As electricity demand grows, alongside wind and solar’s share in the U.S. energy mix, concerns about renewables’ reliability are being raised more frequently — including at the highest levels of the federal government.
“With the electricity grid, you have to match supply and demand in every moment in time,” Energy Secretary Chris Wright said recently on Fox News. “With wind and solar, you don’t know when they’re going to be there, and you don’t know when they’re going to go away.”
Wright went on to say the development of renewables has led to an “extra distribution grid” that has raised energy prices.
But utility planners, grid operators and analysts say wind, solar and batteries are an important part of an evolving power system in which intermittent resources can be reliably scheduled and called upon using sophisticated software and other tools.
They also point to both the levelized cost of electricity for renewables and their competitiveness in automated energy markets that select the least cost units to run in each hour.
“System operators don’t decide whether resources bidding into the market are good or bad,” said Rob Gramlich, president of energy sector consultant Grid Strategies, in an interview.
“There is no central decision maker,” he said. “Markets don’t play favorites.”
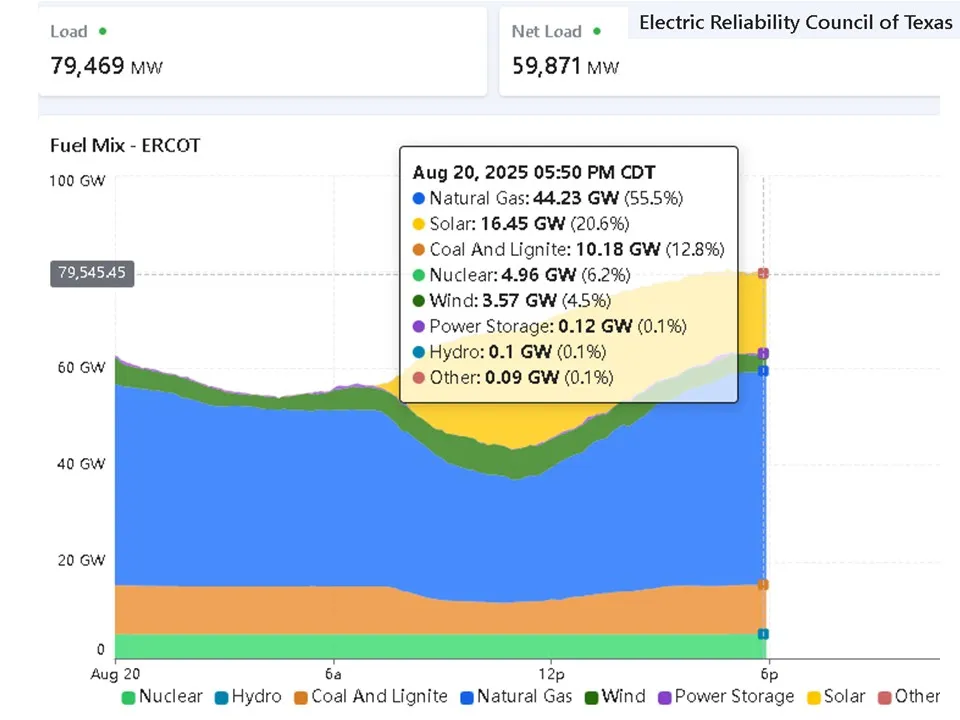
ERCOT’s multi-resource price-selected portfolio for August 20, 2025, at 5:50 PM CDT
With generators retiring, demand rising, and construction, financing, permitting and supply chain challenges growing, operators and analysts acknowledged concerns over the future of the U.S. power system. Many called for diversification of resources, including renewables and storage, to protect electricity reliability and affordability.
“The objective of planning is a portfolio of diverse resources at the least cost possible to avoid outsized impacts from any single one,” said Michael Eugenis, Arizona Public Service’s director of resource planning.
APS is pursuing renewables alongside more natural gas to maintain reliability in its territory, he said.
“That is not the same as a second set or a shadow set of resources,” he added.
Automated markets are selecting renewables
One of the major concerns cited by Wright and others is the intermittent nature of renewables and the impact of that on grid reliability.
One of the ways grid operators measure reliability is using a metric called effective load carrying capability, or ELCC.
ELCC is a complex calculation based on comparing what portion of a resource’s nameplate capacity it produces on average in simulations of decades that include factors that cause it to vary, like performance, supply and demand. For fossil resources, variabilities are caused by things like maintenance outages and fuel supply issues. Weather variations impact wind and solar.
