Introduction
Many of us might have tried to build a RAG application and noticed it falls significantly short of addressing real-life needs. Why is that? It’s because many real-world problems require multiple steps of information retrieval and reasoning. We need our agent to perform those as humans normally do, yet most RAG applications fall short of this.
This article explores how to supercharge your RAG application by making its data retrieval and reasoning process similar to how a human would, under a multi-agent framework. The framework presented here is based on the Self-RAG strategy but has been significantly modified to enhance its capabilities. Prior knowledge of the original strategy is not necessary for reading this article.
Real-life Case
Consider this: I was going to fly from Delhi to Munich (let’s assume I am taking the flight from an EU airline), but I was denied boarding somehow. Now I want to know what the compensation should be.
These two webpages contain relevant information, I go ahead adding them to my vector store, trying to have my agent answer this for me by retrieving the right information.
Now, I pass this question to the vector store: “how much can I receive if I am denied boarding, for flights from Delhi to Munich?”.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Overview of US Flight Compensation Policies To get compensation for delayed flights, you should contact your airline via their customer service or go to the customer service desk. At the same time, you should bear in mind that you will only receive compensation if the delay is not weather-related and is within the carrier`s control. According to the US Department of Transportation, US airlines are not required to compensate you if a flight is cancelled or delayed. You can be compensated if you are bumped or moved from an overbooked flight. If your provider cancels your flight less than two weeks before departure and you decide to cancel your trip entirely, you can receive a refund of both pre-paid baggage fees and your plane ticket. There will be no refund if you choose to continue your journey. In the case of a delayed flight, the airline will rebook you on a different flight. According to federal law, you will not be provided with money or other compensation. Comparative Analysis of EU vs. US Flight Compensation Policies
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
(AUTHOR-ADDED NOTE: IMPORTANT, PAY ATTENTION TO THIS)
Short-distance flight delays – if it is up to 1,500 km, you are due 250 Euro compensation.
Medium distance flight delays – for all the flights between 1,500 and 3,500 km, the compensation should be 400 Euro.
Long-distance flight delays – if it is over 3,500 km, you are due 600 Euro compensation. To receive this kind of compensation, the following conditions must be met; Your flight starts in a non-EU member state or in an EU member state and finishes in an EU member state and is organised by an EU airline. Your flight reaches the final destination with a delay that exceeds three hours. There is no force majeure.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Compensation policies in the EU and US are not the same, which implies that it is worth knowing more about them. While you can always count on Skycop flight cancellation compensation, you should still get acquainted with the information below.
– – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – –
Compensation for flight regulations EU: The EU does regulate flight delay compensation, which is known as EU261. US: According to the US Department of Transportation, every airline has its own policies about what should be done for delayed passengers. Compensation for flight delays EU: Just like in the United States, compensation is not provided when the flight is delayed due to uncontrollable reasons. However, there is a clear approach to compensation calculation based on distance. For example, if your flight was up to 1,500 km, you can receive 250 euros. US: There are no federal requirements. That is why every airline sets its own limits for compensation in terms of length. However, it is usually set at three hours. Overbooking EU: In the EU, they call for volunteers if the flight is overbooked. These people are entitled to a choice of: Re-routing to their final destination at the earliest opportunity. Refund of their ticket cost within a week if not travelling. Re-routing at a later date at the person`s convenience.Unfortunately, they contain only generic flight compensation policies, without telling me how much I can expect when denied boarding from Delhi to Munich specifically. If the RAG agent takes these as the sole context, it can only provide a generic answer about flight compensation policy, without giving the answer we want.
However, while the documents are not immediately useful, there is an important insight contained in the 2nd piece of context: compensation varies according to flight distance. If the RAG agent thinks more like human, it should follow these steps to provide an answer:
- Based on the retrieved context, reason that compensation varies with flight distance
- Next, retrieve the flight distance between Delhi and Munich
- Given the distance (which is around 5900km), classify the flight as a long-distance one
- Combined with the previously retrieved context, figure out I am due 600 EUR, assuming other conditions are fulfilled
This example demonstrates how a simple RAG, in which a single retrieval is made, fall short for several reasons:
- Complex Queries: Users often have questions that a simple search can’t fully address. For example, “What’s the best smartphone for gaming under $500?” requires consideration of multiple factors like performance, price, and features, which a single retrieval step might miss.
- Deep Information: Some information lies across documents. For example, research papers, medical records, or legal documents often include references that need to be made sense of, before one can fully understand the content of a given article. Multiple retrieval steps help dig deeper into the content.
Multiple retrievals supplemented with human-like reasoning allow for a more nuanced, comprehensive, and accurate response, adapting to the complexity and depth of user queries.
