with dispatchable and nondispatchable generation facilities” in December that concluded that “while these analyses indicate that [ancillary service] costs have moderately increased over time, on average, they do not establish a clear link between AS costs and the amount of non-dispatchable capacity on the system.”
HB 3356 was heard by the House State Affairs Committee on Wednesday and reported favorably out of the committee. Its Senate companion, SB 715, was reportedly favorably out of committee the day before, and placed on the Senate’s intent calendar.