Your Gateway to Power, Energy, Datacenters, Bitcoin and AI
Dive into the latest industry updates, our exclusive Paperboy Newsletter, and curated insights designed to keep you informed. Stay ahead with minimal time spent.
Discover What Matters Most to You
AI
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry.

Bitcoin:
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry.

Datacenter:
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry.
Energy:
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry.
Discover What Matter Most to You
Featured Articles

Tech layoffs surpass 45,000 in early 2026
Layoffs spread across tech sectors Beyond Amazon, Meta, and Block, several technology vendors and platform companies have also announced sizable layoffs this year. According to the RationalFX report: Semiconductor and electronics company ams OSRAM has announced 2,000 layoffs. Telecommunications vendor Ericsson has announced 1,900 job cuts. Semiconductor equipment manufacturer ASML has reduced its workforce by 1,700 employees. Enterprise software and platform companies are also reducing headcount. Enterprise software providers Autodesk and Salesforce have each cut about 1,000 jobs. Online grocery technology company Ocado has also eliminated around 1,000 roles. eBay reduced its headcount by about 800 jobs. Social media company Pinterest has cut about 675 positions. The layoffs span multiple segments of the technology sector, including cloud services, enterprise software, semiconductor manufacturing, and digital platforms, according to RationalFX. Layoffs tied to restructuring, emerging tech According to RationalFX, the layoffs often reflect broader corporate restructuring efforts rather than financial distress. Many companies are consolidating teams, reducing management layers, and shifting resources toward emerging technologies and strategic priorities. “A key driver behind many of these reductions remains the growing integration of artificial intelligence and automation,” said RationalFX’s Cohen. “Companies are increasingly restructuring teams and workflows around AI-assisted systems, often reducing headcount in areas where tasks can be automated or handled more efficiently with new tools.”

Hustlers are cashing in on China’s OpenClaw AI craze
Feng Qingyang had always hoped to launch his own company, but he never thought this would be how—or that the day would come this fast. Feng, a 27-year-old software engineer based in Beijing, started tinkering with OpenClaw, a popular new open-source AI tool that can take over a device and autonomously complete tasks for a user, in January. He was immediately hooked, and before long he was helping other curious tech workers with less technical proficiency install the AI agent. Feng soon realized this could be a lucrative opportunity. By the end of January, he had set up a page on Xianyu, a secondhand shopping site, advertising “OpenClaw installation support.” “No need to know coding or complex terms. Fully remote,” reads the posting. “Anyone can quickly own an AI assistant, available within 30 minutes.” At the same time, the broader Chinese public was beginning to catch on—and the tool, which had begun as a niche interest among tech workers, started to evolve into a popular sensation.
Feng quickly became inundated with requests, and he started chatting with customers and managing orders late into the night. At the end of February, he quit his job. Now his side gig has now grown into a full-fledged professional operation with over 100 employees. So far, the store has handled 7,000 orders, each worth about 248 RMB or approximately $34. “Opportunities are always fleeting,” says Feng. “As programmers, we are the first to feel the winds shift.”
Feng is among a small cohort of savvy early adopters turning China’s OpenClaw craze into cash. As users with little technical background want in, a cottage industry of people offering installation services and preconfigured hardware has sprung up to meet them. The sudden rise of these tinkerers and impromptu consultants shows just how eager the general public in China is to adopt cutting-edge AI—even when there are huge security risks. A “lobster craze” “Have you raised a lobster yet?” Xie Manrui, a 36-year-old software engineer in Shenzhen, says he has heard this question nonstop over the past month. “Lobster” is the nickname Chinese users have given to OpenClaw—a reference to its logo. Xie, like Feng, has been experimenting with OpenClaw since January. He’s built new open-source tools on top of the ecosystem, including one that visualizes the agent’s progress as an animated little desktop worker and another that lets users voice-chat with it. “I’ve met so many new people through ‘lobster raising,’” says Xie. “Many are lawyers or doctors, with little technical background, but all dedicated to learning new things.” Lobsters are indeed popping up everywhere in China right now—on and offline. In February, for instance, the entrepreneur and tech influencer Fu Sheng hosted a livestream showing off OpenClaw’s capabilities that got 20,000 views. And just last weekend, Xie attended three different OpenClaw events in Shenzhen, each drawing more than 500 people. These self-organized, unofficial gatherings feature power users, influencers, and sometimes venture capitalists as speakers. The biggest event Xie attended, on March 7, drew more than 1,000 people; in the packed venue, he says, people were shoulder to shoulder, with many attendees unable to even get a seat. Now China’s AI giants are starting to piggyback on the trend too, promoting their models, APIs, and cloud services (which can be used with OpenClaw), as well as their own OpenClaw-like agents. Earlier this month, Tencent held a public event offering free installation support for OpenClaw, drawing long lines of people waiting for help, including elderly users and children.
This sudden burst in popularity has even prompted local governments to get involved. Earlier this month the government of Longgang, a district in Shenzhen, released several policies to support OpenClaw-related ventures, including free computing credits and cash rewards for standout projects. Other cities, including Wuxi, have begun rolling out similar measures. These policies only catalyze what’s already in the air. “It was not until my father, who is 77, asked me to help install a ‘lobster’ for him that I realized this thing is truly viral,” says Henry Li, a software engineer based in Beijing. A programmer gold rush What’s making this moment particularly lucrative for people with technical skills, like Feng, is that so many people want OpenClaw, but not nearly as many have the capabilities to access it. Setting it up requires a level of technical knowledge most people do not possess, from typing commands into a black terminal window to navigating unfamiliar developer platforms. On the hardware side, an older or budget laptop may struggle to run it smoothly. And if the tool is not installed on a device separate from someone’s everyday computer, or if the data accessible to OpenClaw is not properly partitioned, the user’s privacy could be at risk—opening the door to data leaks and even malicious attacks. Chris Zhao, known as “Qi Shifu” online, organizes OpenClaw social media groups and events in Beijing. On apps like Rednote and Jike, Zhao routinely shares his thoughts on AI, and he asks other interested users to leave their WeChat ID so he can invite them to a semi-private group chat. The proof required to join is a screenshot that shows your “lobster” up and running. Zhao says that even in group chats for experienced users, hardware and cloud setup remain a constant topic of discussion. The relatively high bar for setting up OpenClaw has generated a sense of exclusivity, creating a natural opening for a service industry to start unfolding around it. On Chinese e-commerce platforms like Taobao and JD, a simple search for “OpenClaw” now returns hundreds of listings, most of them installation guides and technical support packages aimed at nontechnical users, priced anywhere from 100 to 700 RMB (approximately $15 to $100). At the higher end, many vendors offer to come to help you in person. Like Feng, most providers of these services are early adopters with some technical ability who are looking for a side gig. But as demand has surged, some have found themselves overwhelmed. Xie, the developer in Shenzhen who created tools to layer on OpenClaw, was asked by a friend who runs one such business to help out over the weekend; the friend had a customer who worked in e-commerce and had little technical experience, so Xie had to show up in person to get it done. He walked away with 600 RMB ($87) for the afternoon. The growing demand has also pushed vendors like Feng to expand quickly. He has now standardized his operation into tiers: a basic installation, a custom package where users can make specific requests like configuring a preferred chat app, and an ongoing tutoring service for those who want a hand to hold as they find their footing with the technology.
Other vendors in China are making money combining OpenClaw with hardware. Li Gong, a Shenzhen-based seller of refurbished Mac computers, was among the first online sellers to do this—offering Mac minis and MacBooks with OpenClaw preinstalled. Because OpenClaw is designed to operate with deep access to a hard drive and can run continuously in the background unattended, many users prefer to install it on a separate device rather than on the one they use every day. This would help prevent bad actors from infiltrating the program and immediately gaining access to a wide swathe of someone’s personal information. Many turn to secondhand or refurbished options to keep the cost down. Li says that in the last two weeks, orders have increased eightfold. Though OpenClaw itself is a new technology, the general practice of buying software bundles, downloading third-party packages, and seeking out modified devices is nothing new for many Chinese internet users, says Tianyu Fang, a PhD candidate studying the history of technology at Harvard University. Many users pay for one-off IT support services for tasks from installing Adobe software to jailbreaking a Kindle.
Still, not everyone is getting swept up. Jiang Yunhui, a tech worker based in Ningbo, worries that ordinary users who struggle with setup may not be the right audience for a technology that is still effectively in testing. “The hype in first-tier cities can be a little overblown,” he says. “The agent is still a proof of concept, and I doubt it would be of any life-changing use to the average person for now.” He argues that using it safely and getting anything meaningful out of it requires a level of technical fluency and independent judgment that most new users simply don’t have yet. He’s not alone in his concerns. On March 10, the Chinese cybersecurity regulator CNCERT issued a warning about the security and data risks tied to OpenClaw, saying it heightens users’ exposure to data breaches. Despite the potential pitfalls, though, China’s enthusiasm for OpenClaw doesn’t seem to be slowing. Feng, now flush with the earnings from his operation, wants to use the momentum—and the capital—to keep building out his own venture with AI tools at the center of it. “With OpenClaw and other AI agents, I want to see if I can run a one-person company,” he says. “I’m giving myself one year.”

The Download: Pokémon Go to train world models, and the US-China race to find aliens
This is today’s edition of The Download, our weekday newsletter that provides a daily dose of what’s going on in the world of technology. How Pokémon Go is giving delivery robots an inch-perfect view of the world Pokémon Go was the world’s first augmented-reality megahit. Released in 2016 by Niantic, the AR twist on the juggernaut Pokémon franchise fast became a global phenomenon. “500 million people installed that app in 60 days,” says Brian McClendon, CTO at Niantic Spatial, an AI company that Niantic spun out last year. Now Niantic Spatial is using that vast trove of crowdsourced data to build a kind of world model—a buzzy new technology that grounds the smarts of LLMs in real environments. The firm wants to use it to help robots navigate more precisely. Read the full story. —Will Douglas Heaven
MIT Technology Review Narrated: America was winning the race to find Martian life. Then China jumped in. In July 2024, after more than three years on Mars, the Perseverance rover came across a peculiar rocky outcrop. Instead of the usual crystals or sedimentary layers, this one had spots. Those specks were the best hint yet of alien life. NASA began a new mission to bring the rocks back to Earth to study. But now, just over a year and a half later, the project is on life support. As a result, those oh-so-promising rocks may be stuck out there forever.
This also means that, in the race to find evidence of alien life, America has effectively ceded its pole position to its greatest geopolitical rival: China. The superpower is moving full steam ahead with its own version of NASA’s mission. —Robin George Andrews This is our latest story to be turned into an MIT Technology Review Narrated podcast, which we’re publishing each week on Spotify and Apple Podcasts. Just navigate to MIT Technology Review Narrated on either platform, and follow us to get all our new content as it’s released. The must-reads I’ve combed the internet to find you today’s most fun/important/scary/fascinating stories about technology. 1 Viral AI fakes of the Iran war are flooding X And Grok is failing to flag them. (Wired $) + The conflict could wreak havoc on data centers and electricity costs. (The Verge) + Pro-Iran bots are weaponizing posts about Epstein. (Gizmodo) + AI is turning the Iran conflict into a show. (MIT Technology Review) 2 Anthropic fears the loss of billions due to the Pentagon’s blacklisting That’s what the company has told a judge as it seeks to block its designation as a supply-chain risk. (Bloomberg $) + Microsoft has backed the company in its legal fight with the Pentagon. (FT $) + OpenAI’s “compromise” with the DoD dealt a big blow to Anthropic. (MIT Technology Review) 3 Meta has bought a social network that’s exclusively for bots Moltbook is a Reddit-like site where AI agents interact with each other. (NYT $) + The platform is AI theater. (MIT Technology Review) 4 Ukraine is eagerly offering the US its expertise and tech to counter Iranian drones Kyiv has sent drones and UAV specialists to military bases in Jordan. (WSJ $) + A radio-obsessed civilian is shaping Ukraine’s drone defense. (MIT Technology Review) 5 OnlyFans “chatters” are earning $2 per hour to impersonate models A worker in the Philippines described the job as “heartbreaking” and “icky.” (BBC) 6 The DHS has removed officials who objected to “illegal” orders about surveillance tech The officers had refused to mislabel records about the technologies in order to block their release. (Wired) 7 This startup is building data centers run on brain cells The “biological data centers” are coming to Melbourne and Singapore. (New Scientist $) 8 Anduril is expanding into space defense The company is buying ExoAnalytic, which specializes in missile defense tracking. (Reuters) + We saw a demo of an AI system powering Anduril’s vision for war. (MIT Technology Review) 9 Big tech has a new big idea: AI compute as compensation Silicon Valley is pitching it as a job perk. (Business Insider) 10 Wordle’s creator is back with a new game It’s inspired by cryptic crosswords. (The New Yorker $) Quote of the day “You come for the Epstein content, and you stay for the propaganda.” —Bret Schafer, an expert on information manipulation, tells the Washington Post how pro-Iran networks are gaining traction with posts about Epstein.
One More Thing MEREDITH MIOTKE | PHOTO: NASA/JPL-CALTECH/MSSS The quest to figure out farming on Mars If ever a blade of grass grew on Mars, those days are over. But could they begin again? What would it take to grow plants to feed future astronauts on Mars? To grow food there, we can’t just drop seeds in the ground and add water. We will need to create a layer of soil that can support life. And to do that, we first have to get rid of the red planet’s toxic salts. Researchers recently discovered a potential solution—and the early signs are promising. Read the full story. We can still have nice things A place for comfort, fun and distraction to brighten up your day. (Got any ideas? Drop me a line) + Finally, a rebellion arises against mint’s tyranny over our teeth: Peanut Butter Cup toothpaste. + DIY decorators rejoice! The humble paint tray has received an ingeniously simple renovation. + Saudi surgeons have successfully separated two conjoined twins. + If you’re looking for real innovation, check out British Pie Week’s beef rendang, jerk chicken, and double-size pasties.

