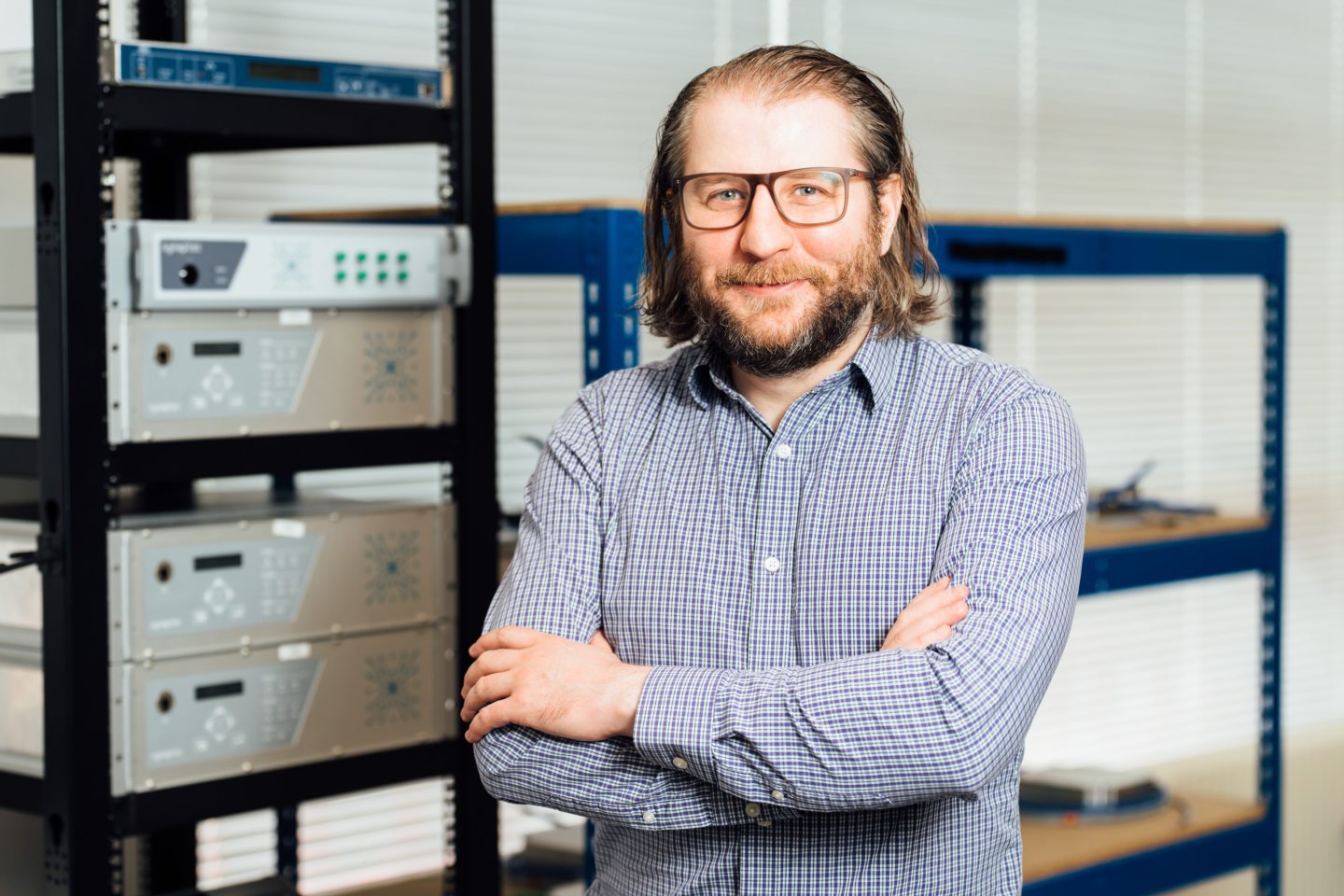
Glasgow-based Synaptec has developed new technology designed to tackle the issue of cable failures on offshore wind farms that can cost operators millions.
The company’s Greenlight provides automated monitoring of the joints and terminations in a cable network, delivering early warnings of emerging faults before they become failures.
The system is based on Synaptec’s Distributed Electrical Sensing (DES) technology, which was Synaptec previously deployed on the latest phase of the Dogger Bank wind farm.
Cable failures are a major issue facing offshore wind farms, with a single fault in transmission networks and offshore wind developments capable of costing up to £1m per day in lost revenue.
Allianz, the insurer for UK offshore wind projects including Dogger Bank and East Anglia Three, warned that damage to cables is the main cause of offshore wind insurance claims, accounting for 53% of claims across its global portfolio from 2014-2020.
Around 70% of these failures originate in the joints and terminations rather than the cables themselves.
The Global Underwater Hub (GUH) recently launched a forum to tackle rising costs and reliability issues facing subsea cable systems on the UK’s offshore wind farms.
Synaptec vice-president of applications, Dr Steven Blair, said: “Greenlight gives operators control over the most unpredictable and expensive aspect of offshore cable operations and maintenance.
“It’s a system designed not just to collect data, but to deliver clear, early, and location-specific insight that finds the early warning signs of failure.
“The return on investment is immediate – it pays for itself the first time it pre-empts an issue that would otherwise shut down a wind farm.”
Synaptec has made the first commercial installations of Greenlight with offshore wind operators and transmission systems internationally. There are plans for further large-scale installations throughout 2025.
The firm previously raised £6.5m in funding last year, with participation from Megger Group, Proserv, and Equity Gap.
The company aims to use the funds to support its expansion, including the development of new manufacturing facilities in Scotland.
The company had previously said that it aims to increase its revenues fourfold in the next two to three years, along with doubling its headcount as it takes advantage of the 24.4GW pipeline of floating offshore wind capacity off Scotland’s shores.