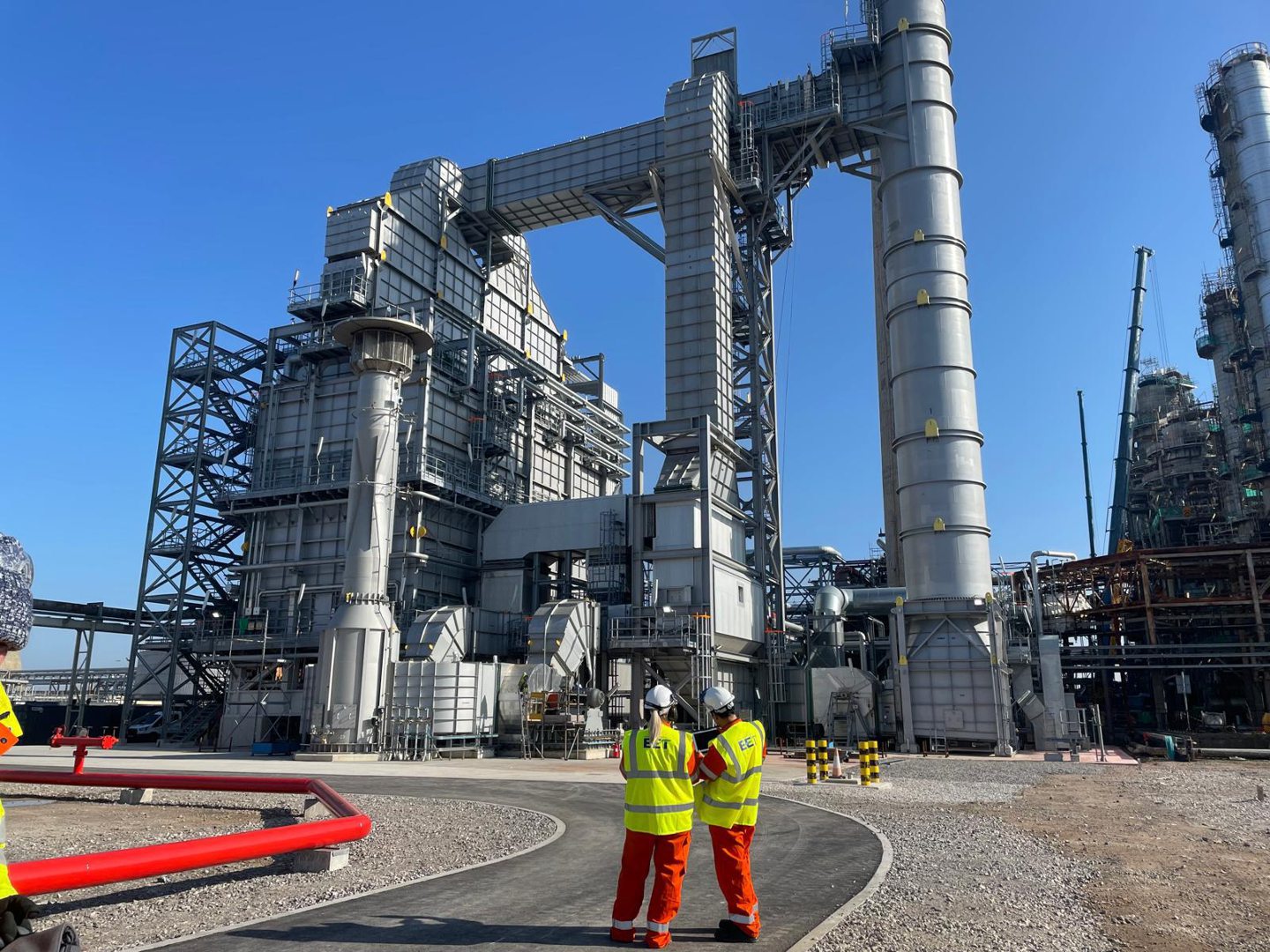
Essar Energy Transition (EET) Fuels has completed the installation and connection of a hydrogen-ready furnace at its Stanlow refinery site, in a landmark moment for UK industry.
Formerly Essar Oil, EET Fuels aims to create the “world’s leading low-carbon process refinery” at Ellesmere Port, Cheshire, having taken delivery of the furnace in 2022.
The new furnace will consume around 10% of Stanlow’s total energy usage and replace three existing furnaces at the refinery, the company said.
