Thanks to Ben Lichtman (B3NNY) at the Seattle Rust Meetup for pointing me in the right direction on SIMD.
SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) operations have been a feature of Intel/AMD and ARM CPUs since the early 2000s. These operations enable you to, for example, add an array of eight i32 to another array of eight i32 with just one CPU operation on a single core. Using SIMD operations greatly speeds up certain tasks. If you’re not using SIMD, you may not be fully using your CPU’s capabilities.
Is this “Yet Another Rust and SIMD” article? Yes and no. Yes, I did apply SIMD to a programming problem and then feel compelled to write an article about it. No, I hope that this article also goes into enough depth that it can guide you through your project. It explains the newly available SIMD capabilities and settings in Rust nightly. It includes a Rust SIMD cheatsheet. It shows how to make your SIMD code generic without leaving safe Rust. It gets you started with tools such as Godbolt and Criterion. Finally, it introduces new cargo commands that make the process easier.
The range-set-blaze crate uses its RangeSetBlaze::from_iter method to ingest potentially long sequences of integers. When the integers are “clumpy”, it can do this 30 times faster than Rust’s standard HashSet::from_iter. Can we do even better if we use Simd operations? Yes!
See this documentation for the definition of “clumpy”. Also, what happens if the integers are not clumpy?
RangeSetBlazeis 2 to 3 times slower thanHashSet.
On clumpy integers, RangeSetBlaze::from_slice — a new method based on SIMD operations — is 7 times faster than RangeSetBlaze::from_iter. That makes it more than 200 times faster than HashSet::from_iter. (When the integers are not clumpy, it is still 2 to 3 times slower than HashSet.)
Over the course of implementing this speed up, I learned nine rules that can help you accelerate your projects with SIMD operations.
The rules are:
- Use nightly Rust and
core::simd, Rust’s experimental standard SIMD module. - CCC: Check, Control, and Choose your computer’s SIMD capabilities.
- Learn
core::simd, but selectively. - Brainstorm candidate algorithms.
- Use Godbolt and AI to understand your code’s assembly, even if you don’t know assembly language.
- Generalize to all types and LANES with in-lined generics, (and when that doesn’t work) macros, and (when that doesn’t work) traits.
See Part 2 for these rules:
7. Use Criterion benchmarking to pick an algorithm and to discover that LANES should (almost) always be 32 or 64.
8. Integrate your best SIMD algorithm into your project with as_simd, special code for i128/u128, and additional in-context benchmarking.
9. Extricate your best SIMD algorithm from your project (for now) with an optional cargo feature.
Aside: To avoid wishy-washiness, I call these “rules”, but they are, of course, just suggestions.
Rule 1: Use nightly Rust and core::simd, Rust’s experimental standard SIMD module.
Rust can access SIMD operations either via the stable core::arch module or via nighty’s core::simd module. Let’s compare them:
core::arch
core::simd
- Nightly
- Delightfully easy and portable.
- Limits downstream users to nightly.
I decided to go with “easy”. If you decide to take the harder road, starting first with the easier path may still be worthwhile.
In either case, before we try to use SIMD operations in a larger project, let’s make sure we can get them working at all. Here are the steps:
First, create a project called simd_hello:
cargo new simd_hello
cd simd_helloEdit src/main.rs to contain (Rust playground):
// Tell nightly Rust to enable 'portable_simd'
#![feature(portable_simd)]
use core::simd::prelude::*;
// constant Simd structs
const LANES: usize = 32;
const THIRTEENS: Simd = Simd::::from_array([13; LANES]);
const TWENTYSIXS: Simd = Simd::::from_array([26; LANES]);
const ZEES: Simd = Simd::::from_array([b'Z'; LANES]);
fn main() {
// create a Simd struct from a slice of LANES bytes
let mut data = Simd::::from_slice(b"URYYBJBEYQVQBUBCRVGFNYYTBVATJRYY");
data += THIRTEENS; // add 13 to each byte
// compare each byte to 'Z', where the byte is greater than 'Z', subtract 26
let mask = data.simd_gt(ZEES); // compare each byte to 'Z'
data = mask.select(data - TWENTYSIXS, data);
let output = String::from_utf8_lossy(data.as_array());
assert_eq!(output, "HELLOWORLDIDOHOPEITSALLGOINGWELL");
println!("{}", output);
}Next — full SIMD capabilities require the nightly version of Rust. Assuming you have Rust installed, install nightly (rustup install nightly). Make sure you have the latest nightly version (rustup update nightly). Finally, set this project to use nightly (rustup override set nightly).
