Join our daily and weekly newsletters for the latest updates and exclusive content on industry-leading AI coverage. Learn More
Enterprise companies need to take note of OpenAI’s Deep Research. It provides a powerful product based on new capabilities, and is so good that it could put a lot of people out of jobs.
Deep Research is on the bleeding edge of a growing trend: integrating large language models (LLMs) with search engines and other tools to greatly expand their capabilities. (Just as this article was being reported, for example, Elon Musk’s xAI unveiled Grok 3, which claims similar capabilities, including a Deep Search product. However, it’s too early to assess Grok 3’s real-world performance, since most subscribers haven’t actually gotten their hands on it yet.)
OpenAI’s Deep Research, released on February 3, requires a Pro account with OpenAI, costing $200 per month, and is currently available only to U.S. users. So far, this restriction may have limited early feedback from the global developer community, which is typically quick to dissect new AI advancements.
With Deep Research mode, users can ask OpenAI’s leading o3 model any question. The result? A report often superior to what human analysts produce, delivered faster and at a fraction of the cost.
How Deep Research works
While Deep Research has been widely discussed, its broader implications have yet to fully register. Initial reactions praised its impressive research capabilities, despite its occasional hallucinations in its citations. There was the guy who said he used it to help his wife who had breast cancer. It provided deeper analysis than what her oncologists provided on how radiation therapy was the right course of action, he said. The consensus, summarized by Wharton AI professor Ethan Mollick, is that its advantages far outweigh occasional inaccuracies, as fact-checking takes less time than what the AI saves overall. This is something I agree with, based on my own usage.
Financial institutions are already exploring applications. BNY Mellon, for instance, sees potential in using Deep Research for credit risk assessments. Its impact will extend across industries, from healthcare to retail, manufacturing, and supply chain management — virtually any field that relies on knowledge work.
A smarter research agent
Unlike traditional AI models that attempt one-shot answers, Deep Research first asks clarifying questions. It might ask four or more questions to make sure it understands exactly what you want. It then develops a structured research plan, conducts multiple searches, revises its plan based on new insights, and iterates in a loop until it compiles a comprehensive, well-formatted report. This can take between a few minutes and half an hour. Reports range from 1,500 to 20,000 words, and typically include citations from 15 to 30 sources with exact URLs, at least according to my usage over the past week and a half.
The technology behind Deep Research: reasoning LLMs and agentic RAG
Deep Research does this by merging two technologies in a way we haven’t seen before in a mass-market product.
Reasoning LLMs: The first is OpenAI’s cutting-edge model, o3, which leads in logical reasoning and extended chain-of-thought processes. When it was announced in December 2024, o3 scored an unprecedented 87.5% on the super-difficult ARC-AGI benchmark designed to test novel problem-solving abilities. What’s interesting is that o3 hasn’t been released as a standalone model for developers to use. Indeed, OpenAI’s CEO Sam Altman announced last week that the model instead would be wrapped into a “unified intelligence” system, which would unite models with agentic tools like search, coding agents and more. Deep Research is an example of such a product. And while competitors like DeepSeek-R1 have approached o3’s capabilities (one of the reasons why there was so much excitement a few weeks ago), OpenAI is still widely considered to be slightly ahead.
Agentic RAG: The second, agentic RAG, is a technology that has been around for about a year now. It uses agents to autonomously seek out information and context from other sources, including searching the internet. This can include other tool-calling agents to find non-web information via APIs; coding agents that can complete complex sequences more efficiently; and database searches. Initially, OpenAI’s Deep Research is primarily searching the open web, but company leaders have suggested it would be able to search more sources over time.
OpenAI’s competitive edge (and its limits)
While these technologies are not entirely new, OpenAI’s refinements — enabled by things like its jump-start on working on these technologies, massive funding, and its closed-source development model — have taken Deep Research to a new level. It can work behind closed doors, and leverage feedback from the more than 300 million active users of OpenAI’s popular ChatGPT product. OpenAI has led in research in these areas, for example in how to do verification step by step to get better results. And it has clearly implemented search in an interesting way, perhaps borrowing from Microsoft’s Bing and other technologies.
While it is still hallucinating some results from its searches, it’s doing so less than competitors, perhaps in part because the underlying o3 model itself has set an industry low for these hallucinations at 8%. And there are ways to reduce mistakes still further, by using mechanisms like confidence thresholds, citation requirements and other sophisticated credibility checks.
At the same time, there are limits to OpenAI’s lead and capabilities. Within two days of Deep Research’s launch, HuggingFace introduced an open-source AI research agent called Open Deep Research that got results that weren’t too far off of OpenAI’s — similarly merging leading models and freely available agentic capabilities. There are few moats. Open-source competitors like DeepSeek appear set to stay close in the area of reasoning models, and Microsoft’s Magentic-One offers a framework for most of OpenAI’s agentic capabilities, to name just two more examples.