Eridu exits stealth with $200M to rebuild AI networking
That gap is not static. Promode Nedungadi, Chief Technology Officer, said the architectural and algorithmic trends driving AI are making the network problem harder, not easier. Techniques like mixture-of-experts models and the disaggregation of inference into separate prefill and decode stages all require more data movement. “Every one of those requires more data to be moved around,” he said. “The amount of data being moved per token is growing.” The scale challenge also has more than one dimension. Perkins described three: scale-up, which refers to interconnecting GPUs within a single training domain; scale-out, which covers the broader cluster fabric; and what he called scale-across, an emerging requirement that standards bodies are beginning to address. “We think that scale-across is quite interesting as well,” Perkins said. Architecture: silicon, packaging, and software A key differentiator for Eridu will come from silicon. “There’s no doubt that we are developing our own silicon. We’re developing the most advanced silicon in the networking sector, bar none, period, and that’s absolutely necessary,” Perkins said. “You don’t get to an order-of-magnitude higher scale using off-the-shelf silicon.” Eridu has a partnership with TSMC for process technology and advanced system integration. Perkins said TSMC sees the networking bottleneck as tied directly to its own business. The silicon approach is likely to benefit from chiplet-based architecture and advanced packaging. “We believe you need to be on a different technology arc than what the mainstream technology is,” Omar Hassen, Chief Product Officer, told Network World. “In terms of things like advanced packaging, you’ve got to take advantage of everything you can from chiplet-based architecture, clean-sheet design, and advanced packaging. We believe we’re on the right technology arc that can take us beyond what the existing incumbents are doing.” Fundamentally, Eridu’s approach is an attempt to break through the architectural ceiling facing
From games to biology and beyond: 10 years of AlphaGo’s impact
Catalyzing breakthroughs in scienceBy proving it could navigate the massive search space of a Go board, AlphaGo demonstrated the potential for AI to help us better understand the vast complexities of the physical world. We started by attempting to solve the protein folding problem, a 50-year grand challenge of predicting the 3D structure of proteins – information that is crucial for understanding diseases and developing new drugs.In 2020, we finally cracked this longstanding scientific problem with our AlphaFold 2 system. From there, we folded the structures for all 200 million proteins known to science and made them freely available to scientists in an open-source database. Today, over 3 million researchers around the world use the AlphaFold database to accelerate their important work on everything from malaria vaccines to plastic-eating enzymes. And in 2024, it was the honor of a lifetime for John Jumper and I to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for leading this project, on behalf of the entire AlphaFold team.Since AlphaGo’s win, we’ve applied its groundbreaking approach to many other areas of science and mathematics, including:Mathematical reasoning: The most direct descendant of AlphaGo’s architecture, AlphaProof learned to prove formal mathematical statements using a combination of language models and AlphaZero’s reinforcement learning and search algorithms. Alongside AlphaGeometry 2, it became the first system to achieve a medal-standard (silver) at the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO), proving AlphaGo’s methods could unlock advanced mathematical reasoning and laying the foundation for our most capable general models.Gemini, our largest and most capable model, recently went even further. An advanced version of its Deep Think mode achieved gold-medal level performance at the 2025 IMO using an approach inspired by AlphaGo. Since then, Deep Think has been applied to even more complex, open-ended challenges across science and engineering.Algorithm discovery: Just as AlphaGo searched for the best move in a game, our coding agent AlphaEvolve explores the space of computer code to discover more efficient algorithms. It had its own Move 37 moment when it found a novel way to multiply matrices, a fundamental mathematical operation powering nearly all modern neural networks. AlphaEvolve is now being tested on problems ranging from data center optimization to quantum computing.Scientific collaboration: We are integrating the search and reasoning principles pioneered with AlphaGo into an AI co-scientist. By having agents ‘debate’ scientific ideas and hypotheses, this system acts as a collaborator capable of performing the rigorous thinking necessary to identify patterns in data and solve sophisticated problems. In validation studies at Imperial College London, it analyzed decades of literature and independently arrived at the same hypothesis about antimicrobial resistance that researchers had spent years developing and validating experimentally.We’ve also used AI to better understand the genome, advance fusion energy research, improve weather prediction and more.As impressive as our scientific models are, they are highly specialized. To achieve fundamental breakthroughs like creating limitless clean energy or solving diseases that we don’t understand today, we need general AI systems that can find underlying structure and connections between different subject areas, and help us to come up with new hypotheses like the best scientists do.Future of intelligenceFor an AI to be truly general, it needs to understand the physical world. We built Gemini to be multimodal from the beginning so it could understand not just language, but also audio, video, images and code to build a model of the world.To think and reason across these modalities, the latest Gemini models use some of the techniques we pioneered with AlphaGo and AlphaZero.The next generation of AI systems will also need to be able to call upon specialized tools. For example, if a model needed to know the structure of a protein it could use AlphaFold for that.We think the combination of Gemini’s world models, AlphaGo’s search and planning techniques, and specialized AI tool use will prove to be critical for AGI.True creativity is a key capability that such an AGI system would need to exhibit. Move 37 was a glimpse of AI’s potential to think outside the box, but true original invention will require something more. It would need to not only come up with a novel Go strategy, as AlphaGo impressively did, but actually invent a game as deep and elegant, and as worthy of study as Go.Ten years after AlphaGo’s legendary victory, our ultimate goal is on the horizon. The creative spark first seen in Move 37 catalyzed breakthroughs that are now converging to pave the path towards AGI – and usher in a new golden age of scientific discovery.
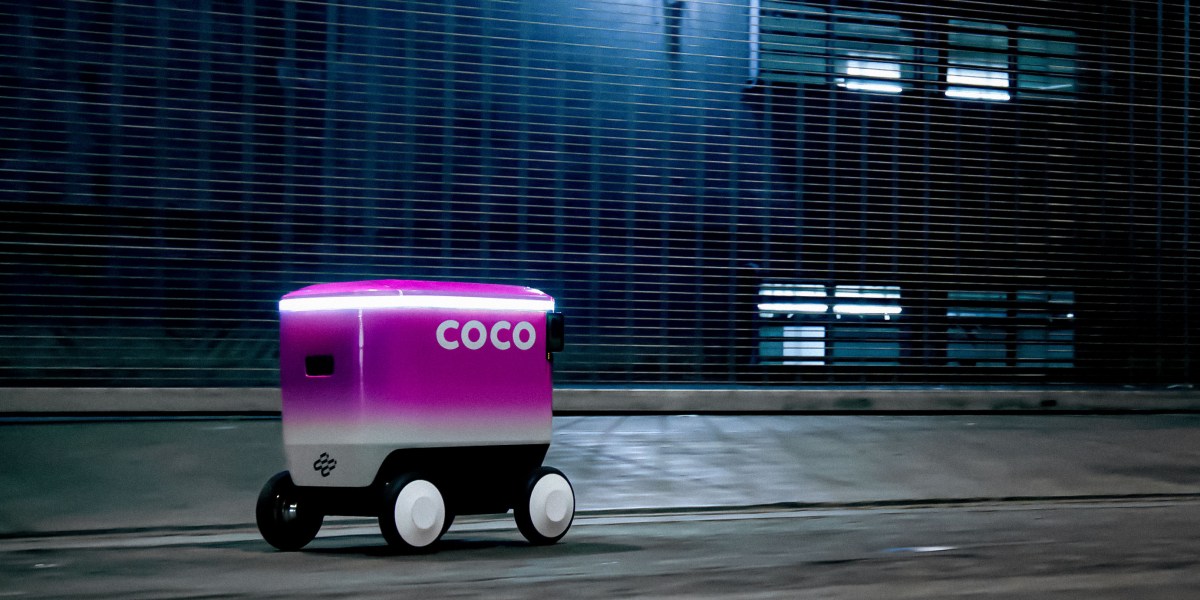