You can now run the program with cargo run. The program applies ROT13 decryption to 32 bytes of upper-case letters. With SIMD, the program can decrypt all 32 bytes simultaneously.
Let’s look at each section of the program to see how it works. It starts with:
#![feature(portable_simd)]
use core::simd::prelude::*;Rust nightly offers its extra capabilities (or “features”) only on request. The #![feature(portable_simd)] statement requests that Rust nightly make available the new experimental core::simd module. The use statement then imports the module’s most important types and traits.
In the code’s next section, we define useful constants:
const LANES: usize = 32;
const THIRTEENS: Simd = Simd::::from_array([13; LANES]);
const TWENTYSIXS: Simd = Simd::::from_array([26; LANES]);
const ZEES: Simd = Simd::::from_array([b'Z'; LANES]);The Simd struct is a special kind of Rust array. (It is, for example, always memory aligned.) The constant LANES tells the length of the Simd array. The from_array constructor copies a regular Rust array to create a Simd. In this case, because we want const Simd’s, the arrays we construct from must also be const.
The next two lines copy our encrypted text into data and then adds 13 to each letter.
let mut data = Simd::::from_slice(b"URYYBJBEYQVQBUBCRVGFNYYTBVATJRYY");
data += THIRTEENS;What if you make an error and your encrypted text isn’t exactly length LANES (32)? Sadly, the compiler won’t tell you. Instead, when you run the program, from_slice will panic. What if the encrypted text contains non-upper-case letters? In this example program, we’ll ignore that possibility.
The += operator does element-wise addition between the Simd data and Simd THIRTEENS. It puts the result in data. Recall that debug builds of regular Rust addition check for overflows. Not so with SIMD. Rust defines SIMD arithmetic operators to always wrap. Values of type u8 wrap after 255.
Coincidentally, Rot13 decryption also requires wrapping, but after ‘Z’ rather than after 255. Here is one approach to coding the needed Rot13 wrapping. It subtracts 26 from any values on beyond ‘Z’.
let mask = data.simd_gt(ZEES);
data = mask.select(data - TWENTYSIXS, data);This says to find the element-wise places beyond ‘Z’. Then, subtract 26 from all values. At the places of interest, use the subtracted values. At the other places, use the original values. Does subtracting from all values and then using only some seem wasteful? With SIMD, this takes no extra computer time and avoids jumps. This strategy is, thus, efficient and common.
The program ends like so:
let output = String::from_utf8_lossy(data.as_array());
assert_eq!(output, "HELLOWORLDIDOHOPEITSALLGOINGWELL");
println!("{}", output);Notice the .as_array() method. It safely transmutes a Simd struct into a regular Rust array without copying.
Surprisingly to me, this program runs fine on computers without SIMD extensions. Rust nightly compiles the code to regular (non-SIMD) instructions. But we don’t just want to run “fine”, we want to run faster. That requires us to turn on our computer’s SIMD power.
Rule 2: CCC: Check, Control, and Choose your computer’s SIMD capabilities.
To make SIMD programs run faster on your machine, you must first discover which SIMD extensions your machine supports. If you have an Intel/AMD machine, you can use my simd-detect cargo command.
Run with:
rustup override set nightly
cargo install cargo-simd-detect --force
cargo simd-detectOn my machine, it outputs:
extension width available enabled
sse2 128-bit/16-bytes true true
avx2 256-bit/32-bytes true false
avx512f 512-bit/64-bytes true falseThis says that my machine supports the sse2, avx2, and avx512f SIMD extensions. Of those, by default, Rust enables the ubiquitous twenty-year-old sse2 extension.
