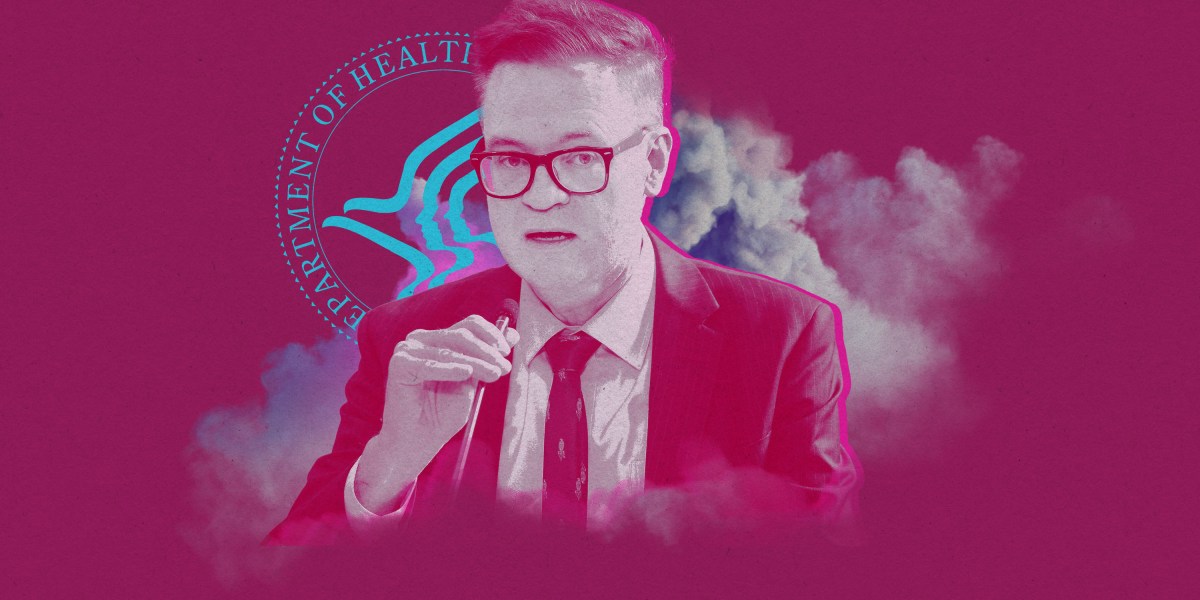
Over the past year, Jim O’Neill has become one of the most powerful people in public health. As the US deputy health secretary, he holds two roles at the top of the country’s federal health and science agencies. He oversees a department with a budget of over a trillion dollars. And he signed the decision memorandum on the US’s deeply controversial new vaccine schedule.
He’s also a longevity enthusiast. In an exclusive interview with MIT Technology Review earlier this month, O’Neill described his plans to increase human healthspan through longevity-focused research supported by ARPA-H, a federal agency dedicated to biomedical breakthroughs. At the same time, he defended reducing the number of broadly recommended childhood vaccines, a move that has been widely criticized by experts in medicine and public health.
In MIT Technology Review’s profile of O’Neill last year, people working in health policy and consumer advocacy said they found his libertarian views on drug regulation “worrisome” and “antithetical to basic public health.”
He was later named acting director of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, putting him in charge of the nation’s public health agency.
But fellow longevity enthusiasts said they hope O’Neill will bring attention and funding to their cause: the search for treatments that might slow, prevent, or even reverse human aging. Here are some takeaways from the interview.
Vaccine recommendations could change further
Last month, the US cut the number of vaccines recommended for children. The CDC no longer recommends vaccinations against flu, rotavirus, hepatitis A, or meningococcal disease for all children. The move was widely panned by medical groups and public health experts. Many worry it will become more difficult for children to access those vaccines. The majority of states have rejected the recommendations.
In the confirmation hearing for his role as deputy secretary of health and human services, which took place in May last year, O’Neill said he supported the CDC’s vaccine schedule. MIT Technology Review asked him if that was the case and, if so, what made him change his mind. “Researching and examining and reviewing safety data and efficacy data about vaccines is one of CDC’s obligations,” he said. “CDC gives important advice about vaccines and should always be open to new data and new ways of looking at data.”