ELCCs vary by region and by each system’s portfolio makeup, but nuclear power generally has the highest ELCC, meaning on average over the years, it produces the closest percentage of its nameplate capacity.
Fixed-tilt solar had the lowest at 8%, and tracking solar was 11%. Onshore wind was 41%, offshore was 69%; storage was between 50% and 72%; gas was between 60% and 78%, and coal was 83%.
“System operators don’t decide whether resources bidding into the market are good or bad … Markets don’t play favorites.”

Rob Gramlich
president of Grid Strategies
But despite their relatively low ELCCs, automated markets are consistently choosing renewables over other resources because they are cheaper at the time the grid needs them.
“The automated market mechanisms use all the relevant variables that affect load to pick the cheapest resources,” said Richard Doying, Grid Strategies vice president and a former executive vice president for market and grid strategy for the former Midcontinent Independent System Operator.
Those resources are bid out, and “then the next cheapest resources, and so on,” Doying said.
“The markets are selecting wind and solar despite their low ELCCs and low capacity values because the return justifies the investment,” he added.
When they are both generating at the same time, renewables are often cheaper than fossil fuel power.
One reason for this is that the fuel and maintenance costs for fossil-based resources are significant, continuous and volatile. Natural gas prices, for example, have nearly doubled since 2024, but are still lower than they were in 2022 following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
The fuels for wind and solar are cost-free, maintenance outage costs are significantly less, and the capital expenditures to build projects are typically amortized over 20 years.
“If natural gas was the cheapest option to meet the peak, the markets would select it,” said Sean Kelly, co-founder and CEO of forecast provider Amperon and a former energy analyst.
When the sun’s not shining
Kelly said today’s advanced load and weather forecasting enhances the reliability of a resource portfolio with a high renewables penetration.
While good forecasting can alleviate much of the need for backup generation, he said, rising demand for power will likely require more firm generation to fill the gaps when there is no sun or wind.
The ability to choose the cheapest available power source in real time is why grid operators say renewables are an important part of the same, increasingly flexible power system — not a separate system.
“We don’t have different systems; we have a portfolio of resources and capabilities that meet the needs of the system,” said Mark Rothleder, senior vice president and COO for the California Independent System Operator, in an interview.
California has one of the highest renewables penetrations in the United States. California also has some of the highest electricity rates. Some observers link those to things to argue that renewables drive up energy costs.
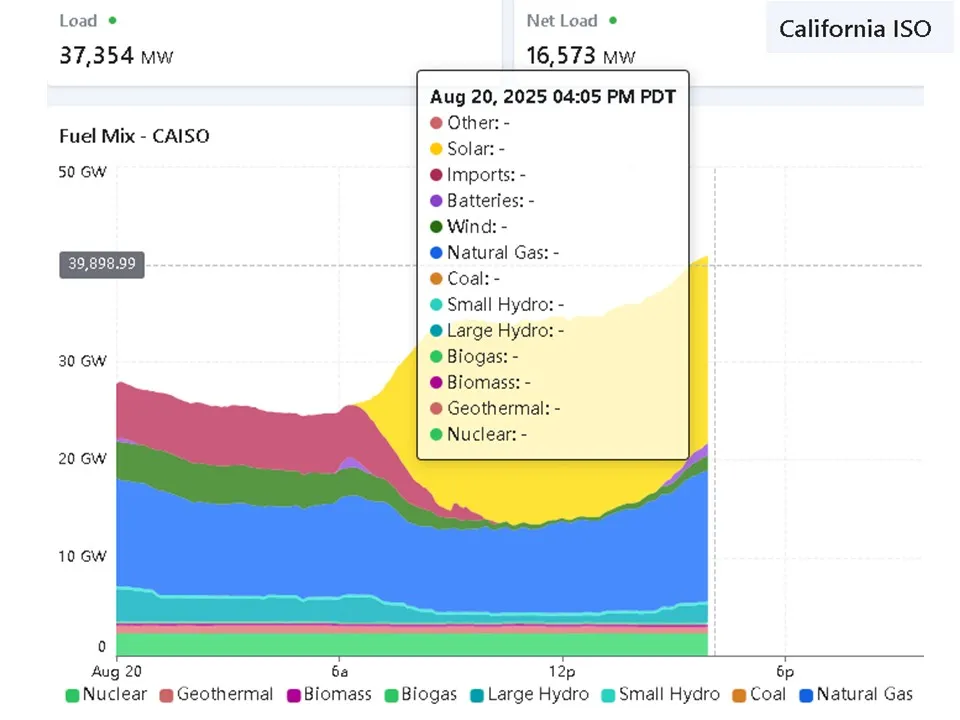
CAISO’s multi-resource price-selected portfolio for August 20, 2025, at 4:05 PM PDT
But other states with high levels of renewable power have comparatively low rates compared to the national average.