How Pokémon Go is helping robots deliver pizza on time
Pokémon Go was the world’s first augmented-reality megahit. Released in 2016 by the Google spinout Niantic, the AR twist on the juggernaut Pokémon franchise fast became a global phenomenon. From Chicago to Oslo to Enoshima, players hit the streets in the urgent hope of catching a Jigglypuff or a Squirtle or (with a huge amount of luck) an ultra-rare Galarian Zapdos hovering just out of reach, superimposed on the everyday world. In short, we’re talking about a huge number of people pointing their phones at a huge number of buildings. “Five hundred million people installed that app in 60 days,” says Brian McClendon, CTO at Niantic Spatial, an AI company that Niantic spun out in May last year. According to the video-game firm Scopely, which bought Pokémon Go from Niantic at the same time, the game still drew more than 100 million players in 2024, eight years after it launched. Now Niantic Spatial is using that vast and unparalleled trove of crowdsourced data—images of urban landmarks tagged with super-accurate location markers taken from the phones of hundreds of millions of Pokémon Go players around the world—to build a kind of world model, a buzzy new technology that grounds the smarts of LLMs in real environments. The company’s latest product is a model that it says can pinpoint your location on a map to within a few centimeters, based on a handful of snapshots of the buildings or other landmarks in view. The firm wants to use it to help robots navigate with greater precision in places where GPS is unreliable.
In the first big test of its technology, Niantic Spatial has just teamed up with Coco Robotics, a startup that deploys last-mile delivery robots in a number of cities across the US and Europe. “Everybody thought that AR was the future, that AR glasses were coming,” says McClendon. “And then robots became the audience.” From Pikachu to pizza delivery Coco Robotics deploys around 1,000 flight-case-size robots—built to carry up to eight extra-large pizzas or four grocery bags—in Los Angeles, Chicago, Jersey City, Miami, and Helsinki. According to CEO Zach Rash, the robots have made more than half a million deliveries to date, covering a few million miles in all weather conditions.
But to compete with human couriers, Coco’s robots, which trundle along sidewalks at around five miles per hour, must be as reliable as possible. “The best way we can do our job is by arriving exactly when we told you we were going to arrive,” says Rash. And that means not getting lost. The problem Coco faces is that it cannot rely on GPS, which can be weak in cities because radio signals bounce off buildings and interfere with each other. “We do deliveries in a lot of dense areas with high-rises and underpasses and freeways, and those are the areas where GPS just never really works,” says Rash. “The urban canyon is the worst place in the world for GPS,” says McClendon. “If you look at that blue dot on your phone, you’ll often see it drift 50 meters, which puts you on a different block going a different direction on the wrong side of the street.” That’s where Niantic Spatial comes in. For the last few years, Niantic Spatial has been taking the data collected from players of Pokémon Go and Ingress (Niantic’s previous phone-based AR game, launched in 2013) and building a visual positioning system, technology that tells you where you are based on what you can see. “It turns out that getting Pikachu to realistically run around and getting Coco’s robot to safely and accurately move through the world is actually the same problem,” says John Hanke, CEO of Niantic Spatial. “Visual positioning is not a very new technology,” says Konrad Wenzel at ESRI, a company that develops digital mapping and geospatial analysis software. “But it’s obvious that the more cameras we have out there, the better it becomes.” Niantic Spatial has trained its model on 30 billion images captured in urban environments. In particular, the images are clustered around hot spots—places that served as important locations in Niantic’s games that players were encouraged to visit, such as Pokémon battle arenas. “We had a million-plus locations around the world where we can locate you precisely,” says McClendon. “We know where you’re standing within several centimeters of accuracy and, most importantly, where you’re looking.” The upshot is that for each of those million locations, Niantic Spatial has many thousands of images taken in more or less the same place but from different angles, at different times of day, and in different weather conditions. Each of those images comes with detailed metadata that pinpoints where in space the phone was at the time it captured the image, including which way the phone was facing, which way up it was, whether or not it was moving, how fast and in which direction, and more. The firm has used this data set to train a model to predict exactly where it is by taking into account what it is looking at—even for locations other than those million hot spots, where good sources of image and location data are scarcer.
In addition to GPS, Coco’s robots, which are fitted with four cameras, will now use this model to try to figure out where they are and where they are headed. The robots’ cameras are hip-height and point in all directions at once, so their viewpoint is a little different from a Pokémon Go player’s, but adapting the data was straightforward, says Rash. Rival companies use visual positioning systems too. For example, Starship Technologies, a robot delivery firm founded in Estonia in 2014, says its robots use their sensors to build a 3D map of their surroundings, plotting the edges of buildings and the position of streetlights. But Rash is betting that Niantic Spatial’s tech will give Coco an edge. He claims it will allow his robots to position themselves in the correct pickup spots outside restaurants, making sure they don’t get in anybody’s way, and stop just outside the customer’s door instead of a few steps away, which might have happened in the past. A Cambrian explosion in robotics When Niantic Spatial started work on its visual positioning system, the idea was to apply it to augmented reality, says Hanke. “If you are wearing AR glasses and you want the world to lock in to where you’re looking, then you need some method for doing that,” he says. “But now we’re seeing a Cambrian explosion in robotics.” Some of those robots may need to share spaces with humans—spaces such as construction sites and sidewalks. “If robots are ever going to assimilate into that environment in a way that’s not disruptive for human beings, they’re going to have to have a similar level of spatial understanding,” says Hanke. “We can help robots find exactly where they are when they’ve been jostled and bumped.” The Coco Robotics partnership is the start. What Niantic Spatial is putting in place, says Hanke, are the first pieces of what he calls a living map: a hyper-detailed virtual simulation of the world that changes as the world changes. As robots from Coco and other firms move about the world, they will provide new sources of map data, feeding into more and more detailed digital replicas of the world. But the way Hanke and McClendon see it, maps are not only becoming more detailed; they are being used more and more by machines. That shifts what maps are for. Maps have long been used to help people locate themselves in the world. As they moved from 2D to 3D to 4D (think of real-time simulations, such as digital twins), the basic principle hasn’t changed: Points on the map correspond to points in space or time. And yet maps for machines may need to become more like guidebooks, full of information that humans take for granted. Companies like Niantic Spatial and ESRI want to add descriptions that tell machines what they’re actually looking at, with every object tagged with a list of its properties. “This era is about building useful descriptions of the world for machines to comprehend,” says Hanke. “The data that we have is a great starting point in terms of building up an understanding of how the connective tissue of the world works.” There is a lot of buzz about world models right now—and Niantic Spatial knows it. LLMs may seem like know-it-alls, but they have very little common sense when it comes to interpreting and interacting with everyday environments. World models aim to fix that. Some firms, such as Google DeepMind and World Labs, are developing models that generate virtual fantasy worlds on the fly, which can then be used as training dojos for AI agents. Niantic Spatial says it is coming at the problem from a different angle. Push map-making far enough and you’ll end up capturing everything, says McClendon: “I’m very focused on trying to re-create the real world. We’re not there yet, but we want to be there.”

Tech layoffs surpass 45,000 in early 2026
Layoffs spread across tech sectors Beyond Amazon, Meta, and Block, several technology vendors and platform companies have also announced sizable layoffs this year. According to the RationalFX report: Semiconductor and electronics company ams OSRAM has announced 2,000 layoffs. Telecommunications vendor Ericsson has announced 1,900 job cuts. Semiconductor equipment manufacturer ASML has reduced its workforce by 1,700 employees. Enterprise software and platform companies are also reducing headcount. Enterprise software providers Autodesk and Salesforce have each cut about 1,000 jobs. Online grocery technology company Ocado has also eliminated around 1,000 roles. eBay reduced its headcount by about 800 jobs. Social media company Pinterest has cut about 675 positions. The layoffs span multiple segments of the technology sector, including cloud services, enterprise software, semiconductor manufacturing, and digital platforms, according to RationalFX. Layoffs tied to restructuring, emerging tech According to RationalFX, the layoffs often reflect broader corporate restructuring efforts rather than financial distress. Many companies are consolidating teams, reducing management layers, and shifting resources toward emerging technologies and strategic priorities. “A key driver behind many of these reductions remains the growing integration of artificial intelligence and automation,” said RationalFX’s Cohen. “Companies are increasingly restructuring teams and workflows around AI-assisted systems, often reducing headcount in areas where tasks can be automated or handled more efficiently with new tools.”

Hustlers are cashing in on China’s OpenClaw AI craze
Feng Qingyang had always hoped to launch his own company, but he never thought this would be how—or that the day would come this fast. Feng, a 27-year-old software engineer based in Beijing, started tinkering with OpenClaw, a popular new open-source AI tool that can take over a device and autonomously complete tasks for a user, in January. He was immediately hooked, and before long he was helping other curious tech workers with less technical proficiency install the AI agent. Feng soon realized this could be a lucrative opportunity. By the end of January, he had set up a page on Xianyu, a secondhand shopping site, advertising “OpenClaw installation support.” “No need to know coding or complex terms. Fully remote,” reads the posting. “Anyone can quickly own an AI assistant, available within 30 minutes.” At the same time, the broader Chinese public was beginning to catch on—and the tool, which had begun as a niche interest among tech workers, started to evolve into a popular sensation.
Feng quickly became inundated with requests, and he started chatting with customers and managing orders late into the night. At the end of February, he quit his job. Now his side gig has now grown into a full-fledged professional operation with over 100 employees. So far, the store has handled 7,000 orders, each worth about 248 RMB or approximately $34. “Opportunities are always fleeting,” says Feng. “As programmers, we are the first to feel the winds shift.”
Feng is among a small cohort of savvy early adopters turning China’s OpenClaw craze into cash. As users with little technical background want in, a cottage industry of people offering installation services and preconfigured hardware has sprung up to meet them. The sudden rise of these tinkerers and impromptu consultants shows just how eager the general public in China is to adopt cutting-edge AI—even when there are huge security risks. A “lobster craze” “Have you raised a lobster yet?” Xie Manrui, a 36-year-old software engineer in Shenzhen, says he has heard this question nonstop over the past month. “Lobster” is the nickname Chinese users have given to OpenClaw—a reference to its logo. Xie, like Feng, has been experimenting with OpenClaw since January. He’s built new open-source tools on top of the ecosystem, including one that visualizes the agent’s progress as an animated little desktop worker and another that lets users voice-chat with it. “I’ve met so many new people through ‘lobster raising,’” says Xie. “Many are lawyers or doctors, with little technical background, but all dedicated to learning new things.” Lobsters are indeed popping up everywhere in China right now—on and offline. In February, for instance, the entrepreneur and tech influencer Fu Sheng hosted a livestream showing off OpenClaw’s capabilities that got 20,000 views. And just last weekend, Xie attended three different OpenClaw events in Shenzhen, each drawing more than 500 people. These self-organized, unofficial gatherings feature power users, influencers, and sometimes venture capitalists as speakers. The biggest event Xie attended, on March 7, drew more than 1,000 people; in the packed venue, he says, people were shoulder to shoulder, with many attendees unable to even get a seat. Now China’s AI giants are starting to piggyback on the trend too, promoting their models, APIs, and cloud services (which can be used with OpenClaw), as well as their own OpenClaw-like agents. Earlier this month, Tencent held a public event offering free installation support for OpenClaw, drawing long lines of people waiting for help, including elderly users and children.
This sudden burst in popularity has even prompted local governments to get involved. Earlier this month the government of Longgang, a district in Shenzhen, released several policies to support OpenClaw-related ventures, including free computing credits and cash rewards for standout projects. Other cities, including Wuxi, have begun rolling out similar measures. These policies only catalyze what’s already in the air. “It was not until my father, who is 77, asked me to help install a ‘lobster’ for him that I realized this thing is truly viral,” says Henry Li, a software engineer based in Beijing. A programmer gold rush What’s making this moment particularly lucrative for people with technical skills, like Feng, is that so many people want OpenClaw, but not nearly as many have the capabilities to access it. Setting it up requires a level of technical knowledge most people do not possess, from typing commands into a black terminal window to navigating unfamiliar developer platforms. On the hardware side, an older or budget laptop may struggle to run it smoothly. And if the tool is not installed on a device separate from someone’s everyday computer, or if the data accessible to OpenClaw is not properly partitioned, the user’s privacy could be at risk—opening the door to data leaks and even malicious attacks. Chris Zhao, known as “Qi Shifu” online, organizes OpenClaw social media groups and events in Beijing. On apps like Rednote and Jike, Zhao routinely shares his thoughts on AI, and he asks other interested users to leave their WeChat ID so he can invite them to a semi-private group chat. The proof required to join is a screenshot that shows your “lobster” up and running. Zhao says that even in group chats for experienced users, hardware and cloud setup remain a constant topic of discussion. The relatively high bar for setting up OpenClaw has generated a sense of exclusivity, creating a natural opening for a service industry to start unfolding around it. On Chinese e-commerce platforms like Taobao and JD, a simple search for “OpenClaw” now returns hundreds of listings, most of them installation guides and technical support packages aimed at nontechnical users, priced anywhere from 100 to 700 RMB (approximately $15 to $100). At the higher end, many vendors offer to come to help you in person. Like Feng, most providers of these services are early adopters with some technical ability who are looking for a side gig. But as demand has surged, some have found themselves overwhelmed. Xie, the developer in Shenzhen who created tools to layer on OpenClaw, was asked by a friend who runs one such business to help out over the weekend; the friend had a customer who worked in e-commerce and had little technical experience, so Xie had to show up in person to get it done. He walked away with 600 RMB ($87) for the afternoon. The growing demand has also pushed vendors like Feng to expand quickly. He has now standardized his operation into tiers: a basic installation, a custom package where users can make specific requests like configuring a preferred chat app, and an ongoing tutoring service for those who want a hand to hold as they find their footing with the technology.
Other vendors in China are making money combining OpenClaw with hardware. Li Gong, a Shenzhen-based seller of refurbished Mac computers, was among the first online sellers to do this—offering Mac minis and MacBooks with OpenClaw preinstalled. Because OpenClaw is designed to operate with deep access to a hard drive and can run continuously in the background unattended, many users prefer to install it on a separate device rather than on the one they use every day. This would help prevent bad actors from infiltrating the program and immediately gaining access to a wide swathe of someone’s personal information. Many turn to secondhand or refurbished options to keep the cost down. Li says that in the last two weeks, orders have increased eightfold. Though OpenClaw itself is a new technology, the general practice of buying software bundles, downloading third-party packages, and seeking out modified devices is nothing new for many Chinese internet users, says Tianyu Fang, a PhD candidate studying the history of technology at Harvard University. Many users pay for one-off IT support services for tasks from installing Adobe software to jailbreaking a Kindle.
Still, not everyone is getting swept up. Jiang Yunhui, a tech worker based in Ningbo, worries that ordinary users who struggle with setup may not be the right audience for a technology that is still effectively in testing. “The hype in first-tier cities can be a little overblown,” he says. “The agent is still a proof of concept, and I doubt it would be of any life-changing use to the average person for now.” He argues that using it safely and getting anything meaningful out of it requires a level of technical fluency and independent judgment that most new users simply don’t have yet. He’s not alone in his concerns. On March 10, the Chinese cybersecurity regulator CNCERT issued a warning about the security and data risks tied to OpenClaw, saying it heightens users’ exposure to data breaches. Despite the potential pitfalls, though, China’s enthusiasm for OpenClaw doesn’t seem to be slowing. Feng, now flush with the earnings from his operation, wants to use the momentum—and the capital—to keep building out his own venture with AI tools at the center of it. “With OpenClaw and other AI agents, I want to see if I can run a one-person company,” he says. “I’m giving myself one year.”