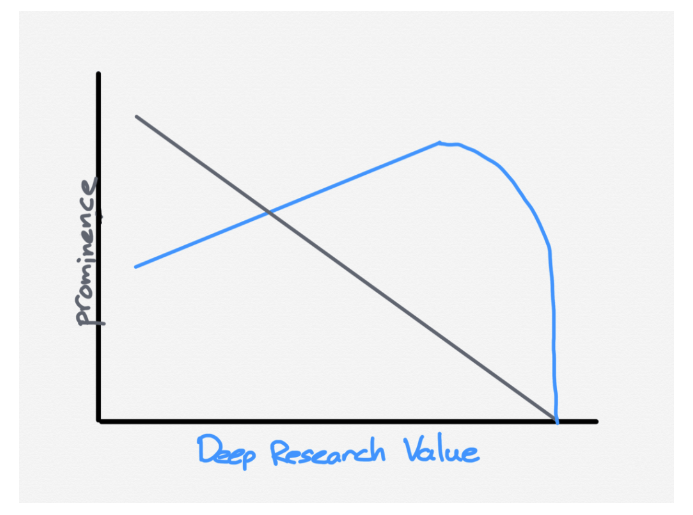
Furthermore, Deep Research has limitations. The product is really efficient at researching obscure information that can be found on the web. But in areas where there is not much online and where domain expertise is largely private — whether in peoples’ heads or in private databases — it doesn’t work at all. So this isn’t going to threaten the jobs of high-end hedge-fund researchers, for example, who are paid to go talk with real experts in an industry to find out otherwise very hard-to-obtain information, as Ben Thompson argued in a recent post (see graphic below). In most cases, OpenAI’s Deep Research is going to affect lower-skilled analyst jobs.
The most intelligent product yet
When you merge top-tier reasoning with agentic retrieval, it’s not really surprising that you get such a powerful product. OpenAI’s Deep Research achieved 26.6% on Humanity’s Last Exam, arguably the best benchmark for intelligence. This is a relatively new AI benchmark designed to be the most difficult for any AI model to complete, covering 3,000 questions across 100 different subjects. On this benchmark, OpenAI’s Deep Research significantly outperforms Perplexity’s Deep Research (20.5%) and earlier models like o3-mini (13%) and DeepSeek-R1 (9.4%) that weren’t hooked up with agentic RAG. But early reviews suggest OpenAI leads in both quality and depth. Google’s Deep Research has yet to be tested against this benchmark, but early reviews suggest OpenAI leads in both quality and depth.
How it’s different: the first mass-market AI that could displace jobs
What’s different with this product is its potential to eliminate jobs. Sam Witteveen, cofounder of Red Dragon and a developer of AI agents, observed in a deep-dive video discussion with me that a lot of people are going to say: “Holy crap, I can get these reports for $200 that I could get from some top-4 consulting company that would cost me $20,000.” This, he said, is going to cause some real changes, including likely putting people out of jobs.
Which brings me back to my interview last week with Sarthak Pattanaik, head of engineering and AI at BNY Mellon, a major U.S. bank.
To be sure, Pattanaik didn’t say anything about the product’s ramifications for actual job counts at his bank. That’s going to be a particularly sensitive topic that any enterprise is probably going to shy away from addressing publicly. But he said he could see OpenAI’s Deep Research being used for credit underwriting reports and other “topline” activities, and having significant impact on a variety of jobs: “Now that doesn’t impact every job, but that does impact a set of jobs around strategy [and] research, like comparison vendor management, comparison of product A versus product B.” He added: “So I think everything which is more on system two thinking — more exploratory, where it may not have a right answer, because the right answer can be mounted once you have that scenario definition — I think that’s an opportunity.”
A historical perspective: job loss and job creation
Technological revolutions have historically displaced workers in the short term while creating new industries in the long run. From automobiles replacing horse-drawn carriages to computers automating clerical work, job markets evolve. New opportunities created by the disruptive technologies tend to spawn new hiring. Companies that fail to embrace these advances will fall behind their competitors.
OpenAI’s Altman acknowledged the link, even if indirect, between Deep Research and labor. At the AI Summit in Paris last week, he was asked about his vision for artificial general intelligence (AGI), or the stage at which AI can perform pretty much any task that a human can. As he answered, his first reference was to Deep Research: “It’s a model I think is capable of doing like a low-single-digit percentage of all the tasks in the economy in the world right now, which is a crazy statement, and a year ago I don’t think something that people thought is going to be coming.” (See minute three of this video). He continued: “For 50 cents of compute, you can do like $500 or $5,000 of work. Companies are implementing that to just be way more efficient.”
The takeaway: a new era for knowledge work
Deep Research represents a watershed moment for AI in knowledge-based industries. By integrating cutting-edge reasoning with autonomous research capabilities, OpenAI has created a tool that is smarter, faster and significantly more cost-effective than human analysts.
The implications are vast, from financial services to healthcare to enterprise decision-making. Organizations that leverage this technology effectively will gain a significant competitive edge. Those that ignore it do so at their peril.
For a deeper discussion on how OpenAI’s Deep Research works, and how it is reshaping knowledge work, check out my in-depth conversation with Sam Witteveen in our latest video:
Daily insights on business use cases with VB Daily
If you want to impress your boss, VB Daily has you covered. We give you the inside scoop on what companies are doing with generative AI, from regulatory shifts to practical deployments, so you can share insights for maximum ROI.
Read our Privacy Policy
Thanks for subscribing. Check out more VB newsletters here.
An error occured.