The SIMD extensions form a hierarchy with avx512f above avx2 above sse2. Enabling a higher-level extension also enables the lower-level extensions.
Most Intel/AMD computers also support the ten-year-old avx2 extension. You enable it by setting an environment variable:
# For Windows Command Prompt
set RUSTFLAGS=-C target-feature=+avx2
# For Unix-like shells (like Bash)
export RUSTFLAGS="-C target-feature=+avx2"“Force install” and run simd-detect again and you should see that avx2 is enabled.
# Force install every time to see changes to 'enabled'
cargo install cargo-simd-detect --force
cargo simd-detectextension width available enabled
sse2 128-bit/16-bytes true true
avx2 256-bit/32-bytes true true
avx512f 512-bit/64-bytes true falseAlternatively, you can turn on every SIMD extension that your machine supports:
# For Windows Command Prompt
set RUSTFLAGS=-C target-cpu=native
# For Unix-like shells (like Bash)
export RUSTFLAGS="-C target-cpu=native"On my machine this enables avx512f, a newer SIMD extension supported by some Intel computers and a few AMD computers.
You can set SIMD extensions back to their default (sse2 on Intel/AMD) with:
# For Windows Command Prompt
set RUSTFLAGS=
# For Unix-like shells (like Bash)
unset RUSTFLAGSYou may wonder why target-cpu=native isn’t Rust’s default. The problem is that binaries created using avx2 or avx512f won’t run on computers missing those SIMD extensions. So, if you are compiling only for your own use, use target-cpu=native. If, however, you are compiling for others, choose your SIMD extensions thoughtfully and let people know which SIMD extension level you are assuming.
Happily, whatever level of SIMD extension you pick, Rust’s SIMD support is so flexible you can easily change your decision later. Let’s next learn details of programming with SIMD in Rust.
Rule 3: Learn core::simd, but selectively.
To build with Rust’s new core::simd module you should learn selected building blocks. Here is a cheatsheet with the structs, methods, etc., that I’ve found most useful. Each item includes a link to its documentation.
Structs
Simd– a special, aligned, fixed-length array ofSimdElement. We refer to a position in the array and the element stored at that position as a “lane”. By default, we copySimdstructs rather than reference them.Mask– a special Boolean array showing inclusion/exclusion on a per-lane basis.
SimdElements
- Floating-Point Types:
f32,f64 - Integer Types:
i8,u8,i16,u16,i32,u32,i64,u64,isize,usize - — but not
i128,u128
Simd constructors
Simd::from_array– creates aSimdstruct by copying a fixed-length array.Simd::from_slice– creates aSimdstruct by copying the firstLANEelements of a slice.Simd::splat– replicates a single value across all lanes of aSimdstruct.slice::as_simd– without copying, safely transmutes a regular slice into an aligned slice ofSimd(plus unaligned leftovers).
Simd conversion
Simd::as_array– without copying, safely transmutes anSimdstruct into a regular array reference.
Simd methods and operators
simd[i]– extract a value from a lane of aSimd.simd + simd– performs element-wise addition of twoSimdstructs. Also, supported-,*,/,%, remainder, bitwise-and, -or, xor, -not, -shift.simd += simd– adds anotherSimdstruct to the current one, in place. Other operators supported, too.Simd::simd_gt– compares twoSimdstructs, returning aMaskindicating which elements of the first are greater than those of the second. Also, supportedsimd_lt,simd_le,simd_ge,simd_lt,simd_eq,simd_ne.Simd::rotate_elements_left– rotates the elements of aSimdstruct to the left by a specified amount. Also,rotate_elements_right.simd_swizzle!(simd, indexes)– rearranges the elements of aSimdstruct based on the specified const indexes.simd == simd– checks for equality between twoSimdstructs, returning a regularboolresult.Simd::reduce_and– performs a bitwise AND reduction across all lanes of aSimdstruct. Also, supported:reduce_or,reduce_xor,reduce_max,reduce_min,reduce_sum(but noreduce_eq).
