In November 2024, the United Nations World Meteorological Organization (WMO) issued a global Red Alert highlighting the accelerating pace of climate change and the ever-increasing levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations have risen from around 278 ppm in 1750 to around 420 ppm in 2023, marking a 51% increase.
This surge has trapped heat and contributed to rising global temperatures, underscoring the urgent need to develop and deploy solutions to combat this crisis.
According to the WMO, the past decade was the warmest on record, and 2024 is projected to be the first year where global mean surface air temperatures exceed 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
The imperative to shift our economies towards a more sustainable footing has never been more essential.
Despite commitments made at COP28 in the United Arab Emirates (2023) and COP29 in Azerbaijan (2024), fossil fuels will dominate the global energy mix for years to come.
This reality makes achieving the goals of the Paris Agreement increasingly difficult. Encouragingly, there has been significant progress in renewable energy adoption.
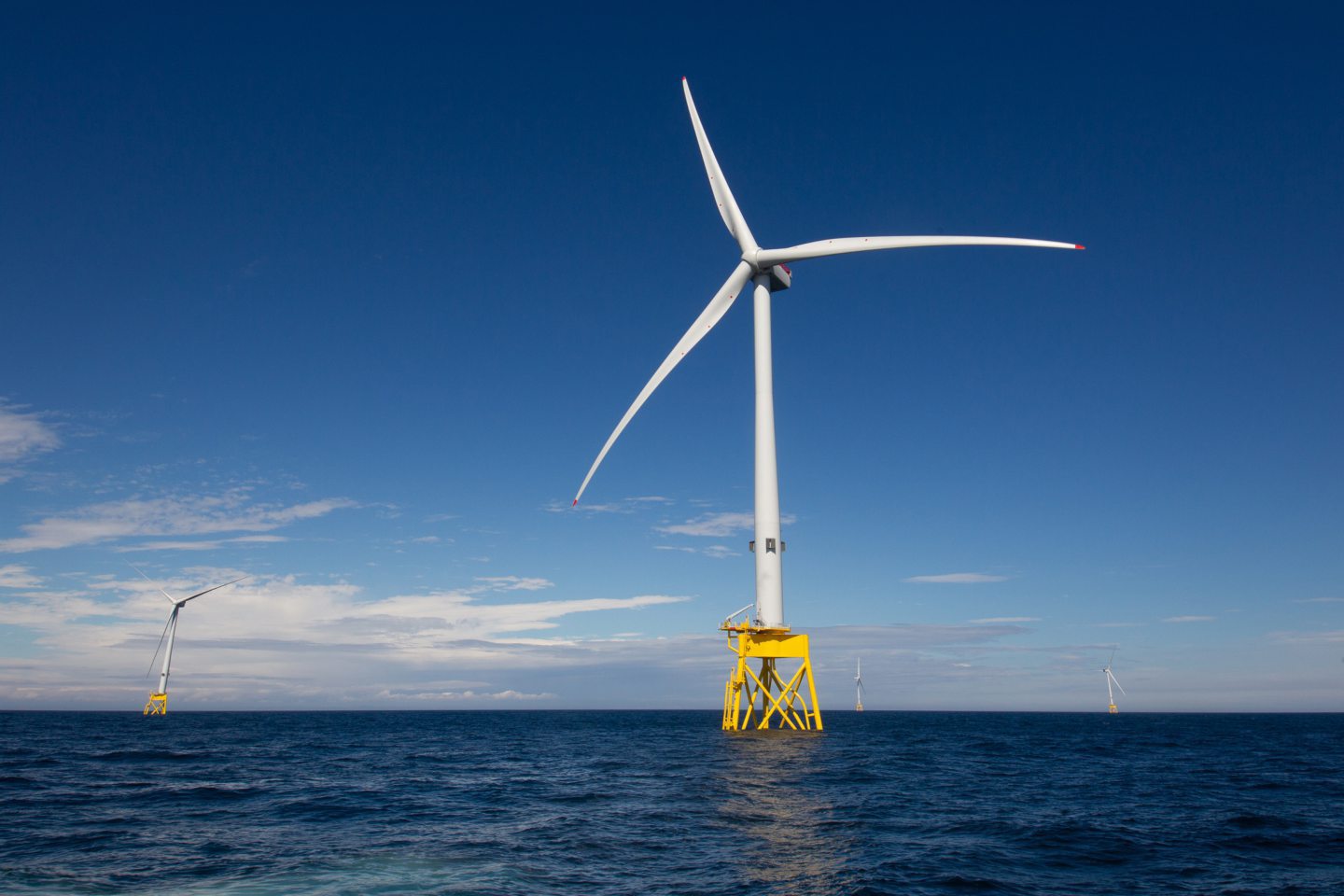
Global renewables rollout
Solar and wind power have experienced unprecedented growth, showcasing how sustainable technologies can reshape our energy landscape.
