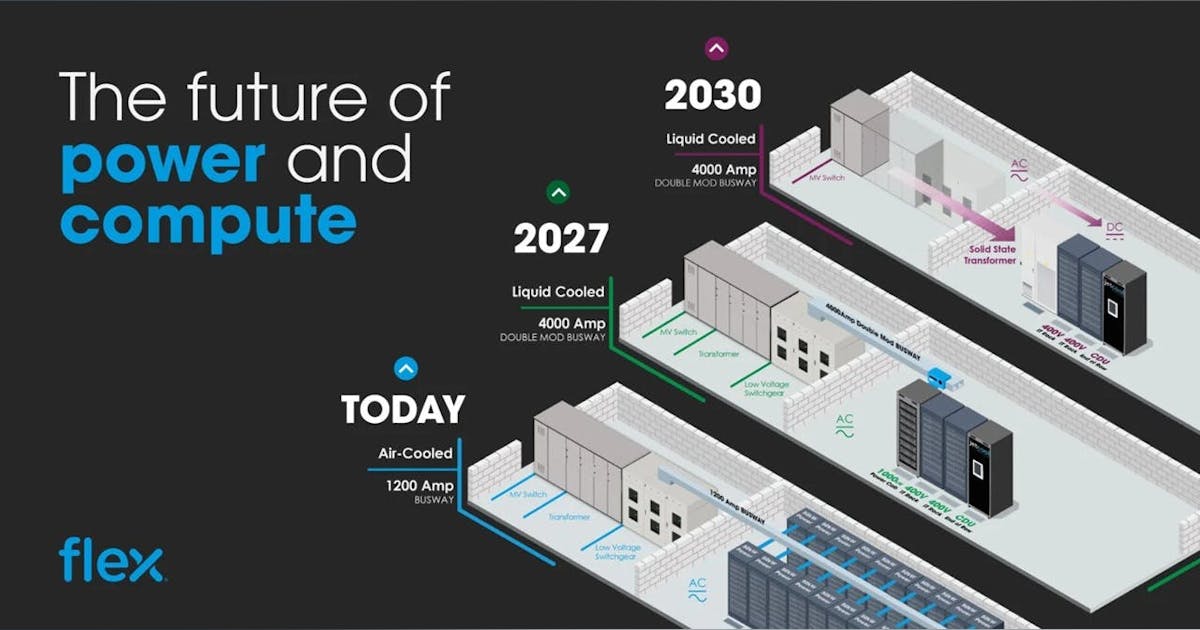
Vera Rubin MGX brings together Nvidia’s Vera CPUs and Rubin CPX GPUs, all using the same open MGX rack footprint as Blackwell. The system allows for numerous configurations and integrations.
“MGX is a flexible, modular building block-based approach to server and rack scale design,” Delaere said. “It allows our ecosystem to create a wide range of configurations, and do so very quickly.”
Vera Rubin MGX will deliver almost eight times more performance than Nvidia’s GB 300 for certain types of calculation, he said. The architecture is liquid-cooled and cable-free, allowing for faster assembly and serviceability. Operators can quickly mix and match components such as CPUs, GPUs, or storage, supporting interoperability, Nvidia said.
Matt Kimball, principal data center analyst at Moor Insights and Strategy, highlighted the modularity and cleanness of the MGX tray design.
“This simplifies the manufacturing process significantly,” he said. For enterprises managing tens or even hundreds of thousands of racks, “this design enables a level of operational efficiency that can deliver real savings in time and cost.”
Nvidia is also showing innovation with cooling, Kimball said. “Running cooling to the midplane is a very clean design and more efficient.”