Mask methods and operators
Mask::select– selects elements from twoSimdstruct based on a mask.Mask::all– tells if the mask is alltrue.Mask::any– tells if the mask contains anytrue.
All about lanes
Simd::LANES– a constant indicating the number of elements (lanes) in aSimdstruct.SupportedLaneCount– tells the allowed values ofLANES. Use by generics.simd.lanes– const method that tells aSimdstruct’s number of lanes.
Low-level alignment, offsets, etc.
When possible, use to_simd instead.
More, perhaps of interest
With these building blocks at hand, it’s time to build something.
Rule 4: Brainstorm candidate algorithms.
What do you want to speed up? You won’t know ahead of time which SIMD approach (of any) will work best. You should, therefore, create many algorithms that you can then analyze (Rule 5) and benchmark (Rule 7).
I wanted to speed up range-set-blaze, a crate for manipulating sets of “clumpy” integers. I hoped that creating is_consecutive, a function to detect blocks of consecutive integers, would be useful.
Background: Crate
range-set-blazeworks on “clumpy” integers. “Clumpy”, here, means that the number of ranges needed to represent the data is small compared to the number of input integers. For example, these 1002 input integers
100, 101,…,489, 499, 501, 502,…,998, 999, 999, 100, 0Ultimately become three Rust ranges:
0..=0, 100..=499, 501..=999.(Internally, the
RangeSetBlazestruct represents a set of integers as a sorted list of disjoint ranges stored in a cache efficient BTreeMap.)Although the input integers are allowed to be unsorted and redundant, we expect them to often be “nice”. RangeSetBlaze’s
from_iterconstructor already exploits this expectation by grouping up adjacent integers. For example,from_iterfirst turns the 1002 input integers into four ranges
100..=499, 501..=999, 100..=100, 0..=0.with minimal, constant memory usage, independent of input size. It then sorts and merges these reduced ranges.
I wondered if a new
from_slicemethod could speed construction from array-like inputs by quickly finding (some) consecutive integers. For example, could it— with minimal, constant memory — turn the 1002 inputs integers into five Rust ranges:
100..=499, 501..=999, 999..=999, 100..=100, 0..=0.If so,
from_itercould then quickly finish the processing.
Let’s start by writing is_consecutive with regular Rust:
pub const LANES: usize = 16;
pub fn is_consecutive_regular(chunk: &[u32; LANES]) -> bool {
for i in 1..LANES {
if chunk[i - 1].checked_add(1) != Some(chunk[i]) {
return false;
}
}
true
}The algorithm just loops through the array sequentially, checking that each value is one more than its predecessor. It also avoids overflow.
Looping over the items seemed so easy, I wasn’t sure if SIMD could do any better. Here was my first attempt:
Splat0
use std::simd::prelude::*;
const COMPARISON_VALUE_SPLAT0: Simd =
Simd::from_array([15, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]);
pub fn is_consecutive_splat0(chunk: Simd) -> bool {
if chunk[0].overflowing_add(LANES as u32 - 1) != (chunk[LANES - 1], false) {
return false;
}
let added = chunk + COMPARISON_VALUE_SPLAT0;
Simd::splat(added[0]) == added
}Here is an outline of its calculations:
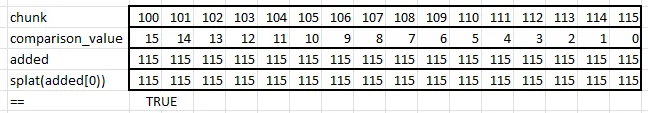
It first (needlessly) checks that the first and last items are 15 apart. It then creates added by adding 15 to the 0th item, 14 to the next, etc. Finally, to see if all items in added are the same, it creates a new Simd based on added’s 0th item and then compares. Recall that splat creates a Simd struct from one value.
Splat1 & Splat2
When I mentioned the is_consecutive problem to Ben Lichtman, he independently came up with this, Splat1:
const COMPARISON_VALUE_SPLAT1: Simd =
Simd::from_array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]);
pub fn is_consecutive_splat1(chunk: Simd) -> bool {
let subtracted = chunk - COMPARISON_VALUE_SPLAT1;
Simd::splat(chunk[0]) == subtracted
}Splat1 subtracts the comparison value from chunk and checks if the result is the same as the first element of chunk, splatted.