The Download: Pokémon Go to train world models, and the US-China race to find aliens
This is today’s edition of The Download, our weekday newsletter that provides a daily dose of what’s going on in the world of technology. How Pokémon Go is giving delivery robots an inch-perfect view of the world Pokémon Go was the world’s first augmented-reality megahit. Released in 2016 by Niantic, the AR twist on the juggernaut Pokémon franchise fast became a global phenomenon. “500 million people installed that app in 60 days,” says Brian McClendon, CTO at Niantic Spatial, an AI company that Niantic spun out last year. Now Niantic Spatial is using that vast trove of crowdsourced data to build a kind of world model—a buzzy new technology that grounds the smarts of LLMs in real environments. The firm wants to use it to help robots navigate more precisely. Read the full story. —Will Douglas Heaven
MIT Technology Review Narrated: America was winning the race to find Martian life. Then China jumped in. In July 2024, after more than three years on Mars, the Perseverance rover came across a peculiar rocky outcrop. Instead of the usual crystals or sedimentary layers, this one had spots. Those specks were the best hint yet of alien life. NASA began a new mission to bring the rocks back to Earth to study. But now, just over a year and a half later, the project is on life support. As a result, those oh-so-promising rocks may be stuck out there forever.
This also means that, in the race to find evidence of alien life, America has effectively ceded its pole position to its greatest geopolitical rival: China. The superpower is moving full steam ahead with its own version of NASA’s mission. —Robin George Andrews This is our latest story to be turned into an MIT Technology Review Narrated podcast, which we’re publishing each week on Spotify and Apple Podcasts. Just navigate to MIT Technology Review Narrated on either platform, and follow us to get all our new content as it’s released. The must-reads I’ve combed the internet to find you today’s most fun/important/scary/fascinating stories about technology. 1 Viral AI fakes of the Iran war are flooding X And Grok is failing to flag them. (Wired $) + The conflict could wreak havoc on data centers and electricity costs. (The Verge) + Pro-Iran bots are weaponizing posts about Epstein. (Gizmodo) + AI is turning the Iran conflict into a show. (MIT Technology Review) 2 Anthropic fears the loss of billions due to the Pentagon’s blacklisting That’s what the company has told a judge as it seeks to block its designation as a supply-chain risk. (Bloomberg $) + Microsoft has backed the company in its legal fight with the Pentagon. (FT $) + OpenAI’s “compromise” with the DoD dealt a big blow to Anthropic. (MIT Technology Review) 3 Meta has bought a social network that’s exclusively for bots Moltbook is a Reddit-like site where AI agents interact with each other. (NYT $) + The platform is AI theater. (MIT Technology Review) 4 Ukraine is eagerly offering the US its expertise and tech to counter Iranian drones Kyiv has sent drones and UAV specialists to military bases in Jordan. (WSJ $) + A radio-obsessed civilian is shaping Ukraine’s drone defense. (MIT Technology Review) 5 OnlyFans “chatters” are earning $2 per hour to impersonate models A worker in the Philippines described the job as “heartbreaking” and “icky.” (BBC) 6 The DHS has removed officials who objected to “illegal” orders about surveillance tech The officers had refused to mislabel records about the technologies in order to block their release. (Wired) 7 This startup is building data centers run on brain cells The “biological data centers” are coming to Melbourne and Singapore. (New Scientist $) 8 Anduril is expanding into space defense The company is buying ExoAnalytic, which specializes in missile defense tracking. (Reuters) + We saw a demo of an AI system powering Anduril’s vision for war. (MIT Technology Review) 9 Big tech has a new big idea: AI compute as compensation Silicon Valley is pitching it as a job perk. (Business Insider) 10 Wordle’s creator is back with a new game It’s inspired by cryptic crosswords. (The New Yorker $) Quote of the day “You come for the Epstein content, and you stay for the propaganda.” —Bret Schafer, an expert on information manipulation, tells the Washington Post how pro-Iran networks are gaining traction with posts about Epstein.
One More Thing MEREDITH MIOTKE | PHOTO: NASA/JPL-CALTECH/MSSS The quest to figure out farming on Mars If ever a blade of grass grew on Mars, those days are over. But could they begin again? What would it take to grow plants to feed future astronauts on Mars? To grow food there, we can’t just drop seeds in the ground and add water. We will need to create a layer of soil that can support life. And to do that, we first have to get rid of the red planet’s toxic salts. Researchers recently discovered a potential solution—and the early signs are promising. Read the full story. We can still have nice things A place for comfort, fun and distraction to brighten up your day. (Got any ideas? Drop me a line) + Finally, a rebellion arises against mint’s tyranny over our teeth: Peanut Butter Cup toothpaste. + DIY decorators rejoice! The humble paint tray has received an ingeniously simple renovation. + Saudi surgeons have successfully separated two conjoined twins. + If you’re looking for real innovation, check out British Pie Week’s beef rendang, jerk chicken, and double-size pasties.

Eridu exits stealth with $200M to rebuild AI networking
That gap is not static. Promode Nedungadi, Chief Technology Officer, said the architectural and algorithmic trends driving AI are making the network problem harder, not easier. Techniques like mixture-of-experts models and the disaggregation of inference into separate prefill and decode stages all require more data movement. “Every one of those requires more data to be moved around,” he said. “The amount of data being moved per token is growing.” The scale challenge also has more than one dimension. Perkins described three: scale-up, which refers to interconnecting GPUs within a single training domain; scale-out, which covers the broader cluster fabric; and what he called scale-across, an emerging requirement that standards bodies are beginning to address. “We think that scale-across is quite interesting as well,” Perkins said. Architecture: silicon, packaging, and software A key differentiator for Eridu will come from silicon. “There’s no doubt that we are developing our own silicon. We’re developing the most advanced silicon in the networking sector, bar none, period, and that’s absolutely necessary,” Perkins said. “You don’t get to an order-of-magnitude higher scale using off-the-shelf silicon.” Eridu has a partnership with TSMC for process technology and advanced system integration. Perkins said TSMC sees the networking bottleneck as tied directly to its own business. The silicon approach is likely to benefit from chiplet-based architecture and advanced packaging. “We believe you need to be on a different technology arc than what the mainstream technology is,” Omar Hassen, Chief Product Officer, told Network World. “In terms of things like advanced packaging, you’ve got to take advantage of everything you can from chiplet-based architecture, clean-sheet design, and advanced packaging. We believe we’re on the right technology arc that can take us beyond what the existing incumbents are doing.” Fundamentally, Eridu’s approach is an attempt to break through the architectural ceiling facing
From games to biology and beyond: 10 years of AlphaGo’s impact
Catalyzing breakthroughs in scienceBy proving it could navigate the massive search space of a Go board, AlphaGo demonstrated the potential for AI to help us better understand the vast complexities of the physical world. We started by attempting to solve the protein folding problem, a 50-year grand challenge of predicting the 3D structure of proteins – information that is crucial for understanding diseases and developing new drugs.In 2020, we finally cracked this longstanding scientific problem with our AlphaFold 2 system. From there, we folded the structures for all 200 million proteins known to science and made them freely available to scientists in an open-source database. Today, over 3 million researchers around the world use the AlphaFold database to accelerate their important work on everything from malaria vaccines to plastic-eating enzymes. And in 2024, it was the honor of a lifetime for John Jumper and I to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for leading this project, on behalf of the entire AlphaFold team.Since AlphaGo’s win, we’ve applied its groundbreaking approach to many other areas of science and mathematics, including:Mathematical reasoning: The most direct descendant of AlphaGo’s architecture, AlphaProof learned to prove formal mathematical statements using a combination of language models and AlphaZero’s reinforcement learning and search algorithms. Alongside AlphaGeometry 2, it became the first system to achieve a medal-standard (silver) at the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO), proving AlphaGo’s methods could unlock advanced mathematical reasoning and laying the foundation for our most capable general models.Gemini, our largest and most capable model, recently went even further. An advanced version of its Deep Think mode achieved gold-medal level performance at the 2025 IMO using an approach inspired by AlphaGo. Since then, Deep Think has been applied to even more complex, open-ended challenges across science and engineering.Algorithm discovery: Just as AlphaGo searched for the best move in a game, our coding agent AlphaEvolve explores the space of computer code to discover more efficient algorithms. It had its own Move 37 moment when it found a novel way to multiply matrices, a fundamental mathematical operation powering nearly all modern neural networks. AlphaEvolve is now being tested on problems ranging from data center optimization to quantum computing.Scientific collaboration: We are integrating the search and reasoning principles pioneered with AlphaGo into an AI co-scientist. By having agents ‘debate’ scientific ideas and hypotheses, this system acts as a collaborator capable of performing the rigorous thinking necessary to identify patterns in data and solve sophisticated problems. In validation studies at Imperial College London, it analyzed decades of literature and independently arrived at the same hypothesis about antimicrobial resistance that researchers had spent years developing and validating experimentally.We’ve also used AI to better understand the genome, advance fusion energy research, improve weather prediction and more.As impressive as our scientific models are, they are highly specialized. To achieve fundamental breakthroughs like creating limitless clean energy or solving diseases that we don’t understand today, we need general AI systems that can find underlying structure and connections between different subject areas, and help us to come up with new hypotheses like the best scientists do.Future of intelligenceFor an AI to be truly general, it needs to understand the physical world. We built Gemini to be multimodal from the beginning so it could understand not just language, but also audio, video, images and code to build a model of the world.To think and reason across these modalities, the latest Gemini models use some of the techniques we pioneered with AlphaGo and AlphaZero.The next generation of AI systems will also need to be able to call upon specialized tools. For example, if a model needed to know the structure of a protein it could use AlphaFold for that.We think the combination of Gemini’s world models, AlphaGo’s search and planning techniques, and specialized AI tool use will prove to be critical for AGI.True creativity is a key capability that such an AGI system would need to exhibit. Move 37 was a glimpse of AI’s potential to think outside the box, but true original invention will require something more. It would need to not only come up with a novel Go strategy, as AlphaGo impressively did, but actually invent a game as deep and elegant, and as worthy of study as Go.Ten years after AlphaGo’s legendary victory, our ultimate goal is on the horizon. The creative spark first seen in Move 37 catalyzed breakthroughs that are now converging to pave the path towards AGI – and usher in a new golden age of scientific discovery.