Multi-Agent Self-RAG
Here I explain the reasoning process behind this strategy, afterwards I will provide the code to show you how to achieve this!
Note: For readers interested in knowing how my approach differs from the original Self-RAG, I will describe the discrepancies in quotation boxes like this. But general readers who are unfamiliar with the original Self-RAG can skip them.
In the below graphs, each circle represents a step (aka Node), which is performed by a dedicated agent working on the specific problem. We orchestrate them to form a multi-agent RAG application.
1st iteration: Simple RAG
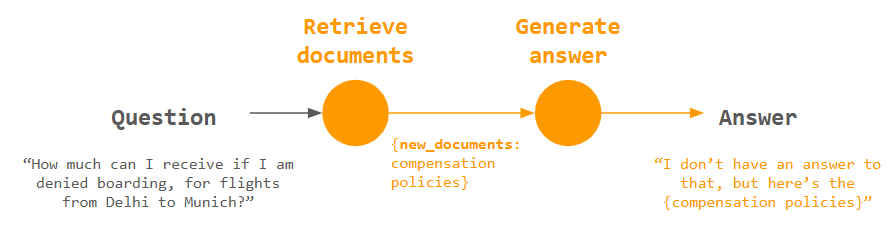
This is just the vanilla RAG approach I described in “Real-life Case”, represented as a graph. After Retrieve documents, the new_documents will be used as input for Generate Answer. Nothing special, but it serves as our starting point.
2nd iteration: Digest documents with “Grade documents”
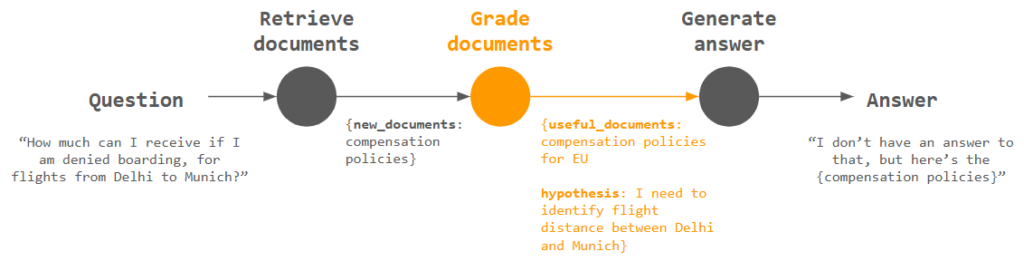
Remember I said in the “Real-life Case” section, that as a next step, the agent should “reason that compensation varies with flight distance”? The Grade documents step is exactly for this purpose.
Given the new_documents, the agent will try to output two items:
useful_documents: Comparing the question asked, it determines if the documents are useful, and retain a memory for those deemed useful for future reference. As an example, since our question does not concern compensation policies for US, documents describing those are discarded, leaving only those for EUhypothesis: Based on the documents, the agent forms a hypothesis about how the question can be answered, that is, flight distance needs to be identified
Notice how the above reasoning resembles human thinking! But still, while these outputs are useful, we need to instruct the agent to use them as input for performing the next document retrieval. Without this, the answer provided in Generate answer is still not useful.
useful_documentsare appended for each document retrieval loop, instead of being overwritten, to keep a memory of documents that are previously deemed useful.hypothesisis formed fromuseful_documentsandnew_documentsto provide an “abstract reasoning” to inform how query is to be transformed subsequently.The
hypothesisis especially useful when no useful documents can be identified initially, as the agent can still form hypothesis from documents not immediately deemed as useful / only bearing indirect relationship to the question at hand, for informing what questions to ask next
3rd iteration: Brainstorm new questions to ask
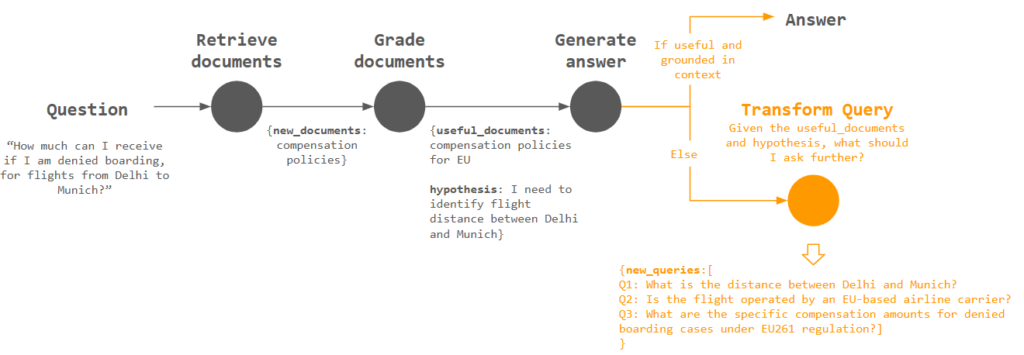
We have the agent reflect upon whether the answer is useful and grounded in context. If not, it should proceed to Transform query to ask further questions.