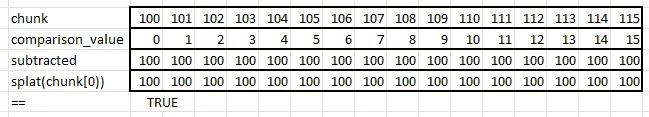
He also came up with a variation called Splat2 that splats the first element of subtracted rather than chunk. That would seemingly avoid one memory access.
I’m sure you are wondering which of these is best, but before we discuss that let’s look at two more candidates.
Swizzle
Swizzle is like Splat2 but uses simd_swizzle! instead of splat. Macro simd_swizzle! creates a new Simd by rearranging the lanes of an old Simd according to an array of indexes.
pub fn is_consecutive_sizzle(chunk: Simd) -> bool {
let subtracted = chunk - COMPARISON_VALUE_SPLAT1;
simd_swizzle!(subtracted, [0; LANES]) == subtracted
}Rotate
This one is different. I had high hopes for it.
const COMPARISON_VALUE_ROTATE: Simd =
Simd::from_array([4294967281, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]);
pub fn is_consecutive_rotate(chunk: Simd) -> bool {
let rotated = chunk.rotate_elements_right::();
chunk - rotated == COMPARISON_VALUE_ROTATE
}The idea is to rotate all the elements one to the right. We then subtract the original chunk from rotated. If the input is consecutive, the result should be “-15” followed by all 1’s. (Using wrapped subtraction, -15 is 4294967281u32.)
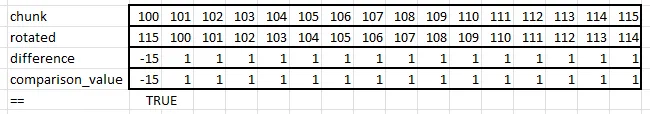
Now that we have candidates, let’s start to evaluate them.
Rule 5: Use Godbolt and AI to understand your code’s assembly, even if you don’t know assembly language.
We’ll evaluate the candidates in two ways. First, in this rule, we’ll look at the assembly language generated from our code. Second, in Rule 7, we’ll benchmark the code’s speed.
Don’t worry if you don’t know assembly language, you can still get something out of looking at it.
The easiest way to see the generated assembly language is with the Compiler Explorer, AKA Godbolt. It works best on short bits of code that don’t use outside crates. It looks like this:
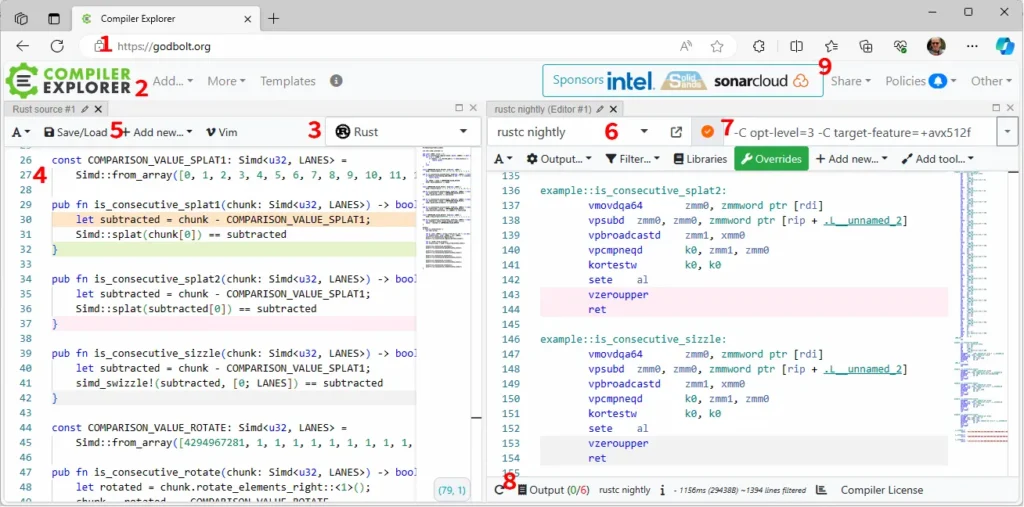
Referring to the numbers in the figure above, follow these steps to use Godbolt:
- Open godbolt.org with your web browser.