In Iowa, for example, wind turbines generated 59% of the state’s electricity in 2023, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration. Iowa was also in the 10 states with the lowest average electricity price that year.
While solar and wind are not always available locally when demand is high, storage penetrations are rising and some states are moving toward more regional energy markets where cheaply-produced energy from renewables can be more easily traded across state boundaries.
The New York Independent System Operator said in a recent report that although “duration-limited” generators like wind and solar require standby resources when the availability of the renewable fleet diminishes, “no generating type operates at full power, full time.”
Thinking of resources as either intermittent or backup oversimplifies the complexity of the grid, experts said.
“Wind and solar don’t have to produce 100% of the time because people aren’t consuming all available electricity 100% of the time,” said Beth Garza, a senior fellow at the R Street Institute think tank and former ERCOT market monitor CEO.
“It is easy to vilify solar and wind,” Garza said. But regardless of the resource mix, “the average electricity load is only about half the peak demand.”
When demand peaks
Power systems have long been required to have reserve margins over the highest expected peak demand, and the growth of wind and solar has not changed that, said Julia Matevosyan, an associate director and chief engineer with the Energy Systems Integration Group and a former ERCOT planning engineer.
But advancements in software and market shifts have democratized incentives for energy production, conservation and storage in ways that can smooth demand peaks and deploy resources as needed.
This flexibility can optimize wind, solar and batteries to deliver low cost electricity more reliably than “a more limited set of traditional resources,” Matevosyan said.
Over the summer, California deployed what some advocates have called the largest virtual power plant in the world when several aggregators discharged 539 MW of average output from more than 100,000 customer-sited batteries during peak demand between 7 and 9 p.m.
A Brattle Group study of the deployment commissioned by Sunrun and Tesla Energy, both of which participated in the VPP program, concluded that it could reduce the need for gas peaker plants and potentially save ratepayers $206 million between 2025 and 2028.
Ryan Hledik, one of the report’s authors, said the VPP makes better use of assets that have already been deployed.
“There are a growing number of examples of VPPs scaling faster and at a lower cost than conventional resources,” Hledik said.
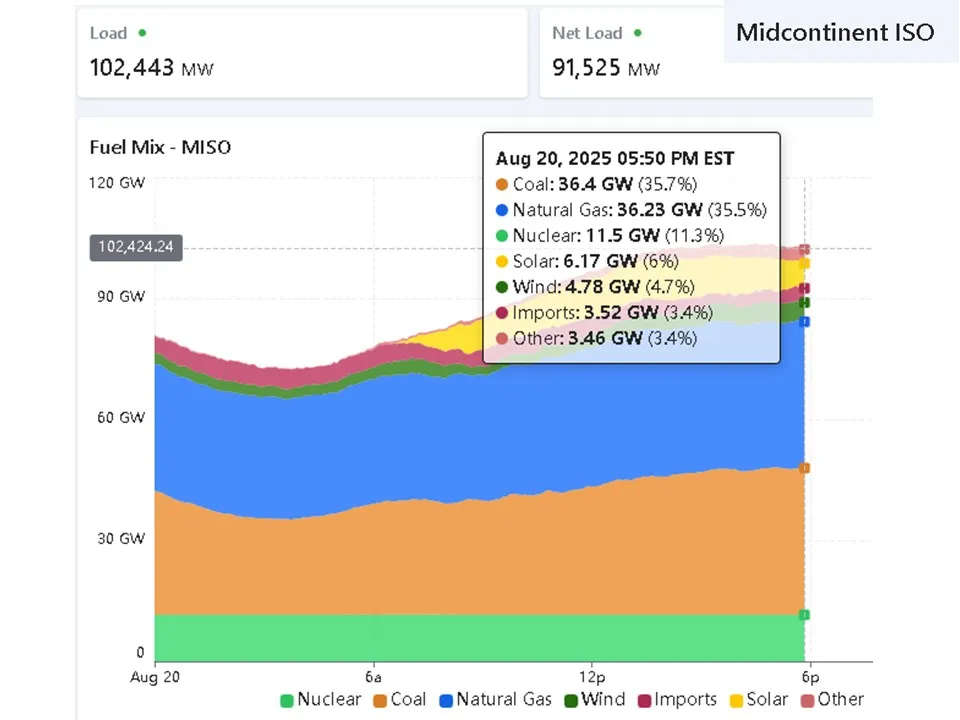
MISO’s multi-resource price-selected portfolio for August 20, 2025, at 5:50 PM EST
Renewables continue to dominate new generation as demand rises
Demand is rising for the first time in two decades. Last year, the U.S. used more electricity than ever before, and the EIA projects demand to grow more than 2% per year until at least 2026. Farther out, the predictions vary widely and are highly dependent on the growth of data centers, electrification and manufacturing.
