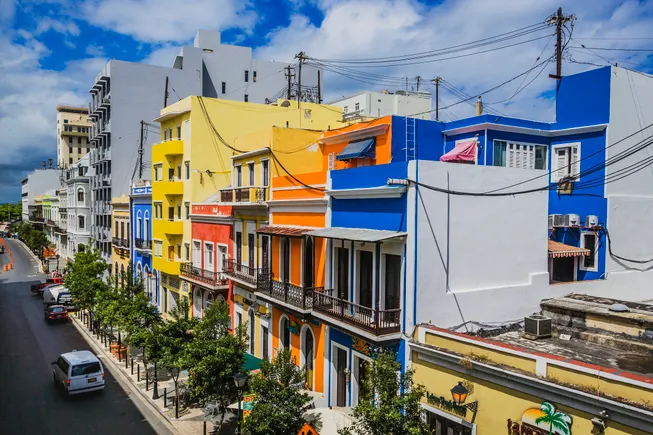
In 2017, Puerto Rico was plunged into darkness. Hurricane Maria devastated the island, collapsing the power grid and triggering the longest blackout in American history. Millions were left without electricity. This event exposed the deep vulnerabilities of an electrical system strained by decades of underinvestment, aging infrastructure and increased exposure to extreme weather.
Rather than rebuild what was lost, Puerto Ricans turned the devastation into an opportunity for growth and innovation. In 2019, it enacted Act 17, restructuring the island’s energy system and setting an ambitious target of 100% renewable energy by 2050. This shift spurred a rapid surge in home solar panel and battery installations, as the population sought greater energy resilience and independence. Act 17 also paved the way for grid modernization by separating the island’s power generation assets from its transmission and distribution system (T&D), a move that allowed LUMA Energy, the island’s grid operator, to assume control of the T&D system in 2021, under a 15-year public-private partnership. This brought the private expertise and resources needed to upgrade the island’s grid.
As more homes became “mini power plants”, generating electricity from rooftop solar and storing it in batteries, the island’s grid faced a new challenge: modernizing to manage a decentralized, variable system. The energy landscape was rapidly shifting away from the traditional model – dominated by a few large power plants – toward thousands of smaller, distributed generation sources.
From crisis to opportunity: The challenges of grid modernization
The challenges faced by Puerto Rico are not unique. Across the U.S., much of the power grid was built for a different era. One defined by a few large fossil-fuel power plants, predictable energy demand and a more stable climate. Today, the grid is under severe pressure from rising electricity consumption, volatile weather and the rapid integration of variable renewable energy sources.
To meet this challenge, utilities are starting to adopt innovative schemes like demand response programs, to better manage fluctuations in supply and demand. California, for instance, incentivizes households to install batteries in return for rebates and Hawaii offers performance-based cash payments or monthly bill credits to customers, in return for using their stored energy to support the grid.
The rise of the ‘mini power plant’: Managing distributed energy
Before Hurricane Maria, Puerto Rico’s solar industry was small, with a few households mainly installing rooftop panels to lower energy bills. Fast forward to today, Puerto Rico leads the U.S. in per capita adoption of rooftop solar and residential battery storage, with more than 10% of electricity consumption on the island now coming from rooftop solar. LUMA estimates this will increase as much as 60% by 2028 (Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis).
As solar and battery adoption swelled, LUMA saw an opportunity to leverage this distributed network of energy resources to support the grid during generation shortfall and grid emergencies, using residential batteries to balance supply and demand, improve resilience and reduce reliance on costly peaker power plants. This vision became the foundation for the utility’s energy efficiency and demand response plan in 2023, with its Customer Battery Energy Sharing (CBES) pilot at its core.
Building a virtual power plant: The CBES solution
LUMA’s CBES pilot program launched in 2023, with the goal of increasing the amount of energy available to the grid during times of peak demand or low power generation, known as demand response events. During these times, LUMA can draw power from participating customers’ batteries to support the grid. In return, participating households earn money for the energy their batteries provide.
The program is built around equity, aiming to make the benefits of clean energy accessible to all. Administered by Resource Innovations and ScottMadden, the pilot is open even to households without their own batteries. This has been made possible through collaborations with third-party aggregators, which allow customers to join the CBES program via financing or lease options while still benefiting from performance-based incentives.
“The CBES program is a powerful example of what’s possible when utilities, technology partners, and communities work together. Working with Resource Innovations was instrumental in bringing the CBES program to life. Their expertise in battery storage and demand response enabled us to design and scale the Virtual Power Plant program that’s now helping stabilize Puerto Rico’s grid during critical moments.”
-Graziella Siciliano
Director of Energy Transformation, LUMA Energy
The amount of money a customer earns for participating in the program can be as high as $600 per battery, Sunrun says on its website. The exact amount depends on how much energy they choose to send back to the grid – sending more energy increases potential earnings, while keeping more energy for personal backup reduces them. This flexibility allows customers to balance financial rewards with energy security, giving them control over how their batteries are used. “We’re seeing a fundamental shift in how customers engage with the grid. They are no longer passive consumers, they are active partners in building energy resilience and grid stability. Programs like CBES empower them to shape a more flexible, responsive grid, and that collaboration is central to the future of utility innovation.” says Vrinda Gaba, Head of Load Flexibility at Resource Innovations.
As more homes and businesses across Puerto Rico join the program, thousands of batteries across the island have been aggregated into a single, coordinated energy resource that functions much like a large, centralized power plant. Known as a ‘virtual power plant’ this network of connected batteries and other distributed energy resources (DERs) powered by customers can enable utilities to tap into these assets as an aggregated flexible resource to stabilize the grid and ensure a reliable supply of power during periods of high demand.
Powering a cleaner, resilient future
LUMA’S CBES program has grown into the nation’s largest behind-the-meter virtual power plant, with more than 81,000 customers enrolled. Participation rates are as high as 82% during demand response events, reflecting strong community engagement in the scheme. Thanks to this high participation rate, LUMA recently used about 70,000 home batteries to send 48MW of electricity to the grid. This helped cover a gap of nearly 50MW in power supply in the Summer, preventing grid overloads and keeping the lights on longer in communities across Puerto Rico.
Building on this success, LUMA has secured regulatory approval to scale the pilot into a three-year permanent program. Resource Innovations is continuing to play a strategic role with the utility in advancing the program. Their guidance spans program design, scalability, incentive structures, and use cases like time-of-use optimization and backup power. They’ve developed real-time dashboards to track solar generation, battery usage, and grid interaction, enabling smarter dispatch strategies. Additionally, Resource Innovations is supporting the grid-edge DERMS strategy and enablement to automate dispatch and test advanced use cases, laying the foundation for Puerto Rico’s future distributed energy roadmap.
Gaba states, “With CBES, we’re not just building a program, we’re building a scalable model for the future of grid resilience. Designing the right program is critical, not just for technical success, but for long-term scalability and continued customer engagement. What’s worked in Puerto Rico through CBES offers a strong blueprint for other utilities, though regulatory frameworks, incentive structures, rate design, and customer motivations all need to be carefully aligned. Our work with LUMA has focused on building a demand response strategy that’s not only resilient and data-driven, but also adaptable. It is grounded in performance tracking, customer feedback, and dispatch testing to ensure it delivers value to both the grid and the people it serves.”
The CBES program shows how a collaborative approach between customers, technology providers and utilities can turn distributed energy into a powerful, flexible resource. By leveraging thousands of home batteries as a single VPP, Puerto Rico is not only improving grid reliability and resilience but also advancing a cleaner, more sustainable energy future that empowers its residents to take an active role in shaping the island’s energy system.