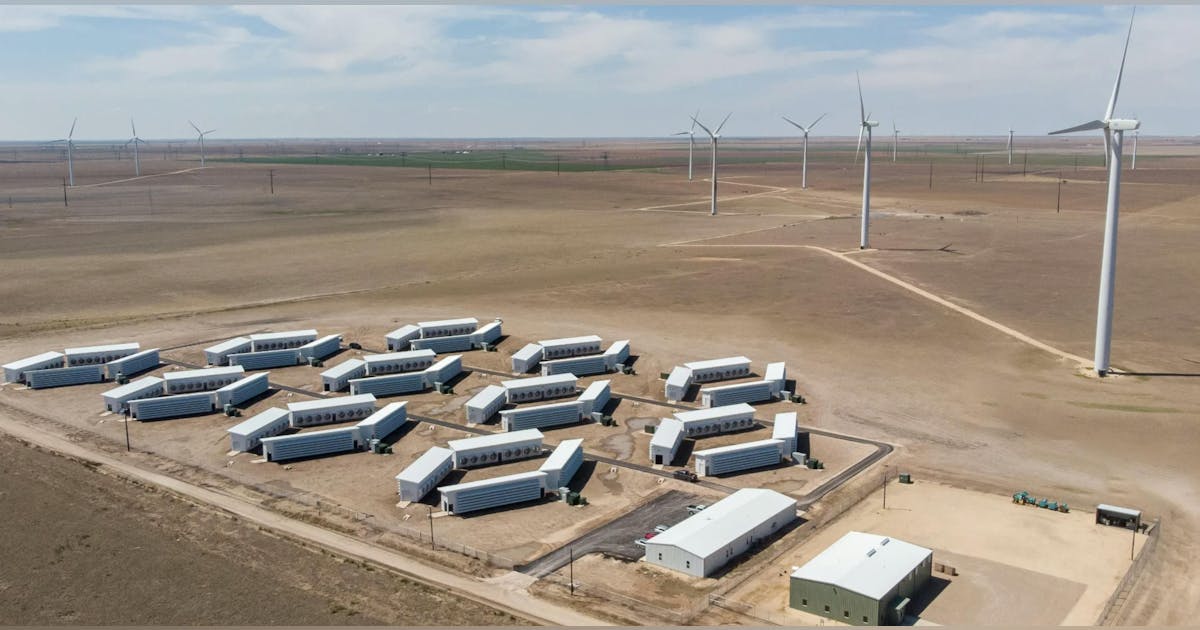
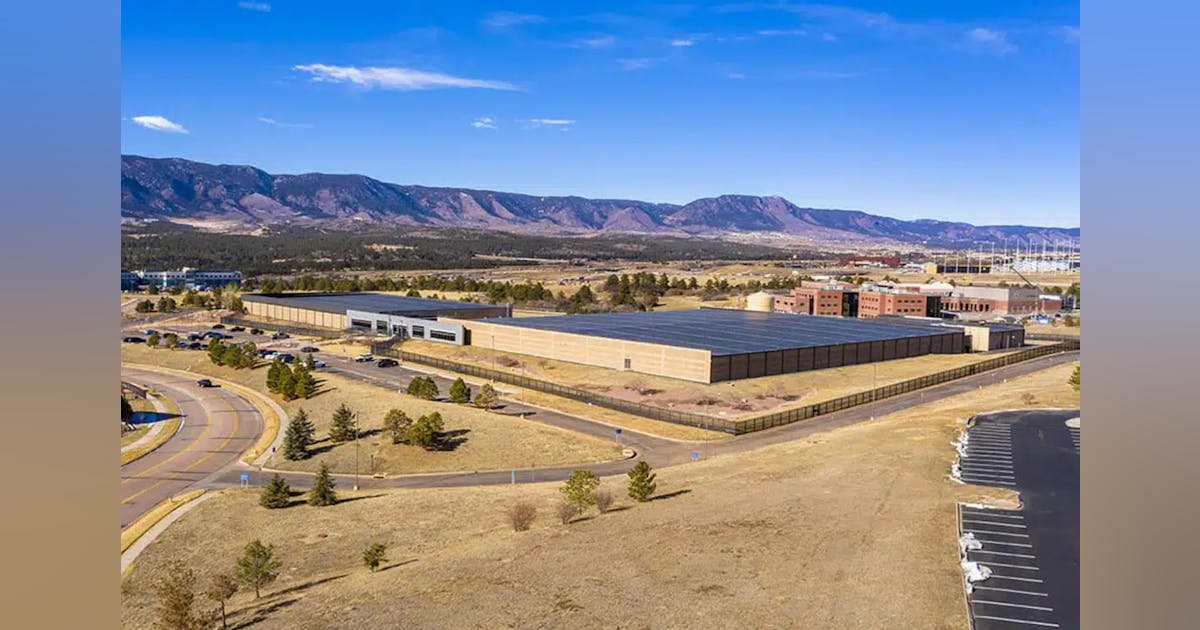
Artificial intelligence has, without question, crossed the threshold—from a speculative academic pursuit into the defining infrastructure of 21st-century commerce, governance, and innovation. What began in the realm of research labs and open-source models is now embedded in the capital stack of every major hyperscaler, semiconductor roadmap, and national industrial strategy. But as AI scales, so does its energy footprint. From Nvidia-powered GPU clusters to exascale training farms, the conversation across boardrooms and site selection teams has fundamentally shifted. It’s no longer just about compute density, thermal loads, or software frameworks. It’s about power—how to find it, finance it, future-proof it, and increasingly, how to generate it onsite. That refrain—“It’s all about power now”—has moved from a whisper to a full-throated consensus across the data center industry. The latest report from the International Energy Agency (IEA) gives this refrain global context and hard numbers, affirming what developers, utilities, and infrastructure operators have already sensed on the ground: the AI revolution will be throttled or propelled by the availability of scalable, sustainable, and dispatchable electricity. Why Energy Is the Real Bottleneck to Intelligence at Scale The major new IEA report puts it plainly: The transformative promise of AI will be throttled—or unleashed—by the world’s ability to deliver scalable, reliable, and sustainable electricity. The stakes are enormous. Countries that can supply the power AI craves will shape the future. Those that can’t may find themselves sidelined. Importantly, while AI poses clear challenges, the report emphasizes how it also offers solutions: from optimizing energy grids and reducing emissions in industrial sectors to enhancing energy security by supporting infrastructure defenses against cyberattacks. The report calls for immediate investments in both energy generation and grid capabilities, as well as stronger collaboration between the tech and energy sectors to avoid critical bottlenecks. The IEA advises that, for countries