The vast majority of new generation resources coming online now are renewable, with solar in the lead, followed by wind. Thrugh July 2025. In the first seven months of 2025, solar accounted for over 16 GW of the 21.5 GW added to the U.S. power system. Wind accounted for almost 3.3 GW and natural gas for 2.2 GW, the September Federal Energy Regulatory Commission Infrastructure Update reported.
Federal tax credits and other incentives that are being phased out boosted renewable development. But experts say even without that support, the economics are also in renewables’ favor.
“Wind and solar don’t have to produce 100% of the time because people aren’t consuming all available electricity 100% of the time.”

Beth Garza
senior fellow at R Street Institute and former ERCOT market monitor CEO.
The levelized cost of electricity for utility-scale solar and onshore wind remain “the most cost-effective forms of new-build energy generation on an unsubsidized basis,” according to Lazard analysis. Calculating a technology’s LCOE involves its capital cost, fuel cost, capacity factor, and other values that vary by location and time.
Recently, renewable trade groups have warned of a slowdown in the solar industry. But alternative resources, like natural gas, face their own challenges, from lengthy planning and approval processes to rising fuel prices and years-long equipment backlogs.
“The newest, most efficient natural gas peaker plants are expensive to build and are likely to become more expensive to run because of competition for natural gas,” Garza said. “The market’s answer to load growth is still to build more wind, solar, and batteries because they are the cheaper and faster to build.”
Michelle Solomon, a manager of electricity policy at Energy Innovation, offered a similar observation.
Utility planning models “have largely been choosing wind and solar and batteries for several years,” she said. “A diverse set of resources is most likely to be the cheapest portfolio.”
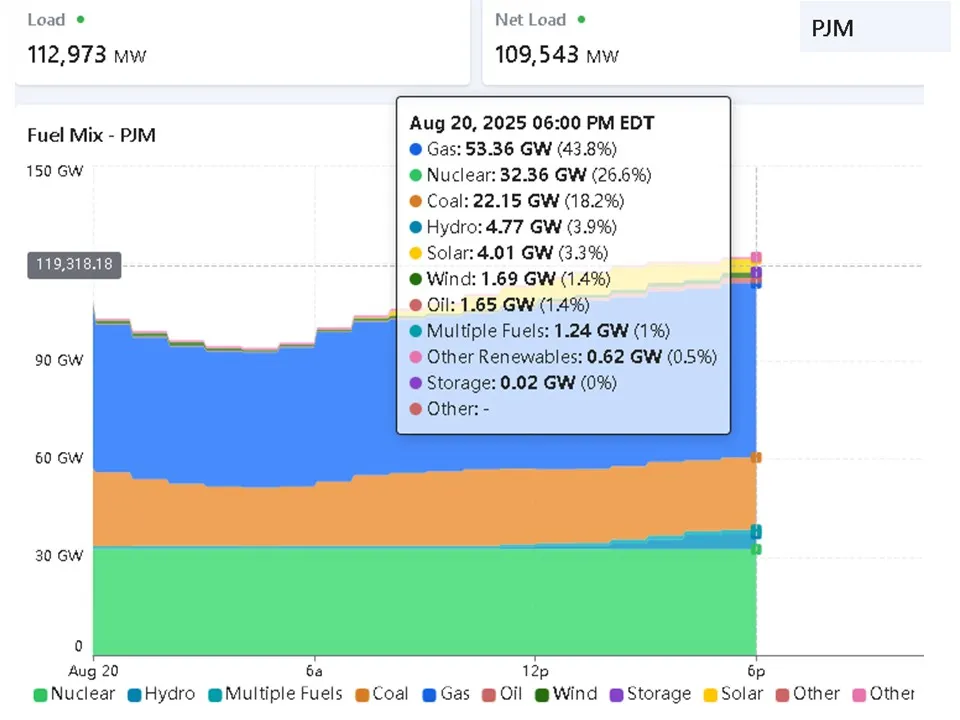
PJM’s multi-resource price-selected portfolio for August 20, 2025, at 6:00 PM EDT