How Pokémon Go is helping robots deliver pizza on time
Pokémon Go was the world’s first augmented-reality megahit. Released in 2016 by the Google spinout Niantic, the AR twist on the juggernaut Pokémon franchise fast became a global phenomenon. From Chicago to Oslo to Enoshima, players hit the streets in the urgent hope of catching a Jigglypuff or a Squirtle or (with a huge amount of luck) an ultra-rare Galarian Zapdos hovering just out of reach, superimposed on the everyday world. In short, we’re talking about a huge number of people pointing their phones at a huge number of buildings. “Five hundred million people installed that app in 60 days,” says Brian McClendon, CTO at Niantic Spatial, an AI company that Niantic spun out in May last year. According to the video-game firm Scopely, which bought Pokémon Go from Niantic at the same time, the game still drew more than 100 million players in 2024, eight years after it launched. Now Niantic Spatial is using that vast and unparalleled trove of crowdsourced data—images of urban landmarks tagged with super-accurate location markers taken from the phones of hundreds of millions of Pokémon Go players around the world—to build a kind of world model, a buzzy new technology that grounds the smarts of LLMs in real environments. The company’s latest product is a model that it says can pinpoint your location on a map to within a few centimeters, based on a handful of snapshots of the buildings or other landmarks in view. The firm wants to use it to help robots navigate with greater precision in places where GPS is unreliable.
In the first big test of its technology, Niantic Spatial has just teamed up with Coco Robotics, a startup that deploys last-mile delivery robots in a number of cities across the US and Europe. “Everybody thought that AR was the future, that AR glasses were coming,” says McClendon. “And then robots became the audience.” From Pikachu to pizza delivery Coco Robotics deploys around 1,000 flight-case-size robots—built to carry up to eight extra-large pizzas or four grocery bags—in Los Angeles, Chicago, Jersey City, Miami, and Helsinki. According to CEO Zach Rash, the robots have made more than half a million deliveries to date, covering a few million miles in all weather conditions.
But to compete with human couriers, Coco’s robots, which trundle along sidewalks at around five miles per hour, must be as reliable as possible. “The best way we can do our job is by arriving exactly when we told you we were going to arrive,” says Rash. And that means not getting lost. The problem Coco faces is that it cannot rely on GPS, which can be weak in cities because radio signals bounce off buildings and interfere with each other. “We do deliveries in a lot of dense areas with high-rises and underpasses and freeways, and those are the areas where GPS just never really works,” says Rash. “The urban canyon is the worst place in the world for GPS,” says McClendon. “If you look at that blue dot on your phone, you’ll often see it drift 50 meters, which puts you on a different block going a different direction on the wrong side of the street.” That’s where Niantic Spatial comes in. For the last few years, Niantic Spatial has been taking the data collected from players of Pokémon Go and Ingress (Niantic’s previous phone-based AR game, launched in 2013) and building a visual positioning system, technology that tells you where you are based on what you can see. “It turns out that getting Pikachu to realistically run around and getting Coco’s robot to safely and accurately move through the world is actually the same problem,” says John Hanke, CEO of Niantic Spatial. “Visual positioning is not a very new technology,” says Konrad Wenzel at ESRI, a company that develops digital mapping and geospatial analysis software. “But it’s obvious that the more cameras we have out there, the better it becomes.” Niantic Spatial has trained its model on 30 billion images captured in urban environments. In particular, the images are clustered around hot spots—places that served as important locations in Niantic’s games that players were encouraged to visit, such as Pokémon battle arenas. “We had a million-plus locations around the world where we can locate you precisely,” says McClendon. “We know where you’re standing within several centimeters of accuracy and, most importantly, where you’re looking.” The upshot is that for each of those million locations, Niantic Spatial has many thousands of images taken in more or less the same place but from different angles, at different times of day, and in different weather conditions. Each of those images comes with detailed metadata that pinpoints where in space the phone was at the time it captured the image, including which way the phone was facing, which way up it was, whether or not it was moving, how fast and in which direction, and more. The firm has used this data set to train a model to predict exactly where it is by taking into account what it is looking at—even for locations other than those million hot spots, where good sources of image and location data are scarcer.
In addition to GPS, Coco’s robots, which are fitted with four cameras, will now use this model to try to figure out where they are and where they are headed. The robots’ cameras are hip-height and point in all directions at once, so their viewpoint is a little different from a Pokémon Go player’s, but adapting the data was straightforward, says Rash. Rival companies use visual positioning systems too. For example, Starship Technologies, a robot delivery firm founded in Estonia in 2014, says its robots use their sensors to build a 3D map of their surroundings, plotting the edges of buildings and the position of streetlights. But Rash is betting that Niantic Spatial’s tech will give Coco an edge. He claims it will allow his robots to position themselves in the correct pickup spots outside restaurants, making sure they don’t get in anybody’s way, and stop just outside the customer’s door instead of a few steps away, which might have happened in the past. A Cambrian explosion in robotics When Niantic Spatial started work on its visual positioning system, the idea was to apply it to augmented reality, says Hanke. “If you are wearing AR glasses and you want the world to lock in to where you’re looking, then you need some method for doing that,” he says. “But now we’re seeing a Cambrian explosion in robotics.” Some of those robots may need to share spaces with humans—spaces such as construction sites and sidewalks. “If robots are ever going to assimilate into that environment in a way that’s not disruptive for human beings, they’re going to have to have a similar level of spatial understanding,” says Hanke. “We can help robots find exactly where they are when they’ve been jostled and bumped.” The Coco Robotics partnership is the start. What Niantic Spatial is putting in place, says Hanke, are the first pieces of what he calls a living map: a hyper-detailed virtual simulation of the world that changes as the world changes. As robots from Coco and other firms move about the world, they will provide new sources of map data, feeding into more and more detailed digital replicas of the world. But the way Hanke and McClendon see it, maps are not only becoming more detailed; they are being used more and more by machines. That shifts what maps are for. Maps have long been used to help people locate themselves in the world. As they moved from 2D to 3D to 4D (think of real-time simulations, such as digital twins), the basic principle hasn’t changed: Points on the map correspond to points in space or time. And yet maps for machines may need to become more like guidebooks, full of information that humans take for granted. Companies like Niantic Spatial and ESRI want to add descriptions that tell machines what they’re actually looking at, with every object tagged with a list of its properties. “This era is about building useful descriptions of the world for machines to comprehend,” says Hanke. “The data that we have is a great starting point in terms of building up an understanding of how the connective tissue of the world works.” There is a lot of buzz about world models right now—and Niantic Spatial knows it. LLMs may seem like know-it-alls, but they have very little common sense when it comes to interpreting and interacting with everyday environments. World models aim to fix that. Some firms, such as Google DeepMind and World Labs, are developing models that generate virtual fantasy worlds on the fly, which can then be used as training dojos for AI agents. Niantic Spatial says it is coming at the problem from a different angle. Push map-making far enough and you’ll end up capturing everything, says McClendon: “I’m very focused on trying to re-create the real world. We’re not there yet, but we want to be there.”

Occidental Petroleum, 1PointFive STRATOS DAC plant nears startup in Texas Permian basin
Occidental Petroleum Corp. and its subsidiary 1PointFive expect Phase 1 of the STRATOS direct air capture (DAC) plant in Texas’ Permian basin to come online in this year’s second quarter. In a post to LinkedIn, 1PointFive said Phase 1 “is in the final stage of startup” and that Phase 2, which incorporates learnings from research and development and Phase 1 construction activities, “will also begin commissioning in Q2, with operational ramp-up continuing through the rest of the year.” Once fully operational, STRATOS is designed to capture up to 500,000 tonnes/year (tpy) of CO2. As part of the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Class VI permitting process and approval, it was reported that STRATOS is expected to include three wells to store about 722,000 tpy of CO2 in saline formations at a depth of about 4,400 ft. The company said a few activities before start-up remain, including ramping up remaining pellet reactors, completing calciner final commissioning in parallel, and beginning CO2 injection. Start-up milestones achieved include: Completed wet commissioning with water circulation. Received Class VI permits to sequester CO2. Ran CO2 compression system at design pressure. Added potassium hydroxide (KOH) to capture CO2 from the atmosphere. Building pellet inventory. Burners tested on calciner.

Brava Energia weighs Phase 3 at Atlanta to extend production plateau
Just 2 months after bringing its flagship Atlanta field onstream with the new FPSO Atlanta, Brazil’s independent operator Brava Energia SA is evaluating a potential third development phase that could add roughly 25 million bbl of reserves and help sustain peak production longer than originally planned. The Phase 3 project, still at an early technical and economic evaluation stage, focuses on the Atlanta Nordeste area; a separate, shallower reservoir discovered in 2006 by Shell’s 9-SHEL-19D-RJS well. According to André Fagundes, vice-president of research (Brazil) at Welligence Energy Analytics, Phase 2 has four wells still to be developed: two expected in 2027 and two in 2029. Phase 3 would involve drilling two additional wells in 2031, bringing total development to 12 producing wells. Until recently, full-field development was understood to comprise 10 wells, but Brava has since updated guidance to reflect a 12-well development concept. Atlanta field upside The primary objective is clear. “We believe its main objective is to extend the production plateau,” Fagundes said. Welligence estimates incremental recovery could reach 25 MMbbl, increasing the field’s overall recovery factor by roughly 1.5%. Lying outside Atlanta’s main Cretaceous reservoir, Atlanta Nordeste represents a genuine upside opportunity, Fagundes explained. The field benefits from strong natural aquifer support, and no water or gas injection is anticipated. Water-handling constraints that affected early production using the Petrojarl I—limited to 11,500 b/d of water treatment—are no longer a bottleneck. FPSO Atlanta can process up to 140,000 b/d of water. Reservoir performance to date has been solid, albeit with difficulties. Recurrent electric submersible pump (ESP) failures and processing limits on the previous FPSO complicated full validation of original reservoir models. With the new 50,000-b/d FPSO in operation since late 2024, reservoir deliverability has become the main constraint. Phase 3 wells would also use ESPs and require additional subsea