- Add a new source editor.
- Select Rust as your language.
- Paste in the code of interest. Make the functions of interest public (
pub fn). Do not include a main or unneeded functions. The tool doesn’t support external crates. - Add a new compiler.
- Set the compiler version to nightly.
- Set options (for now) to
-C opt-level=3 -C target-feature=+avx512f. - If there are errors, look at the output.
- If you want to share or save the state of the tool, click “Share”
From the image above, you can see that Splat2 and Sizzle are exactly the same, so we can remove Sizzle from consideration. If you open up a copy of my Godbolt session, you’ll also see that most of the functions compile to about the same number of assembly operations. The exceptions are Regular — which is much longer — and Splat0 — which includes the early check.
In the assembly, 512-bit registers start with ZMM. 256-bit registers start YMM. 128-bit registers start with XMM. If you want to better understand the generated assembly, use AI tools to generate annotations. For example, here I ask Bing Chat about Splat2:

Try different compiler settings, including -C target-feature=+avx2 and then leaving target-feature completely off.
Fewer assembly operations don’t necessarily mean faster speed. Looking at the assembly does, however, give us a sanity check that the compiler is at least trying to use SIMD operations, inlining const references, etc. Also, as with Splat1 and Swizzle, it can sometimes let us know when two candidates are the same.
You may need disassembly features beyond what Godbolt offers, for example, the ability to work with code the uses external crates. B3NNY recommended the cargo tool
cargo-show-asmto me. I tried it and found it reasonably easy to use.
The range-set-blaze crate must handle integer types beyond u32. Moreover, we must pick a number of LANES, but we have no reason to think that 16 LANES is always best. To address these needs, in the next rule we’ll generalize the code.
Rule 6: Generalize to all types and LANES with in-lined generics, (and when that doesn’t work) macros, and (when that doesn’t work) traits.
Let’s first generalize Splat1 with generics.
#[inline]
pub fn is_consecutive_splat1_gen(
chunk: Simd,
comparison_value: Simd,
) -> bool
where
T: SimdElement + PartialEq,
Simd: Sub, Output = Simd>,
LaneCount: SupportedLaneCount,
{
let subtracted = chunk - comparison_value;
Simd::splat(chunk[0]) == subtracted
}First, note the #[inline] attribute. It’s important for efficiency and we’ll use it on pretty much every one of these small functions.
The function defined above, is_consecutive_splat1_gen, looks great except that it needs a second input, called comparison_value, that we have yet to define.
If you don’t need a generic const
comparison_value, I envy you. You can skip to the next rule if you like. Likewise, if you are reading this in the future and creating a generic constcomparison_valueis as effortless as having your personal robot do your household chores, then I doubly envy you.