At the beginning of December, O’Neill said, President Donald Trump “asked me to look at what other countries were doing in terms of their vaccine schedules.” He said he spoke to health ministries of other countries and consulted with scientists at the CDC and FDA. “It was suggested to me by lots of the operating divisions that the US focus its recommendations on consensus vaccines of other developed nations—in other words, the most important vaccines that are most often part of the core recommendations of other countries,” he said.
“As a result of that, we did an update to the vaccine schedule to focus on a set of vaccines that are most important for all children.”
But some experts in public health have said that countries like Denmark and Japan, whose vaccine schedules the new US one was supposedly modeled on, are not really comparable to the US. When asked about these criticisms, O’Neill replied, “A lot of parents feel that … more than 70 vaccine doses given to young children sounds like a really high number, and some of them ask which ones are the most important. I think we helped answer that question in a way that didn’t remove anyone’s access.”
A few weeks after the vaccine recommendations were changed, Kirk Milhoan, who leads the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, said that vaccinations for measles and polio—which are currently required for entry to public schools—should be optional. (Mehmet Oz, the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services director, has more recently urged people to “take the [measles] vaccine.”)
“CDC still recommends that all children are vaccinated against diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), Pneumococcal conjugate, polio, measles, mumps, rubella, and human papillomavirus (HPV), for which there is international consensus, as well as varicella (chickenpox),” he said when asked for his thoughts on this comment.
He also said that current vaccine guidelines are “still subject to new data coming in, new ways of thinking about things.” “CDC, FDA, and NIH are initiating new studies of the safety of immunizations,” he added. “We will continue to ask the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices to review evidence and make updated recommendations with rigorous science and transparency.”
More support for longevity—but not all science
O’Neill said he wants longevity to become a priority for US health agencies. His ultimate goal, he said, is to “make the damage of aging something that’s under medical control.” It’s “the same way of thinking” as the broader Make America Healthy Again approach, he said: “‘Again’ implies restoration of health, which is what longevity research and therapy is all about.”
O’Neill said his interest in longevity was ignited by his friend Peter Thiel, the billionaire tech entrepreneur, around 2008 to 2009. It was right around the time O’Neill was finishing up a previous role in HHS, under the Bush administration. O’Neill said Thiel told him he “should really start looking into longevity and the idea that aging damage could be reversible.” “I just got more and more excited about that idea,” he said.
When asked if he’s heard of Vitalism, a philosophical movement for “hardcore” longevity enthusiasts who, broadly, believe that death is wrong, O’Neill replied: “Yes.”
The Vitalist declaration lists five core statements, including “Death is humanity’s core problem,” “Obviating aging is scientifically plausible,” and “I will carry the message against aging and death.” O’Neill said he agrees with all of them. “I suppose I am [a Vitalist],” he said with a smile, although he’s not a paying member of the foundation behind it.
As deputy secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services, O’Neill assumes a level of responsibility for huge and influential science and health agencies, including the National Institutes of Health (the world’s largest public funder of biomedical research) and the Food and Drug Administration (which oversees drug regulation and is globally influential) as well as the CDC.
Today, he said, he sees support for longevity science from his colleagues within HHS. “If I could describe one common theme to the senior leadership at HHS, obviously it’s to make America healthy again, and reversing aging damage is all about making people healthy again,” he said. “We are refocusing HHS on addressing and reversing chronic disease, and chronic diseases are what drive aging, broadly.”
Over the last year, thousands of NIH grants worth over $2 billion were frozen or terminated, including funds for research on cancer biology, health disparities, neuroscience, and much more. When asked whether any of that funding will be restored, he did not directly address the question, instead noting: “You’ll see a lot of funding more focused on important priorities that actually improve people’s health.”
Watch ARPA-H for news on organ replacements and more
He promised we’ll hear more from ARPA-H, the three-year-old federal agency dedicated to achieving breakthroughs in medical science and biotechnology. It was established with the official goal of promoting “high-risk, high-reward innovation for the development and translation of transformative health technologies.”