California Resources eyes ‘measured’ capex ramp on way to 12% production growth thanks to Berry buy
@import url(‘https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Inter:[email protected]&display=swap’); a { color: var(–color-primary-main); } .ebm-page__main h1, .ebm-page__main h2, .ebm-page__main h3, .ebm-page__main h4, .ebm-page__main h5, .ebm-page__main h6 { font-family: Inter; } body { line-height: 150%; letter-spacing: 0.025em; font-family: Inter; } button, .ebm-button-wrapper { font-family: Inter; } .label-style { text-transform: uppercase; color: var(–color-grey); font-weight: 600; font-size: 0.75rem; } .caption-style { font-size: 0.75rem; opacity: .6; } #onetrust-pc-sdk [id*=btn-handler], #onetrust-pc-sdk [class*=btn-handler] { background-color: #c19a06 !important; border-color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-policy a, #onetrust-pc-sdk a, #ot-pc-content a { color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-consent-sdk #onetrust-pc-sdk .ot-active-menu { border-color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-consent-sdk #onetrust-accept-btn-handler, #onetrust-banner-sdk #onetrust-reject-all-handler, #onetrust-consent-sdk #onetrust-pc-btn-handler.cookie-setting-link { background-color: #c19a06 !important; border-color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-consent-sdk .onetrust-pc-btn-handler { color: #c19a06 !important; border-color: #c19a06 !important; } The leaders of California Resources Corp., Long Beach, plan to have the company’s total production average 152,000-157,000 boe/d in 2026, with each quarter expected to be in that range. That output would equate to an increase of more than 12% from the operator’s 137,000 boe/d during fourth-quarter 2025, due mostly to the mid-December acquisition of Berry Corp. Fourth-quarter results folded in 14 days of Berry production and included 109,000 b/d of oil, with the company’s assets in the San Joaquin and Los Angeles basins accounting for 99,000 b/d of that total. The company dilled 31 new wells during the quarter and 76 in all of 2025—all in the San Joaquin—but that number will grow significantly to about 260 this year as state officials have resumed issuing permits following the passage last fall of a bill focused on Kern County production. Speaking to analysts after CRC reported fourth-quarter net income of $12 million on $924 million in revenues, president and chief executive officer Francisco Leon and chief financial officer Clio Crespy said the goal is to manage 2026 output decline to roughly 0.5% per quarter while operating four rigs and

Petro-Victory Energy spuds São João well in Brazil
@import url(‘https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Inter:[email protected]&display=swap’); a { color: var(–color-primary-main); } .ebm-page__main h1, .ebm-page__main h2, .ebm-page__main h3, .ebm-page__main h4, .ebm-page__main h5, .ebm-page__main h6 { font-family: Inter; } body { line-height: 150%; letter-spacing: 0.025em; font-family: Inter; } button, .ebm-button-wrapper { font-family: Inter; } .label-style { text-transform: uppercase; color: var(–color-grey); font-weight: 600; font-size: 0.75rem; } .caption-style { font-size: 0.75rem; opacity: .6; } #onetrust-pc-sdk [id*=btn-handler], #onetrust-pc-sdk [class*=btn-handler] { background-color: #c19a06 !important; border-color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-policy a, #onetrust-pc-sdk a, #ot-pc-content a { color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-consent-sdk #onetrust-pc-sdk .ot-active-menu { border-color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-consent-sdk #onetrust-accept-btn-handler, #onetrust-banner-sdk #onetrust-reject-all-handler, #onetrust-consent-sdk #onetrust-pc-btn-handler.cookie-setting-link { background-color: #c19a06 !important; border-color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-consent-sdk .onetrust-pc-btn-handler { color: #c19a06 !important; border-color: #c19a06 !important; } Petro-Victory Energy Corp. has spudded the SJ‑12 well at São João field in Barreirinhas basin, on the Brazilian equatorial margin, Maranhão. Drilling and testing SJ‑12 is aimed at proving enough gas can be produced to sell locally. The well forms part of the single non‑associated gas well commitment under a memorandum of understanding signed in 2024 with Enava. São João contains 50.1 bcf (1.4 billion cu m) non‑associated gas resources. Petro‑Victory 100% owns and operates São João field.

Opinion Poll: Strait of Hormuz disruptions
@import url(‘https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Inter:[email protected]&display=swap’); a { color: var(–color-primary-main); } .ebm-page__main h1, .ebm-page__main h2, .ebm-page__main h3, .ebm-page__main h4, .ebm-page__main h5, .ebm-page__main h6 { font-family: Inter; } body { line-height: 150%; letter-spacing: 0.025em; font-family: Inter; } button, .ebm-button-wrapper { font-family: Inter; } .label-style { text-transform: uppercase; color: var(–color-grey); font-weight: 600; font-size: 0.75rem; } .caption-style { font-size: 0.75rem; opacity: .6; } #onetrust-pc-sdk [id*=btn-handler], #onetrust-pc-sdk [class*=btn-handler] { background-color: #c19a06 !important; border-color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-policy a, #onetrust-pc-sdk a, #ot-pc-content a { color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-consent-sdk #onetrust-pc-sdk .ot-active-menu { border-color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-consent-sdk #onetrust-accept-btn-handler, #onetrust-banner-sdk #onetrust-reject-all-handler, #onetrust-consent-sdk #onetrust-pc-btn-handler.cookie-setting-link { background-color: #c19a06 !important; border-color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-consent-sdk .onetrust-pc-btn-handler { color: #c19a06 !important; border-color: #c19a06 !important; } 388041610 © Ahmad Efendi | Dreamstime.com US, Israel, and Iran flags <!–> ]–> <!–> –> Oil & Gas Journal wants to hear your thoughts about how the collaborative strike on Iran by the US and Israel and disruptions through the Strait of Hormuz may impact oil prices.

Iran war
@import url(‘https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Inter:[email protected]&display=swap’); a { color: var(–color-primary-main); } .ebm-page__main h1, .ebm-page__main h2, .ebm-page__main h3, .ebm-page__main h4, .ebm-page__main h5, .ebm-page__main h6 { font-family: Inter; } body { line-height: 150%; letter-spacing: 0.025em; font-family: Inter; } button, .ebm-button-wrapper { font-family: Inter; } .label-style { text-transform: uppercase; color: var(–color-grey); font-weight: 600; font-size: 0.75rem; } .caption-style { font-size: 0.75rem; opacity: .6; } #onetrust-pc-sdk [id*=btn-handler], #onetrust-pc-sdk [class*=btn-handler] { background-color: #c19a06 !important; border-color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-policy a, #onetrust-pc-sdk a, #ot-pc-content a { color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-consent-sdk #onetrust-pc-sdk .ot-active-menu { border-color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-consent-sdk #onetrust-accept-btn-handler, #onetrust-banner-sdk #onetrust-reject-all-handler, #onetrust-consent-sdk #onetrust-pc-btn-handler.cookie-setting-link { background-color: #c19a06 !important; border-color: #c19a06 !important; } #onetrust-consent-sdk .onetrust-pc-btn-handler { color: #c19a06 !important; border-color: #c19a06 !important; } <!–> –> <!–> ]–> <!–> –> You’ll need free site-access membership to view certain articles below. If you are not already registered with Oil & Gas Journal, sign up now for free. For Offshore articles, sign up here for free. New content will be added as it becomes available. Oil & Gas Journal content <!–> Economics & Markets –> 26184925 © Robert Hale | Dreamstime.com <!–> ]–> <!–> When the market opened after the initial strike on Iran, oil prices traded $75/bbl on the Open, a $7/bbl jump from Friday’s High, indicating a higher risk premium as the market… –> March 6, 2026 96633437 © Titoonz | Dreamstime.com <!–> ]–> <!–> Broader infrastructure risks are emerging as regional attacks threaten production in Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and Iraq, while Europe and Asia face heightened vulnerability due to … –> March 3, 2026 387409148 © Clare Jackson | Dreamstime.com <!–> ]–> <!–> Despite initial market volatility, oil storage levels and pre-positioned supplies have mitigated immediate price shocks. However, ongoing tensions and insurance issues continue… –> March 2, 2026 220736519 © Pavel Muravev | Dreamstime.com <!–> ]–> <!–> About 20 million b/d of

Microsoft will invest $80B in AI data centers in fiscal 2025
And Microsoft isn’t the only one that is ramping up its investments into AI-enabled data centers. Rival cloud service providers are all investing in either upgrading or opening new data centers to capture a larger chunk of business from developers and users of large language models (LLMs). In a report published in October 2024, Bloomberg Intelligence estimated that demand for generative AI would push Microsoft, AWS, Google, Oracle, Meta, and Apple would between them devote $200 billion to capex in 2025, up from $110 billion in 2023. Microsoft is one of the biggest spenders, followed closely by Google and AWS, Bloomberg Intelligence said. Its estimate of Microsoft’s capital spending on AI, at $62.4 billion for calendar 2025, is lower than Smith’s claim that the company will invest $80 billion in the fiscal year to June 30, 2025. Both figures, though, are way higher than Microsoft’s 2020 capital expenditure of “just” $17.6 billion. The majority of the increased spending is tied to cloud services and the expansion of AI infrastructure needed to provide compute capacity for OpenAI workloads. Separately, last October Amazon CEO Andy Jassy said his company planned total capex spend of $75 billion in 2024 and even more in 2025, with much of it going to AWS, its cloud computing division.

John Deere unveils more autonomous farm machines to address skill labor shortage
Join our daily and weekly newsletters for the latest updates and exclusive content on industry-leading AI coverage. Learn More Self-driving tractors might be the path to self-driving cars. John Deere has revealed a new line of autonomous machines and tech across agriculture, construction and commercial landscaping. The Moline, Illinois-based John Deere has been in business for 187 years, yet it’s been a regular as a non-tech company showing off technology at the big tech trade show in Las Vegas and is back at CES 2025 with more autonomous tractors and other vehicles. This is not something we usually cover, but John Deere has a lot of data that is interesting in the big picture of tech. The message from the company is that there aren’t enough skilled farm laborers to do the work that its customers need. It’s been a challenge for most of the last two decades, said Jahmy Hindman, CTO at John Deere, in a briefing. Much of the tech will come this fall and after that. He noted that the average farmer in the U.S. is over 58 and works 12 to 18 hours a day to grow food for us. And he said the American Farm Bureau Federation estimates there are roughly 2.4 million farm jobs that need to be filled annually; and the agricultural work force continues to shrink. (This is my hint to the anti-immigration crowd). John Deere’s autonomous 9RX Tractor. Farmers can oversee it using an app. While each of these industries experiences their own set of challenges, a commonality across all is skilled labor availability. In construction, about 80% percent of contractors struggle to find skilled labor. And in commercial landscaping, 86% of landscaping business owners can’t find labor to fill open positions, he said. “They have to figure out how to do

2025 playbook for enterprise AI success, from agents to evals
Join our daily and weekly newsletters for the latest updates and exclusive content on industry-leading AI coverage. Learn More 2025 is poised to be a pivotal year for enterprise AI. The past year has seen rapid innovation, and this year will see the same. This has made it more critical than ever to revisit your AI strategy to stay competitive and create value for your customers. From scaling AI agents to optimizing costs, here are the five critical areas enterprises should prioritize for their AI strategy this year. 1. Agents: the next generation of automation AI agents are no longer theoretical. In 2025, they’re indispensable tools for enterprises looking to streamline operations and enhance customer interactions. Unlike traditional software, agents powered by large language models (LLMs) can make nuanced decisions, navigate complex multi-step tasks, and integrate seamlessly with tools and APIs. At the start of 2024, agents were not ready for prime time, making frustrating mistakes like hallucinating URLs. They started getting better as frontier large language models themselves improved. “Let me put it this way,” said Sam Witteveen, cofounder of Red Dragon, a company that develops agents for companies, and that recently reviewed the 48 agents it built last year. “Interestingly, the ones that we built at the start of the year, a lot of those worked way better at the end of the year just because the models got better.” Witteveen shared this in the video podcast we filmed to discuss these five big trends in detail. Models are getting better and hallucinating less, and they’re also being trained to do agentic tasks. Another feature that the model providers are researching is a way to use the LLM as a judge, and as models get cheaper (something we’ll cover below), companies can use three or more models to