We can try to create a comparison_value_splat_gen that is generic and const. Sadly, neither From nor alternative T::One are const, so this doesn’t work:
// DOESN'T WORK BECAUSE From is not const
pub const fn comparison_value_splat_gen() -> Simd
where
T: SimdElement + Default + From + AddAssign,
LaneCount: SupportedLaneCount,
{
let mut arr: [T; N] = [T::from(0usize); N];
let mut i_usize = 0;
while i_usize < N {
arr[i_usize] = T::from(i_usize);
i_usize += 1;
}
Simd::from_array(arr)
}Macros are the last refuge of scoundrels. So, let’s use macros:
#[macro_export]
macro_rules! define_is_consecutive_splat1 {
($function:ident, $type:ty) => {
#[inline]
pub fn $function(chunk: Simd) -> bool
where
LaneCount: SupportedLaneCount,
{
define_comparison_value_splat!(comparison_value_splat, $type);
let subtracted = chunk - comparison_value_splat();
Simd::splat(chunk[0]) == subtracted
}
};
}
#[macro_export]
macro_rules! define_comparison_value_splat {
($function:ident, $type:ty) => {
pub const fn $function() -> Simd
where
LaneCount: SupportedLaneCount,
{
let mut arr: [$type; N] = [0; N];
let mut i = 0;
while i < N {
arr[i] = i as $type;
i += 1;
}
Simd::from_array(arr)
}
};
}This lets us run on any particular element type and all number of LANES (Rust Playground):
define_is_consecutive_splat1!(is_consecutive_splat1_i32, i32);
let a: Simd = black_box(Simd::from_array(array::from_fn(|i| 100 + i as i32)));
let ninety_nines: Simd = black_box(Simd::from_array([99; 16]));
assert!(is_consecutive_splat1_i32(a));
assert!(!is_consecutive_splat1_i32(ninety_nines));Sadly, this still isn’t enough for range-set-blaze. It needs to run on all element types (not just one) and (ideally) all LANES (not just one).
Happily, there’s a workaround, that again depends on macros. It also exploits the fact that we only need to support a finite list of types, namely: i8, i16, i32, i64, isize, u8, u16, u32, u64, and usize. If you need to also (or instead) support f32 and f64, that’s fine.
If, on the other hand, you need to support
i128andu128, you may be out of luck. Thecore::simdmodule doesn’t support them. We’ll see in Rule 8 howrange-set-blazegets around that at a performance cost.
The workaround defines a new trait, here called IsConsecutive. We then use a macro (that calls a macro, that calls a macro) to implement the trait on the 10 types of interest.
pub trait IsConsecutive {
fn is_consecutive(chunk: Simd) -> bool
where
Self: SimdElement,
Simd: Sub, Output = Simd>,
LaneCount: SupportedLaneCount;
}
macro_rules! impl_is_consecutive {
($type:ty) => {
impl IsConsecutive for $type {
#[inline] // very important
fn is_consecutive(chunk: Simd) -> bool
where
Self: SimdElement,
Simd: Sub, Output = Simd>,
LaneCount: SupportedLaneCount,
{
define_is_consecutive_splat1!(is_consecutive_splat1, $type);
is_consecutive_splat1(chunk)
}
}
};
}
impl_is_consecutive!(i8);
impl_is_consecutive!(i16);
impl_is_consecutive!(i32);
impl_is_consecutive!(i64);
impl_is_consecutive!(isize);
impl_is_consecutive!(u8);
impl_is_consecutive!(u16);
impl_is_consecutive!(u32);
impl_is_consecutive!(u64);
impl_is_consecutive!(usize);We can now call fully generic code (Rust Playground):
// Works on i32 and 16 lanes
let a: Simd = black_box(Simd::from_array(array::from_fn(|i| 100 + i as i32)));
let ninety_nines: Simd = black_box(Simd::from_array([99; 16]));
assert!(IsConsecutive::is_consecutive(a));
assert!(!IsConsecutive::is_consecutive(ninety_nines));
// Works on i8 and 64 lanes
let a: Simd = black_box(Simd::from_array(array::from_fn(|i| 10 + i as i8)));
let ninety_nines: Simd = black_box(Simd::from_array([99; 64]));
assert!(IsConsecutive::is_consecutive(a));
assert!(!IsConsecutive::is_consecutive(ninety_nines));With this technique, we can create multiple candidate algorithms that are fully generic over type and LANES. Next, it is time to benchmark and see which algorithms are fastest.
Those are the first six rules for adding SIMD code to Rust. In Part 2, we look at rules 7 to 9. These rules will cover how to pick an algorithm and set LANES. Also, how to integrate SIMD operations into your existing code and (importantly) how to make it optional. Part 2 concludes with a discussion of when/if you should use SIMD and ideas for improving Rust’s SIMD experience. I hope to see you there.
Please follow Carl on Medium. I write on scientific programming in Rust and Python, machine learning, and statistics. I tend to write about one article per month.






