O’Neill said that “ARPA-H exists to make the impossible possible in health and medicine.” The agency has a new director—Alicia Jackson, who formerly founded and led a company focused on women’s health and longevity, took on the role in October last year.
O’Neill said he helped recruit Jackson, and that she was hired in part because of her interest in longevity, which will now become a major focus of the agency. He said he meets with her regularly, as well as with Andrew Brack and Jean Hébert, two other longevity supporters who lead departments at ARPA-H. Brack’s program focuses on finding biological markers of aging. Hebert’s aim is to find a way to replace aging brain tissue, bit by bit.
O’Neill is especially excited by that one, he said. “I would try it … Not today, but … if progress goes in a broadly good direction, I would be open to it. We’re hoping to see significant results in the next few years.”
He’s also enthused by the idea of creating all-new organs for transplantation. “Someday we want to be able to grow new organs, ideally from the patients’ own cells,” O’Neill said. An ARPA-H program will receive $170 million over five years to that end, he adds. “I’m very excited about the potential of ARPA-H and Alicia and Jean and Andrew to really push things forward.”
Longevity lobbyists have a friendly ear
O’Neill said he also regularly talks to the team at the lobbying group Alliance for Longevity Initiatives. The organization, led by Dylan Livingston, played an instrumental role in changing state law in Montana to make experimental therapies more accessible. O’Neill said he hasn’t formally worked with them but thinks that “they’re doing really good work on raising awareness, including on Capitol Hill.”
Livingston has told me that A4LI’s main goals center around increasing support for aging research (possibly via the creation of a new NIH institute entirely dedicated to the subject) and changing laws to make it easier and cheaper to develop and access potential anti-aging therapies.
O’Neill gave the impression that the first goal might be a little overambitious—the number of institutes is down to Congress, he said. “I would like to get really all of the institutes at NIH to think more carefully about how many chronic diseases are usefully thought of as pathologies of aging damage,” he said. There’ll be more federal funding for that research, he said, although he won’t say more for now.
Some members of the longevity community have more radical ideas when it comes to regulation: they want to create their own jurisdictions designed to fast-track the development of longevity drugs and potentially encourage biohacking and self-experimentation.
It’s a concept that O’Neill has expressed support for in the past. He has posted on X about his support for limiting the role of government, and in support of building “freedom cities”—a similar concept that involves creating new cities on federal land.
Another longevity enthusiast who supports the concept is Niklas Anzinger, a German tech entrepreneur who is now based in Próspera, a private city within a Honduran “special economic zone,” where residents can make their own suggestions for medical regulations. Anzinger also helped draft Montana’s state law on accessing experimental therapies. O’Neill knows Anzinger and said he talks to him “once or twice a year.”
O’Neill has also supported the idea of seasteading—building new “startup countries” at sea. He served on the board of directors of the Seasteading Institute until March 2024.
In 2009, O’Neill told an audience at a Seasteading Institute conference that “the healthiest societies in 2030 will most likely be on the sea.” When asked if he still thinks that’s the case, he said: “It’s not quite 2030, so I think it’s too soon to say … What I would say now is: the healthiest societies are likely to be the ones that encourage innovation the most.”
We might expect more nutrition advice
When it comes to his own personal ambitions for longevity, O’Neill said, he takes a simple approach that involves minimizing sugar and ultraprocessed food, exercising and sleeping well, and supplementing with vitamin D. He also said he tries to “eat a diet that has plenty of protein and saturated fat,” echoing the new dietary guidance issued by the US Departments of Health and Human Services and Agriculture. That guidance has been criticized by nutrition scientists, who point out that it ignores decades of research into the harms of a diet high in saturated fat.
We can expect to see more nutrition-related updates from HHS, said O’Neill: “We’re doing more research, more randomized controlled trials on nutrition. Nutrition is still not a scientifically solved problem.” Saturated fats are of particular interest, he said. He and his colleagues want to identify “the healthiest fats,” he said.
“Stay tuned.”