OpenAI’s red teaming innovations define new essentials for security leaders in the AI era
Join our daily and weekly newsletters for the latest updates and exclusive content on industry-leading AI coverage. Learn More OpenAI has taken a more aggressive approach to red teaming than its AI competitors, demonstrating its security teams’ advanced capabilities in two areas: multi-step reinforcement and external red teaming. OpenAI recently released two papers that set a new competitive standard for improving the quality, reliability and safety of AI models in these two techniques and more. The first paper, “OpenAI’s Approach to External Red Teaming for AI Models and Systems,” reports that specialized teams outside the company have proven effective in uncovering vulnerabilities that might otherwise have made it into a released model because in-house testing techniques may have missed them. In the second paper, “Diverse and Effective Red Teaming with Auto-Generated Rewards and Multi-Step Reinforcement Learning,” OpenAI introduces an automated framework that relies on iterative reinforcement learning to generate a broad spectrum of novel, wide-ranging attacks. Going all-in on red teaming pays practical, competitive dividends It’s encouraging to see competitive intensity in red teaming growing among AI companies. When Anthropic released its AI red team guidelines in June of last year, it joined AI providers including Google, Microsoft, Nvidia, OpenAI, and even the U.S.’s National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), which all had released red teaming frameworks. Investing heavily in red teaming yields tangible benefits for security leaders in any organization. OpenAI’s paper on external red teaming provides a detailed analysis of how the company strives to create specialized external teams that include cybersecurity and subject matter experts. The goal is to see if knowledgeable external teams can defeat models’ security perimeters and find gaps in their security, biases and controls that prompt-based testing couldn’t find. What makes OpenAI’s recent papers noteworthy is how well they define using human-in-the-middle

Three Aberdeen oil company headquarters sell for £45m
Three Aberdeen oil company headquarters have been sold in a deal worth £45 million. The CNOOC, Apache and Taqa buildings at the Prime Four business park in Kingswells have been acquired by EEH Ventures. The trio of buildings, totalling 275,000 sq ft, were previously owned by Canadian firm BMO. The financial services powerhouse first bought the buildings in 2014 but took the decision to sell the buildings as part of a “long-standing strategy to reduce their office exposure across the UK”. The deal was the largest to take place throughout Scotland during the last quarter of 2024. Trio of buildings snapped up London headquartered EEH Ventures was founded in 2013 and owns a number of residential, offices, shopping centres and hotels throughout the UK. All three Kingswells-based buildings were pre-let, designed and constructed by Aberdeen property developer Drum in 2012 on a 15-year lease. © Supplied by CBREThe Aberdeen headquarters of Taqa. Image: CBRE The North Sea headquarters of Middle-East oil firm Taqa has previously been described as “an amazing success story in the Granite City”. Taqa announced in 2023 that it intends to cease production from all of its UK North Sea platforms by the end of 2027. Meanwhile, Apache revealed at the end of last year it is planning to exit the North Sea by the end of 2029 blaming the windfall tax. The US firm first entered the North Sea in 2003 but will wrap up all of its UK operations by 2030. Aberdeen big deals The Prime Four acquisition wasn’t the biggest Granite City commercial property sale of 2024. American private equity firm Lone Star bought Union Square shopping centre from Hammerson for £111m. © ShutterstockAberdeen city centre. Hammerson, who also built the property, had originally been seeking £150m. BP’s North Sea headquarters in Stoneywood, Aberdeen, was also sold. Manchester-based

2025 ransomware predictions, trends, and how to prepare
Zscaler ThreatLabz research team has revealed critical insights and predictions on ransomware trends for 2025. The latest Ransomware Report uncovered a surge in sophisticated tactics and extortion attacks. As ransomware remains a key concern for CISOs and CIOs, the report sheds light on actionable strategies to mitigate risks. Top Ransomware Predictions for 2025: ● AI-Powered Social Engineering: In 2025, GenAI will fuel voice phishing (vishing) attacks. With the proliferation of GenAI-based tooling, initial access broker groups will increasingly leverage AI-generated voices; which sound more and more realistic by adopting local accents and dialects to enhance credibility and success rates. ● The Trifecta of Social Engineering Attacks: Vishing, Ransomware and Data Exfiltration. Additionally, sophisticated ransomware groups, like the Dark Angels, will continue the trend of low-volume, high-impact attacks; preferring to focus on an individual company, stealing vast amounts of data without encrypting files, and evading media and law enforcement scrutiny. ● Targeted Industries Under Siege: Manufacturing, healthcare, education, energy will remain primary targets, with no slowdown in attacks expected. ● New SEC Regulations Drive Increased Transparency: 2025 will see an uptick in reported ransomware attacks and payouts due to new, tighter SEC requirements mandating that public companies report material incidents within four business days. ● Ransomware Payouts Are on the Rise: In 2025 ransom demands will most likely increase due to an evolving ecosystem of cybercrime groups, specializing in designated attack tactics, and collaboration by these groups that have entered a sophisticated profit sharing model using Ransomware-as-a-Service. To combat damaging ransomware attacks, Zscaler ThreatLabz recommends the following strategies. ● Fighting AI with AI: As threat actors use AI to identify vulnerabilities, organizations must counter with AI-powered zero trust security systems that detect and mitigate new threats. ● Advantages of adopting a Zero Trust architecture: A Zero Trust cloud security platform stops

Hustlers are cashing in on China’s OpenClaw AI craze
Feng Qingyang had always hoped to launch his own company, but he never thought this would be how—or that the day would come this fast. Feng, a 27-year-old software engineer based in Beijing, started tinkering with OpenClaw, a popular new open-source AI tool that can take over a device and autonomously complete tasks for a user, in January. He was immediately hooked, and before long he was helping other curious tech workers with less technical proficiency install the AI agent. Feng soon realized this could be a lucrative opportunity. By the end of January, he had set up a page on Xianyu, a secondhand shopping site, advertising “OpenClaw installation support.” “No need to know coding or complex terms. Fully remote,” reads the posting. “Anyone can quickly own an AI assistant, available within 30 minutes.” At the same time, the broader Chinese public was beginning to catch on—and the tool, which had begun as a niche interest among tech workers, started to evolve into a popular sensation.
Feng quickly became inundated with requests, and he started chatting with customers and managing orders late into the night. At the end of February, he quit his job. Now his side gig has now grown into a full-fledged professional operation with over 100 employees. So far, the store has handled 7,000 orders, each worth about 248 RMB or approximately $34. “Opportunities are always fleeting,” says Feng. “As programmers, we are the first to feel the winds shift.”
Feng is among a small cohort of savvy early adopters turning China’s OpenClaw craze into cash. As users with little technical background want in, a cottage industry of people offering installation services and preconfigured hardware has sprung up to meet them. The sudden rise of these tinkerers and impromptu consultants shows just how eager the general public in China is to adopt cutting-edge AI—even when there are huge security risks. A “lobster craze” “Have you raised a lobster yet?” Xie Manrui, a 36-year-old software engineer in Shenzhen, says he has heard this question nonstop over the past month. “Lobster” is the nickname Chinese users have given to OpenClaw—a reference to its logo. Xie, like Feng, has been experimenting with OpenClaw since January. He’s built new open-source tools on top of the ecosystem, including one that visualizes the agent’s progress as an animated little desktop worker and another that lets users voice-chat with it. “I’ve met so many new people through ‘lobster raising,’” says Xie. “Many are lawyers or doctors, with little technical background, but all dedicated to learning new things.” Lobsters are indeed popping up everywhere in China right now—on and offline. In February, for instance, the entrepreneur and tech influencer Fu Sheng hosted a livestream showing off OpenClaw’s capabilities that got 20,000 views. And just last weekend, Xie attended three different OpenClaw events in Shenzhen, each drawing more than 500 people. These self-organized, unofficial gatherings feature power users, influencers, and sometimes venture capitalists as speakers. The biggest event Xie attended, on March 7, drew more than 1,000 people; in the packed venue, he says, people were shoulder to shoulder, with many attendees unable to even get a seat. Now China’s AI giants are starting to piggyback on the trend too, promoting their models, APIs, and cloud services (which can be used with OpenClaw), as well as their own OpenClaw-like agents. Earlier this month, Tencent held a public event offering free installation support for OpenClaw, drawing long lines of people waiting for help, including elderly users and children.
This sudden burst in popularity has even prompted local governments to get involved. Earlier this month the government of Longgang, a district in Shenzhen, released several policies to support OpenClaw-related ventures, including free computing credits and cash rewards for standout projects. Other cities, including Wuxi, have begun rolling out similar measures. These policies only catalyze what’s already in the air. “It was not until my father, who is 77, asked me to help install a ‘lobster’ for him that I realized this thing is truly viral,” says Henry Li, a software engineer based in Beijing. A programmer gold rush What’s making this moment particularly lucrative for people with technical skills, like Feng, is that so many people want OpenClaw, but not nearly as many have the capabilities to access it. Setting it up requires a level of technical knowledge most people do not possess, from typing commands into a black terminal window to navigating unfamiliar developer platforms. On the hardware side, an older or budget laptop may struggle to run it smoothly. And if the tool is not installed on a device separate from someone’s everyday computer, or if the data accessible to OpenClaw is not properly partitioned, the user’s privacy could be at risk—opening the door to data leaks and even malicious attacks. Chris Zhao, known as “Qi Shifu” online, organizes OpenClaw social media groups and events in Beijing. On apps like Rednote and Jike, Zhao routinely shares his thoughts on AI, and he asks other interested users to leave their WeChat ID so he can invite them to a semi-private group chat. The proof required to join is a screenshot that shows your “lobster” up and running. Zhao says that even in group chats for experienced users, hardware and cloud setup remain a constant topic of discussion. The relatively high bar for setting up OpenClaw has generated a sense of exclusivity, creating a natural opening for a service industry to start unfolding around it. On Chinese e-commerce platforms like Taobao and JD, a simple search for “OpenClaw” now returns hundreds of listings, most of them installation guides and technical support packages aimed at nontechnical users, priced anywhere from 100 to 700 RMB (approximately $15 to $100). At the higher end, many vendors offer to come to help you in person. Like Feng, most providers of these services are early adopters with some technical ability who are looking for a side gig. But as demand has surged, some have found themselves overwhelmed. Xie, the developer in Shenzhen who created tools to layer on OpenClaw, was asked by a friend who runs one such business to help out over the weekend; the friend had a customer who worked in e-commerce and had little technical experience, so Xie had to show up in person to get it done. He walked away with 600 RMB ($87) for the afternoon. The growing demand has also pushed vendors like Feng to expand quickly. He has now standardized his operation into tiers: a basic installation, a custom package where users can make specific requests like configuring a preferred chat app, and an ongoing tutoring service for those who want a hand to hold as they find their footing with the technology.
Other vendors in China are making money combining OpenClaw with hardware. Li Gong, a Shenzhen-based seller of refurbished Mac computers, was among the first online sellers to do this—offering Mac minis and MacBooks with OpenClaw preinstalled. Because OpenClaw is designed to operate with deep access to a hard drive and can run continuously in the background unattended, many users prefer to install it on a separate device rather than on the one they use every day. This would help prevent bad actors from infiltrating the program and immediately gaining access to a wide swathe of someone’s personal information. Many turn to secondhand or refurbished options to keep the cost down. Li says that in the last two weeks, orders have increased eightfold. Though OpenClaw itself is a new technology, the general practice of buying software bundles, downloading third-party packages, and seeking out modified devices is nothing new for many Chinese internet users, says Tianyu Fang, a PhD candidate studying the history of technology at Harvard University. Many users pay for one-off IT support services for tasks from installing Adobe software to jailbreaking a Kindle.
Still, not everyone is getting swept up. Jiang Yunhui, a tech worker based in Ningbo, worries that ordinary users who struggle with setup may not be the right audience for a technology that is still effectively in testing. “The hype in first-tier cities can be a little overblown,” he says. “The agent is still a proof of concept, and I doubt it would be of any life-changing use to the average person for now.” He argues that using it safely and getting anything meaningful out of it requires a level of technical fluency and independent judgment that most new users simply don’t have yet. He’s not alone in his concerns. On March 10, the Chinese cybersecurity regulator CNCERT issued a warning about the security and data risks tied to OpenClaw, saying it heightens users’ exposure to data breaches. Despite the potential pitfalls, though, China’s enthusiasm for OpenClaw doesn’t seem to be slowing. Feng, now flush with the earnings from his operation, wants to use the momentum—and the capital—to keep building out his own venture with AI tools at the center of it. “With OpenClaw and other AI agents, I want to see if I can run a one-person company,” he says. “I’m giving myself one year.”