The output new_queries will be a list of new questions that the agent consider useful for obtaining extra information. Given the useful_documents (compensation policies for EU), and hypothesis (need to identify flight distance between Delhi and Munich), it asks questions like “What is the distance between Delhi and Munich?”
Now we are ready to use the new_queries for further retrieval!
The
transform_querynode will useuseful_documents(which are accumulated per iteration, instead of being overwritten) andhypothesisas input for providing the agent directions to ask new questions.The new questions will be a list of questions (instead of a single question) separated from the original
question, so that the original question is kept in state, otherwise the agent could lose track of the original question after multiple iterations.
Final iteration: Further retrieval with new questions
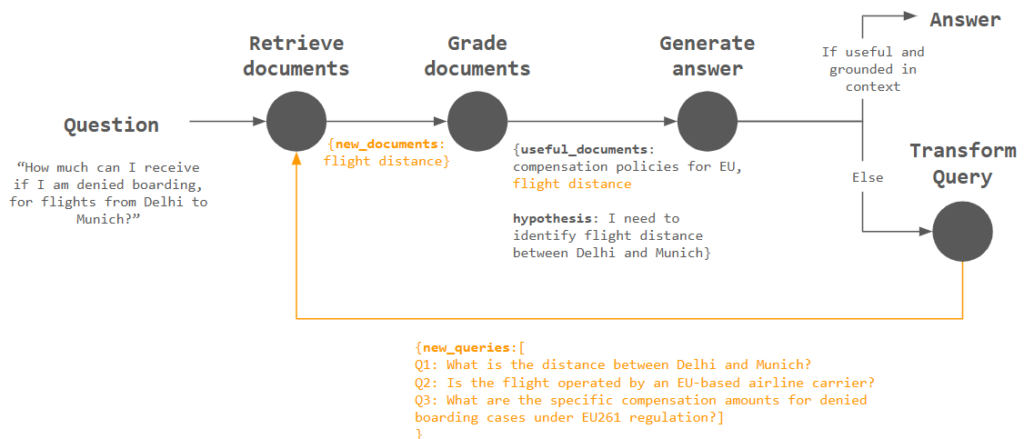
The output new_queries from Transform query will be passed to the Retrieve documents step, forming a retrieval loop.
Since the question “What is the distance between Delhi and Munich?” is asked, we can expect the flight distance is then retrieved as new_documents, and subsequently graded as useful_documents, further used as an input for Generate answer.
The
grade_documentsnode will compare the documents against both the originalquestionandnew_questionslist, so that documents that are considered useful fornew_questions, even if not so for the originalquestion, are kept.This is because those documents might help answer the original
questionindirectly, by being relevant tonew_questions(like “What is the distance between Delhi and Munich?”)
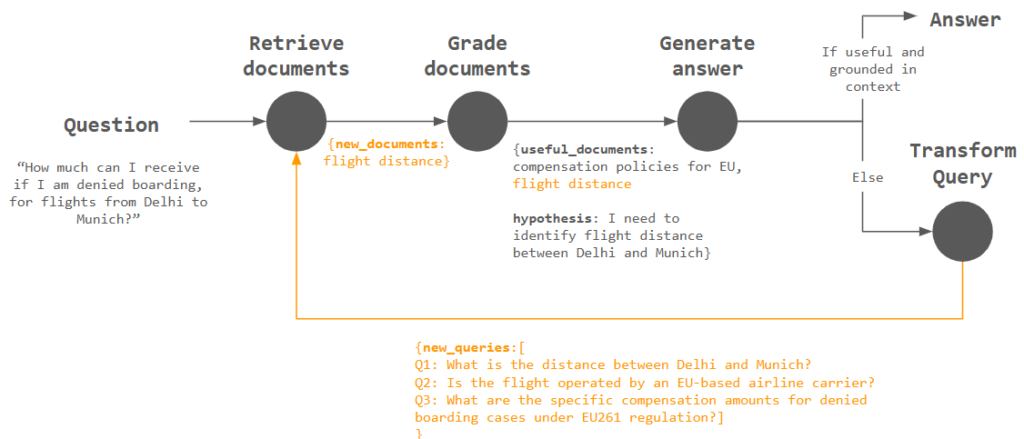
Equipped with this new context about flight distance, the agent is now ready to provide the right answer: 600 EUR!