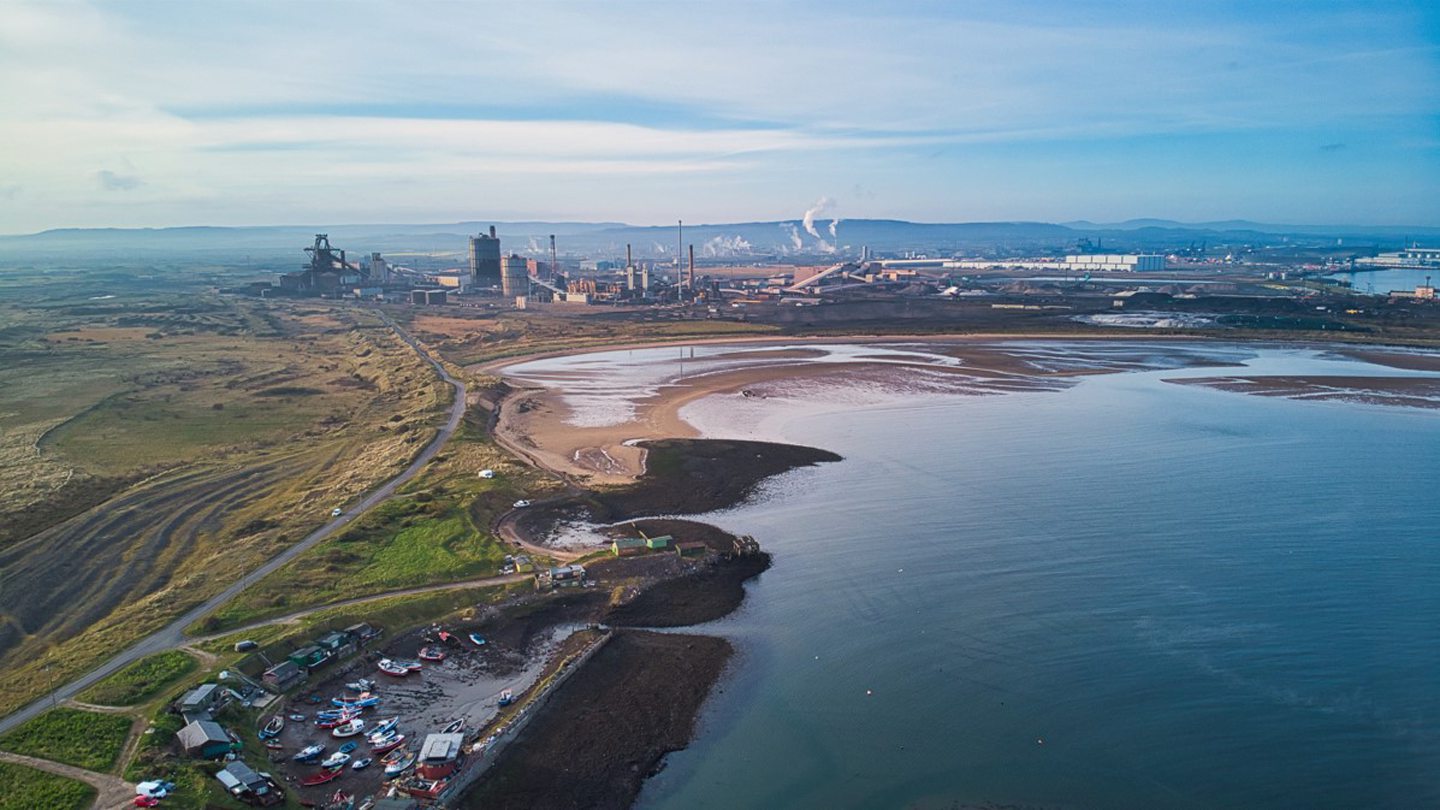
The Stanlow site is one of the largest oil refineries in Europe and supplies close to 16% of all road transport fuels in the UK, processing 4.4 billion litres of diesel each year.
EET Fuels said the new furnace will be capable of running on 100% refinery off gas (ROG), a blend of ROG and hydrogen fuel – or 100% hydrogen.
EET Fuels chief executive Deepak Maheshwari said the installation of the hydrogen-ready furnace is a “major milestone” in the company’s decarbonisation strategy.
“Decommissioning three old furnaces and connecting this new highly efficient hydrogen-ready furnace to our refinery is a significant milestone for EET Fuels,” he said.
“Not only will the new furnace deliver an immediate reduction in CO2 emissions, it will deliver an even bigger reduction once fully powered with low-carbon hydrogen.”
And as Ruth Herbert, EET managing director, business development and strategic initiatives, told Energy Voice editor Mark Selby in our exclusive video interview:
“We are officially hydrogen ready at Stanlow refinery, so for us it’s not in the future – it’s now… and we’re ready to receive the hydrogen.”
Stanlow refinery decarbonisation
Refinery furnaces are critical for heating crude oil and other feedstocks to separate and purify the crude to produce various fuels and chemical products.
EET plans to run the furnace on conventional fuel until 2028, before transitioning to 100% low-carbon hydrogen produced at EET Hydrogen’s HPP1 plant.
Approved in January last year, the 1.35 GW blue hydrogen production facility forms part of the HyNet industrial decarbonisation cluster.
Consisting of two plants (HPP1 and HPP2), EET said the hydrogen hub will enable local industries to switch from fossil fuels to low-carbon energy.
Under the HyNet plans, up to 97% of the carbon emitted from the hydrogen production process will be captured and stored in depleted gas fields under Liverpool Bay.
Italian operator Eni reached a financial deal with the UK government last week to progress the £2 billion carbon capture and storage (CCS) project.
EET said the installation of the hydrogen-ready furnace will “significantly progress” its aim to eliminate 95% of its carbon emissions by 2030.
When running on 100% hydrogen, it will reduce the Stanlow site’s annual CO2 emissions by 200,000 tonnes.
EET said the furnace will also improve air quality at the site by significantly reducing nitrogen oxide emissions, alongside improvements to energy efficiency.
Alongside the hydrogen-ready furnace, EET is also aiming to build Europe’s first hydrogen-ready combine heat and power (CHP) plant at Stanlow by 2027.
EET revealed to Energy Voice last year that it will become the first supplier of hydrogen-generated electricity to the UK grid from the CHP project.
EET is also partnering with SSE to develop the 40 MW Gowy Green electrolytic hydrogen production facility at Stanlow.