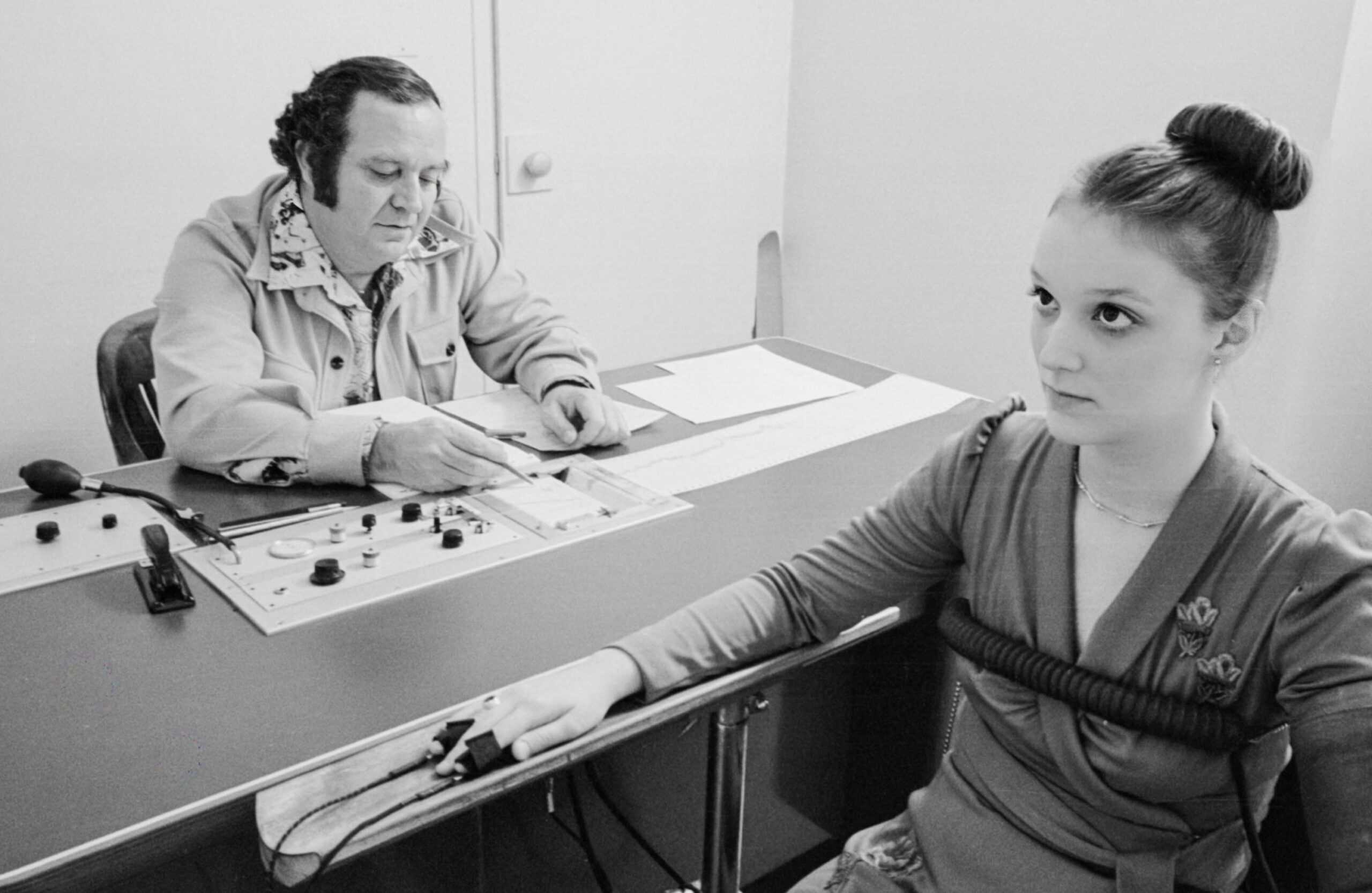
At about the time when personal computers charged into cubicle farms, another machine muscled its way into human resources departments and became a staple of routine employment screenings. By the early 1980s, some 2 million Americans annually found themselves strapped to a polygraph—a metal box that, in many people’s minds, detected deception. Most of those tested were not suspected crooks or spooks.
Then the US Office of Technology Assessment, an independent office that had been created by Congress about a decade earlier to serve as its scientific consulting arm, got involved. The office reached out to Boston University researcher Leonard Saxe with an assignment: Evaluate polygraphs. Tell us the truth about these supposed truth-telling devices.
And so Saxe assembled a team of about a dozen researchers, including Michael Saks of Boston College, to begin a systematic review. The group conducted interviews, pored over existing studies, and embarked on new lines of research. A few months later, the OTA published a technical memo, “Scientific Validity of Polygraph Testing: A Research Review and Evaluation.” Despite the tests’ widespread use, the memo dutifully reported, “there is very little research or scientific evidence to establish polygraph test validity in screening situations, whether they be preemployment, preclearance, periodic or aperiodic, random, or ‘dragnet.’” These machines could not detect lies.