Next, let us now dive into the code to see how this multi-agent RAG application is created.
Implementation
The source code can be found here. Our multi-agent RAG application involves iterations and loops, and LangGraph is a great library for building such complex multi-agent application. If you are not familiar with LangGraph, you are strongly suggested to have a look at LangGraph’s Quickstart guide to understand more about it!
To keep this article concise, I will focus on the key code snippets only.
Important note: I am using OpenRouter as the Llm interface, but the code can be easily adapted for other LLM interfaces. Also, while in my code I am using Claude 3.5 Sonnet as model, you can use any LLM as long as it support tools as parameter (check this list here), so you can also run this with other models, like DeepSeek V3 and OpenAI o1!
State definition
In the previous section, I have defined various elements e.g. new_documents, hypothesis that are to be passed to each step (aka Nodes), in LangGraph’s terminology these elements are called State.
We define the State formally with the following snippet.
from typing import List, Annotated
from typing_extensions import TypedDictdef append_to_list(original: list, new: list) -> list:
original.append(new)
return original
def combine_list(original: list, new: list) -> list:
return original + new
class GraphState(TypedDict):
"""
Represents the state of our graph.
Attributes:
question: question
generation: LLM generation
new_documents: newly retrieved documents for the current iteration
useful_documents: documents that are considered useful
graded_documents: documents that have been graded
new_queries: newly generated questions
hypothesis: hypothesis
"""
question: str
generation: str
new_documents: List[str]
useful_documents: Annotated[List[str], combine_list]
graded_documents: List[str]
new_queries: Annotated[List[str], append_to_list]
hypothesis: str
Graph definition
This is where we combine the different steps to form a “Graph”, which is a representation of our multi-agent application. The definitions of various steps (e.g. grade_documents) are represented by their respective functions.
from langgraph.graph import END, StateGraph, START
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
from IPython.display import Image, displayworkflow = StateGraph(GraphState)
# Define the nodes
workflow.add_node("retrieve", retrieve) # retrieve
workflow.add_node("grade_documents", grade_documents) # grade documents
workflow.add_node("generate", generate) # generatae
workflow.add_node("transform_query", transform_query) # transform_query
# Build graph
workflow.add_edge(START, "retrieve")
workflow.add_edge("retrieve", "grade_documents")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"grade_documents",
decide_to_generate,
{
"transform_query": "transform_query",
"generate": "generate",
},
)
workflow.add_edge("transform_query", "retrieve")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"generate",
grade_generation_v_documents_and_question,
{
"useful": END,
"not supported": "transform_query",
"not useful": "transform_query",
},
)
# Compile
memory = MemorySaver()
app = workflow.compile(checkpointer=memory)
display(Image(app.get_graph(xray=True).draw_mermaid_png()))
Running the above code, you should see this graphical representation of our RAG application. Notice how it is essentially equivalent to the graph I have shown in the final iteration of “Enhanced Self-RAG Strategy”!
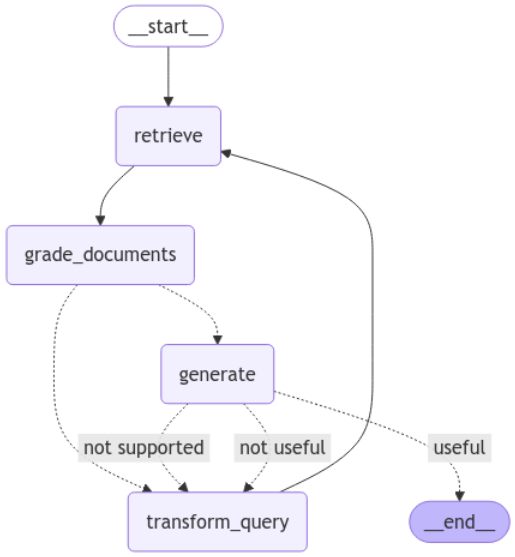
After
generate, if the answer is considered “not supported”, the agent will proceed totransform_queryintead of togenerateagain, so that the agent will look for additional information rather than trying to regenerate answers based on existing context, which might not suffice for providing a “supported” answer
Now we are ready to put the multi-agent application to test! With the below code snippet, we ask this question how much can I receive if I am denied boarding, for flights from Delhi to Munich?
from pprint import pprint
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": str(uuid4())}}# Run
inputs = {
"question": "how much can I receive if I am denied boarding, for flights from Delhi to Munich?",
}
for output in app.stream(inputs, config):
for key, value in output.items():
# Node
pprint(f"Node '{key}':")
# Optional: print full state at each node
# print(app.get_state(config).values)
pprint("n---n")
# Final generation
pprint(value["generation"])
While output might vary (sometimes the application provides the answer without any iterations, because it “guessed” the distance between Delhi and Munich), it should look something like this, which shows the application went through multiple rounds of data retrieval for RAG.