Global solar capacity has reached a record 2 terawatts (TW) in 2024, with more capacity installed in the past two years than in the previous six decades combined.
Meanwhile, global wind capacity is on track to hit 1.2 TW in 2024.
 © Supplied by SSE Renewables
© Supplied by SSE RenewablesIn 2023 alone, a record 117 GW of new wind capacity was added globally, representing a 50% increase compared to 2022.
Wind power aims to triple its cumulative capacity by 2030, while solar power targets a fourfold increase within the same period.
This rapid growth in renewables underscores a fundamental truth: clean energy isn’t just about reducing emissions – it is also a catalyst for sustainable economic development.
By embracing these technologies, economies can continue to expand while cutting their environmental footprint, paving the way for a greener, cleaner, and more prosperous future.
Cleaner generation alone not enough
However, building cleaner and greener energy generation capacity alone will not be sufficient to solve the climate crisis.
Human demands on Earth’s natural resources continue to outpace what can be sustainably produced.
As such, profound and rapid behavioural and cultural changes must accompany this transition.
Sustainability must be embedded at every level of society – starting with individual actions and extending to businesses and governments.
This comprehensive approach ensures that the collective momentum needed to drive meaningful change is inclusive and enduring.
The UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) highlighted that behavioural changes could reduce global emissions by up to 70% by 2050.
This will require systemic societal change – increasing recycling, lowering consumption, reducing high-emission activities, altering lifestyles, and improving energy efficiency.
Achieving these changes must foster a culture of sustainability in which all have a stake – we must enable individuals and businesses to contribute positively to environmental goals.
Can we maintain global sustainability?
Achieving societal and behavioural change, however, is often complex.
The use of social media platforms illustrates this challenge.
Instagram and TikTok have over 2 billion and 1 billion regular users, respectively, presenting opportunities and obstacles in promoting sustainable behaviours.
Analysis by Greenly shows that the average daily time spent on TikTok has grown from around 26 minutes in 2019 to over 45 minutes in 2024.
 © PA
© PAWhile these platforms provide valuable information, and allow users to watch, create, and share videos online, their carbon footprints have expanded dramatically.
TikTok alone is now estimated to have a carbon footprint larger than 140 countries.
According to Greenly, the average TikTok user generates approximately 50 kg CO2e annually, equivalent to driving a petrol-powered car for over 120 miles.
Yet, few recognise the toll this takes on our climate, and there is a pressing need to elevate the debate around responsible digital engagement, where innovation is aligned with environmental stewardship.
A more sustainable and secure energy future
The upcoming Abu Dhabi Sustainability Week in January and International Energy Week in London in February present pivotal opportunities for world leaders, policymakers, industry executives, and stakeholders to address the twin challenges of decarbonising energy supply and demand through collaboration and interconnectivity.
These gatherings are crucial platforms to accelerate commitments to deliver a net zero global energy system while maintaining sustainable growth.
The task is formidable, but coordinated transformative action can steer the world towards a more sustainable, and secure energy future.
As the first generation to experience the tangible effects of climate change and the last generation capable of mitigating its worst impacts, we all must contribute to this global effort – whether it be through innovation, advocacy, or our actions.
However, it is equally important to recognise that real change will only occur when the largest emitters demonstrate genuine climate leadership.
As pressures intensify during 2025, we must deliver the actions necessary for sustainable economic development, and pave the way for a just, fair, and orderly energy system transformation.
Professor Paul de Leeuw is the director of the Energy Transition Institute at Aberdeen’s Robert Gordon University
Recommended for you

The Centrica Interview: Chris O’Shea, chief executive officer