Four years later, in 1987, critics at a congressional hearing invoked the OTA report as authoritative, comparing polygraphs derisively to “tea leaf reading or crystal ball gazing.” Congress soon passed strict limits on the use of polygraphs in the workplace.
Over its 23-year history, the OTA would publish some 750 reports—lengthy, interdisciplinary assessments of specific technologies that proposed means of maximizing their benefits and minimizing harms. Their subjects included electronic surveillance, genetic engineering, hazardous-waste disposal, and remote sensing from outer space. Congress set its course: The office initiated studies only at the request of a committee chairperson, a ranking minority leader, or its 12-person bipartisan board.
The investigations remained independent; staffers and consultants from both inside and outside government collaborated to answer timely and sometimes politicized questions. The reports addressed worries about alarming advances and tamped down scary-sounding hypotheticals. Some of those concerns no longer keep policymakers up at night. For instance, “Do Insects Transmit AIDS?” A 1987 OTA report correctly suggested that they don’t.
The office functioned like a debunking arm. It sussed out the snake oil. Lifted the lid on the Mechanical Turk. The reports saw through the alluring gleam of overhyped technologies.
In the years since its unceremonious defunding, perennial calls have gone out: Rouse the office from the dead! And with advances in robotics, big data, and AI systems, these calls have taken on a new level of urgency.
Like polygraphs, chatbots and search engines powered by so-called artificial intelligence come with a shimmer and a sheen of magical thinking. And if we’re not careful, politicians, employers, and other decision-makers may accept at face value the idea that machines can and should replace human judgment and discretion.
A resurrected OTA might be the perfect body to rein in dangerous and dangerously overhyped technologies. “That’s what Congress needs right now,” says Ryan Calo at the University of Washington’s Tech Policy Lab and the Center for an Informed Public, “because otherwise Congress is going to, like, take Sam Altman’s word for everything, or Eric Schmidt’s.” (The CEO of OpenAI and the former CEO of Google have both testified before Congress.) Leaving it to tech executives to educate lawmakers is like having the fox tell you how to build your henhouse. Wasted resources and inadequate protections might be only the start.

No doubt independent expertise still exists. Congress can turn to the Congressional Research Service, for example, or the National Academies of Sciences, Medicine, and Engineering. Other federal entities, such as the Office of Management and Budget and the Office of Science and Technology Policy, have advised the executive branch (and still existed as we went to press). “But they’re not even necessarily specialists,” Calo says, “and what they’re producing is very lightweight compared to what the OTA did. And so I really think we need OTA back.”
What exists today, as one researcher puts it, is a “diffuse and inefficient” system. There is no central agency that wholly devotes itself to studying emerging technologies in a serious and dedicated way and advising the country’s 535 elected officials about potential impacts. The digestible summaries Congress receives from the Congressional Research Service provide insight but are no replacement for the exhaustive technical research and analytic capacity of a fully staffed and funded think tank. There’s simply nothing like the OTA, and no single entity replicates its incisive and instructive guidance. But there’s also nothing stopping Congress from reauthorizing its budget and bringing it back, except perhaps the lack of political will.
“Congress Smiles, Scientists Wince”
The OTA had not exactly been an easy sell to the research community in 1972. At the time, it was only the third independent congressional agency ever established. As the journal Science put it in a headline that year, “The Office of Technology Assessment: Congress Smiles, Scientists Wince.” One researcher from Bell Labs told Science that he feared legislators would embark on “a clumsy, destructive attempt to manage national R&D,” but mostly the cringe seemed to stem from uncertainty about what exactly technology assessment entailed.
The OTA’s first report, in 1974, examined bioequivalence, an essential part of evaluating generic drugs. Regulators were trying to figure out whether these drugs could be deemed comparable to their name-brand equivalents without lengthy and expensive clinical studies demonstrating their safety and efficacy. Unlike all the OTA’s subsequent assessments, this one listed specific policy recommendations, such as clarifying what data should be required in order to evaluatea generic drug and ensure uniformity and standardization in the regulatory approval process. The Food and Drug Administration later incorporated these recommendations into its own submission requirements.
From then on, though, the OTA did not take sides. The office had not been set up to advise Congress on how to legislate. Rather, it dutifully followed through on its narrowly focused mandate: Do the research and provide policymakers with a well-reasoned set of options that represented a range of expert opinions.
Perhaps surprisingly, given the rise of commercially available PCs, in the first decade of its existence the OTA produced only a few reports on computing. One 1976 report touched on the automated control of trains. Others examined computerized x-ray imaging, better known as CT scans; computerized crime databases; and the use of computers in medical education. Over time, the office’s output steadily increased, eventually averaging 32 reports a year. Its budget swelled to $22 million; its staff peaked at 143.
While it’s sometimes said that the future impact of a technology is beyond anyone’s imagination, several findings proved prescient. A 1982 report on electronic funds transfer, or EFT, predicted that financial transactions would increasingly be carried out electronically (an obvious challenge to paper currency and hard-copy checks). Another predicted that email, or what was then termed “electronic message systems,” would disrupt snail mail and the bottom line of the US Postal Service.