---RETRIEVE---
"Node 'retrieve':"
'n---n'
---CHECK DOCUMENT RELEVANCE TO QUESTION---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT NOT RELEVANT---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT RELEVANT---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT NOT RELEVANT---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT NOT RELEVANT---
---ASSESS GRADED DOCUMENTS---
---DECISION: GENERATE---
"Node 'grade_documents':"
'n---n'
---GENERATE---
---CHECK HALLUCINATIONS---
'---DECISION: GENERATION IS NOT GROUNDED IN DOCUMENTS, RE-TRY---'
"Node 'generate':"
'n---n'
---TRANSFORM QUERY---
"Node 'transform_query':"
'n---n'
---RETRIEVE---
"Node 'retrieve':"
'n---n'
---CHECK DOCUMENT RELEVANCE TO QUESTION---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT NOT RELEVANT---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT NOT RELEVANT---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT RELEVANT---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT NOT RELEVANT---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT NOT RELEVANT---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT NOT RELEVANT---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT NOT RELEVANT---
---ASSESS GRADED DOCUMENTS---
---DECISION: GENERATE---
"Node 'grade_documents':"
'n---n'
---GENERATE---
---CHECK HALLUCINATIONS---
---DECISION: GENERATION IS GROUNDED IN DOCUMENTS---
---GRADE GENERATION vs QUESTION---
---DECISION: GENERATION ADDRESSES QUESTION---
"Node 'generate':"
'n---n'
('Based on the context provided, the flight distance from Munich to Delhi is '
'5,931 km, which falls into the long-distance category (over 3,500 km). '
'Therefore, if you are denied boarding on a flight from Delhi to Munich '
'operated by an EU airline, you would be eligible for 600 Euro compensation, '
'provided that:n'
'1. The flight is operated by an EU airlinen'
'2. There is no force majeuren'
'3. Other applicable conditions are metn'
'n'
"However, it's important to note that this compensation amount is only valid "
'if all the required conditions are met as specified in the regulations.')And the final answer is what we aimed for!
Based on the context provided, the flight distance from Munich to Delhi is
5,931 km, which falls into the long-distance category (over 3,500 km).
Therefore, if you are denied boarding on a flight from Delhi to Munich
operated by an EU airline, you would be eligible for 600 Euro compensation,
provided that:
1. The flight is operated by an EU airline
2. There is no force majeure
3. Other applicable conditions are metHowever, it's important to note that this compensation amount is only valid
if all the required conditions are met as specified in the regulations.
Inspecting the State, we see how the hypothesis and new_queries enhance the effectiveness of our multi-agent RAG application by mimicking human thinking process.
Hypothesis
print(app.get_state(config).values.get('hypothesis',""))--- Output ---
To answer this question accurately, I need to determine:1. Is this flight operated by an EU airline? (Since Delhi is non-EU and Munich is EU)
2. What is the flight distance between Delhi and Munich? (To determine compensation amount)
3. Are we dealing with a denied boarding situation due to overbooking? (As opposed to delay/cancellation)
From the context, I can find information about compensation amounts based on distance, but I need to verify:
- If the flight meets EU compensation eligibility criteria
- The exact distance between Delhi and Munich to determine which compensation tier applies (250€, 400€, or 600€)
- If denied boarding compensation follows the same amounts as delay compensation
The context doesn't explicitly state compensation amounts specifically for denied boarding, though it mentions overbooking situations in the EU require offering volunteers re-routing or refund options.
Would you like me to proceed with the information available, or would you need additional context about denied boarding compensation specifically?
New Queries
for questions_batch in app.get_state(config).values.get('new_queries',""):
for q in questions_batch:
print(q)--- Output ---
What is the flight distance between Delhi and Munich?
Does EU denied boarding compensation follow the same amounts as flight delay compensation?
Are there specific compensation rules for denied boarding versus flight delays for flights from non-EU to EU destinations?
What are the compensation rules when flying with non-EU airlines from Delhi to Munich?
What are the specific conditions that qualify as denied boarding under EU regulations?Conclusion
Simple RAG, while easy to build, might fall short in tackling real-life questions. By incorporating human thinking process into a multi-agent RAG framework, we are making RAG applications much more practical.
*Unless otherwise noted, all images are by the author






















