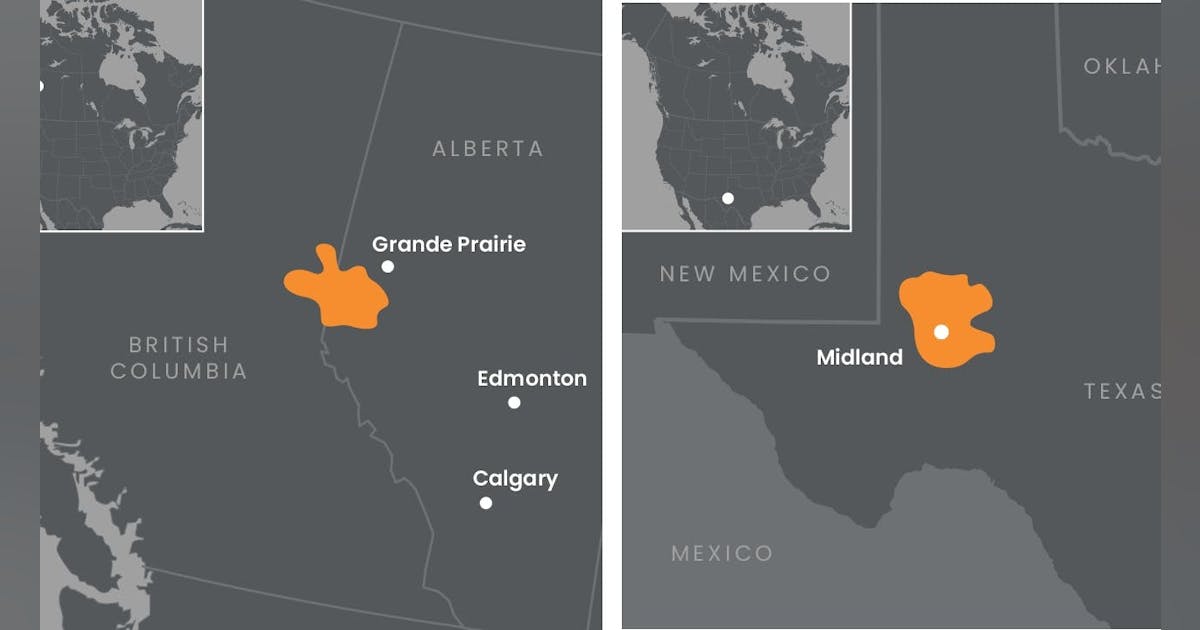
2026 guidance For 2026, Ovintiv plans to invest $2.25–2.35 billion, up slightly from the $2.147 billion spent in 2025. McCracken said capital spend will be highest in first-quarter 2026 at about $625 million, “largely due to $50 million of capital allocated to the Anadarko and some drilling activity in the Montney that we inherited from NuVista.” The program is designed to deliver 205,000–212,000 b/d of oil and condensate, some 2 bcfd of natural gas, and 620,000–645,000 boe/d total company production. For full-year 2025, the company produced 614,500 boe/d. The company is pursuing a “stay‑flat” oil strategy, maintaining liquids output through steady activity rather than aggressive volume growth. Permian Ovintiv plans to run 5 rigs and 1-2 frac crews in the Permian basin this year, bringing 125–135 net wells online. Oil and condensate volumes are expected to average 117,000–123,000 b/d, with natural gas production of 270–295 MMcfd. The company projects 2026 drilling and completion costs below $600/ft, about $25/ft lower than 2025. Chief operating officer Gregory Givens credited faster cycle times and ongoing application of surfactant technology. Ovintiv has now deployed surfactants in about 300 Permian wells, generating a 9% uplift in oil productivity versus comparable control wells. Givens also reiterated that Ovintiv remains committed to its established cube‑development model. Responding to an analyst question, he said the company continues completing entire cubes at once, then returning “18 months later” to develop adjacent cubes—an approach that stabilizes well performance and reduces parent‑child degradation, he said. “We are getting the whole cube at the same time, and that is working quite well for us,” he said. The company plans to drill its first Barnett Woodford test well across Midland basin acreage in 2026. Ovintiv holds Barnett rights across roughly 100,000 acres and intends to move cautiously given the zone’s depth, higher pressure,