In vetting the digital record-keeping that provides the basis for routine background checks, the office commissioned a study that produced a statistic still cited today, suggesting that only about a quarter of the records sent to the FBI were “complete, accurate, and unambiguous.” It was an indicator of a growing issue: computational systems that, despite seeming automated, are not free of human bias and error.
Many of the OTA’s reports focus on specific events or technologies. One looked at Love Canal, the upstate New York neighborhood polluted by hazardous waste (a disaster, the report said, that had not yet been remediated by the Environmental Protection Agency’s Superfund cleanup program); another studied the Boston Elbow, a cybernetic limb (the verdict: decidedly mixed). The office examined the feasibility of a water pipeline connecting Alaska to California, the health effects of the Kuwait oil fires, and the news media’s use of satellite imagery. The office also took on issues we grapple with today—evaluating automatic record checks for people buying guns, scrutinizing the compensation for injuries allegedly caused by vaccines, and pondering whether we should explore Mars.
The OTA made its biggest splash in 1984, when it published a background report criticizing the Strategic Defense Initiative (commonly known as “Star Wars”), a pet project of the Reagan administration that involved several exotic missile defense systems. Its lead author was the MIT physicist Ashton Carter, later secretary of defense in the second Obama administration. And the report concluded that a “perfect or near-perfect” system to defend against nuclear weapons was basically beyond the realm of the plausible; the possibility of deployment was “so remote that it should not serve as the basis of public expectation or national policy.”
The report generated lots of clicks, so to speak, especially after the administration claimed that the OTA had divulged state secrets. These charges did not hold up and Star Wars never materialized, although there have been recent efforts to beef up the military’s offensive capacity in space. But for the work of an advisory body that did not play politics, the report made a big political hubbub. By some accounts, its subsequent assessments became so neutral that the office risked receding to the point of invisibility.
From a purely pragmatic point of view, the OTA wrote to be understood. A dozen reports from the early ’90s received “Blue Pencil Awards,” given by the National Association of Government Communicators for “superior government communication products and those who produce them.” None are copyrighted. All were freely reproduced and distributed, both in print and electronically. The entire archive is stored on CD-ROM, and digitized copies are still freely available for download on a website maintained by Princeton University, like an earnest oasis of competence in the cloistered world of federal documents.
Assessments versus accountability
Looking back, the office took shape just as debates about technology and the law were moving to center stage.
While the gravest of dangers may have changed in form and in scope, the central problem remains: Laws and lawmakers cannot keep up with rapid technological advances. Policymakers often face a choice between regulating with insufficient facts and doing nothing.
In 2018, Adam Kinzinger, then a Republican congressman from Illinois, confessed to a panel on quantum computing: “I can understand about 50% of the things you say.” To some, his admission underscored a broader tech illiteracy afflicting those in power. But other commentators argued that members of Congress should not be expected to know it all—all the more reason to restaff an office like the OTA.
A motley chorus of voices have clamored for an OTA 2.0 over the years. One doctor wrote that the office could help address the “discordance between the amount of money spent and the actual level of health.” Tech fellows have said bringing it back could help Congress understand machine learning and AI. Hillary Clinton, as a Democratic presidential hopeful, floated the possibility of resurrecting the OTA in 2017.
But Meg Leta Jones, a law scholar at Georgetown University, argues that assessing new technologies is the least of our problems. The kind of work the OTA did is now done by other agencies, such as the FTC, FCC, and National Telecommunications and Information Administration, she says: “The energy I would like to put into the administrative state is not on assessments, but it’s on actual accountability and enforcement.”
She sees the existing framework as built for the industrial age, not a digital one, and is among those calling for a more ambitious overhaul. There seems to be little political appetite for the creation of new agencies anyway. That said, Jones adds, “I wouldn’t be mad if they remade the OTA.”
No one can know whether or how future administrations will address AI, Mars colonization, the safety of vaccines, or, for that matter, any other emerging technology that the OTA investigated in an earlier era. But if the new administration makes good on plans to deregulate many sectors, it’s worth noting some historic echoes. In 1995, when conservative politicians defunded the OTA, they did so in the name of efficiency. Critics of that move contend that the office probably saved the government money and argue that the purported cost savings associated with its elimination were largely symbolic.
Jathan Sadowski, a research fellow at Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, who has written about the OTA’s history, says the conditions that led to its demise have only gotten more partisan, more politicized. This makes it difficult to envision a place for the agency today, he says—“There’s no room for the kind of technocratic naïveté that would see authoritative scientific advice cutting through the noise of politics.”
Congress purposely cut off its scientific advisory arm as part of a larger shake-up led by Newt Gingrich, then the House Speaker, whose pugilistic brand of populist conservatism promised “drain the swamp”–type reforms and launched what critics called a “war on science.” As a rationale for why the office was defunded, he said, “We constantly found scientists who thought what they were saying was not correct.”
Once again, Congress smiled and scientists winced. Only this time it was because politicians had pulled the plug.
Peter Andrey Smith, a freelance reporter, has contributed to Undark, the New Yorker, the New York Times Magazine, and WNYC’s Radiolab.