The Download: Pokémon Go to train world models, and the US-China race to find aliens
This is today’s edition of The Download, our weekday newsletter that provides a daily dose of what’s going on in the world of technology. How Pokémon Go is giving delivery robots an inch-perfect view of the world Pokémon Go was the world’s first augmented-reality megahit. Released in 2016 by Niantic, the AR twist on the juggernaut Pokémon franchise fast became a global phenomenon. “500 million people installed that app in 60 days,” says Brian McClendon, CTO at Niantic Spatial, an AI company that Niantic spun out last year. Now Niantic Spatial is using that vast trove of crowdsourced data to build a kind of world model—a buzzy new technology that grounds the smarts of LLMs in real environments. The firm wants to use it to help robots navigate more precisely. Read the full story. —Will Douglas Heaven
MIT Technology Review Narrated: America was winning the race to find Martian life. Then China jumped in. In July 2024, after more than three years on Mars, the Perseverance rover came across a peculiar rocky outcrop. Instead of the usual crystals or sedimentary layers, this one had spots. Those specks were the best hint yet of alien life. NASA began a new mission to bring the rocks back to Earth to study. But now, just over a year and a half later, the project is on life support. As a result, those oh-so-promising rocks may be stuck out there forever.
This also means that, in the race to find evidence of alien life, America has effectively ceded its pole position to its greatest geopolitical rival: China. The superpower is moving full steam ahead with its own version of NASA’s mission. —Robin George Andrews This is our latest story to be turned into an MIT Technology Review Narrated podcast, which we’re publishing each week on Spotify and Apple Podcasts. Just navigate to MIT Technology Review Narrated on either platform, and follow us to get all our new content as it’s released. The must-reads I’ve combed the internet to find you today’s most fun/important/scary/fascinating stories about technology. 1 Viral AI fakes of the Iran war are flooding X And Grok is failing to flag them. (Wired $) + The conflict could wreak havoc on data centers and electricity costs. (The Verge) + Pro-Iran bots are weaponizing posts about Epstein. (Gizmodo) + AI is turning the Iran conflict into a show. (MIT Technology Review) 2 Anthropic fears the loss of billions due to the Pentagon’s blacklisting That’s what the company has told a judge as it seeks to block its designation as a supply-chain risk. (Bloomberg $) + Microsoft has backed the company in its legal fight with the Pentagon. (FT $) + OpenAI’s “compromise” with the DoD dealt a big blow to Anthropic. (MIT Technology Review) 3 Meta has bought a social network that’s exclusively for bots Moltbook is a Reddit-like site where AI agents interact with each other. (NYT $) + The platform is AI theater. (MIT Technology Review) 4 Ukraine is eagerly offering the US its expertise and tech to counter Iranian drones Kyiv has sent drones and UAV specialists to military bases in Jordan. (WSJ $) + A radio-obsessed civilian is shaping Ukraine’s drone defense. (MIT Technology Review) 5 OnlyFans “chatters” are earning $2 per hour to impersonate models A worker in the Philippines described the job as “heartbreaking” and “icky.” (BBC) 6 The DHS has removed officials who objected to “illegal” orders about surveillance tech The officers had refused to mislabel records about the technologies in order to block their release. (Wired) 7 This startup is building data centers run on brain cells The “biological data centers” are coming to Melbourne and Singapore. (New Scientist $) 8 Anduril is expanding into space defense The company is buying ExoAnalytic, which specializes in missile defense tracking. (Reuters) + We saw a demo of an AI system powering Anduril’s vision for war. (MIT Technology Review) 9 Big tech has a new big idea: AI compute as compensation Silicon Valley is pitching it as a job perk. (Business Insider) 10 Wordle’s creator is back with a new game It’s inspired by cryptic crosswords. (The New Yorker $) Quote of the day “You come for the Epstein content, and you stay for the propaganda.” —Bret Schafer, an expert on information manipulation, tells the Washington Post how pro-Iran networks are gaining traction with posts about Epstein.
One More Thing MEREDITH MIOTKE | PHOTO: NASA/JPL-CALTECH/MSSS The quest to figure out farming on Mars If ever a blade of grass grew on Mars, those days are over. But could they begin again? What would it take to grow plants to feed future astronauts on Mars? To grow food there, we can’t just drop seeds in the ground and add water. We will need to create a layer of soil that can support life. And to do that, we first have to get rid of the red planet’s toxic salts. Researchers recently discovered a potential solution—and the early signs are promising. Read the full story. We can still have nice things A place for comfort, fun and distraction to brighten up your day. (Got any ideas? Drop me a line) + Finally, a rebellion arises against mint’s tyranny over our teeth: Peanut Butter Cup toothpaste. + DIY decorators rejoice! The humble paint tray has received an ingeniously simple renovation. + Saudi surgeons have successfully separated two conjoined twins. + If you’re looking for real innovation, check out British Pie Week’s beef rendang, jerk chicken, and double-size pasties.
From games to biology and beyond: 10 years of AlphaGo’s impact
Catalyzing breakthroughs in scienceBy proving it could navigate the massive search space of a Go board, AlphaGo demonstrated the potential for AI to help us better understand the vast complexities of the physical world. We started by attempting to solve the protein folding problem, a 50-year grand challenge of predicting the 3D structure of proteins – information that is crucial for understanding diseases and developing new drugs.In 2020, we finally cracked this longstanding scientific problem with our AlphaFold 2 system. From there, we folded the structures for all 200 million proteins known to science and made them freely available to scientists in an open-source database. Today, over 3 million researchers around the world use the AlphaFold database to accelerate their important work on everything from malaria vaccines to plastic-eating enzymes. And in 2024, it was the honor of a lifetime for John Jumper and I to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for leading this project, on behalf of the entire AlphaFold team.Since AlphaGo’s win, we’ve applied its groundbreaking approach to many other areas of science and mathematics, including:Mathematical reasoning: The most direct descendant of AlphaGo’s architecture, AlphaProof learned to prove formal mathematical statements using a combination of language models and AlphaZero’s reinforcement learning and search algorithms. Alongside AlphaGeometry 2, it became the first system to achieve a medal-standard (silver) at the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO), proving AlphaGo’s methods could unlock advanced mathematical reasoning and laying the foundation for our most capable general models.Gemini, our largest and most capable model, recently went even further. An advanced version of its Deep Think mode achieved gold-medal level performance at the 2025 IMO using an approach inspired by AlphaGo. Since then, Deep Think has been applied to even more complex, open-ended challenges across science and engineering.Algorithm discovery: Just as AlphaGo searched for the best move in a game, our coding agent AlphaEvolve explores the space of computer code to discover more efficient algorithms. It had its own Move 37 moment when it found a novel way to multiply matrices, a fundamental mathematical operation powering nearly all modern neural networks. AlphaEvolve is now being tested on problems ranging from data center optimization to quantum computing.Scientific collaboration: We are integrating the search and reasoning principles pioneered with AlphaGo into an AI co-scientist. By having agents ‘debate’ scientific ideas and hypotheses, this system acts as a collaborator capable of performing the rigorous thinking necessary to identify patterns in data and solve sophisticated problems. In validation studies at Imperial College London, it analyzed decades of literature and independently arrived at the same hypothesis about antimicrobial resistance that researchers had spent years developing and validating experimentally.We’ve also used AI to better understand the genome, advance fusion energy research, improve weather prediction and more.As impressive as our scientific models are, they are highly specialized. To achieve fundamental breakthroughs like creating limitless clean energy or solving diseases that we don’t understand today, we need general AI systems that can find underlying structure and connections between different subject areas, and help us to come up with new hypotheses like the best scientists do.Future of intelligenceFor an AI to be truly general, it needs to understand the physical world. We built Gemini to be multimodal from the beginning so it could understand not just language, but also audio, video, images and code to build a model of the world.To think and reason across these modalities, the latest Gemini models use some of the techniques we pioneered with AlphaGo and AlphaZero.The next generation of AI systems will also need to be able to call upon specialized tools. For example, if a model needed to know the structure of a protein it could use AlphaFold for that.We think the combination of Gemini’s world models, AlphaGo’s search and planning techniques, and specialized AI tool use will prove to be critical for AGI.True creativity is a key capability that such an AGI system would need to exhibit. Move 37 was a glimpse of AI’s potential to think outside the box, but true original invention will require something more. It would need to not only come up with a novel Go strategy, as AlphaGo impressively did, but actually invent a game as deep and elegant, and as worthy of study as Go.Ten years after AlphaGo’s legendary victory, our ultimate goal is on the horizon. The creative spark first seen in Move 37 catalyzed breakthroughs that are now converging to pave the path towards AGI – and usher in a new golden age of scientific discovery.

How Pokémon Go is helping robots deliver pizza on time
Pokémon Go was the world’s first augmented-reality megahit. Released in 2016 by the Google spinout Niantic, the AR twist on the juggernaut Pokémon franchise fast became a global phenomenon. From Chicago to Oslo to Enoshima, players hit the streets in the urgent hope of catching a Jigglypuff or a Squirtle or (with a huge amount of luck) an ultra-rare Galarian Zapdos hovering just out of reach, superimposed on the everyday world. In short, we’re talking about a huge number of people pointing their phones at a huge number of buildings. “Five hundred million people installed that app in 60 days,” says Brian McClendon, CTO at Niantic Spatial, an AI company that Niantic spun out in May last year. According to the video-game firm Scopely, which bought Pokémon Go from Niantic at the same time, the game still drew more than 100 million players in 2024, eight years after it launched. Now Niantic Spatial is using that vast and unparalleled trove of crowdsourced data—images of urban landmarks tagged with super-accurate location markers taken from the phones of hundreds of millions of Pokémon Go players around the world—to build a kind of world model, a buzzy new technology that grounds the smarts of LLMs in real environments. The company’s latest product is a model that it says can pinpoint your location on a map to within a few centimeters, based on a handful of snapshots of the buildings or other landmarks in view. The firm wants to use it to help robots navigate with greater precision in places where GPS is unreliable.
In the first big test of its technology, Niantic Spatial has just teamed up with Coco Robotics, a startup that deploys last-mile delivery robots in a number of cities across the US and Europe. “Everybody thought that AR was the future, that AR glasses were coming,” says McClendon. “And then robots became the audience.” From Pikachu to pizza delivery Coco Robotics deploys around 1,000 flight-case-size robots—built to carry up to eight extra-large pizzas or four grocery bags—in Los Angeles, Chicago, Jersey City, Miami, and Helsinki. According to CEO Zach Rash, the robots have made more than half a million deliveries to date, covering a few million miles in all weather conditions.
But to compete with human couriers, Coco’s robots, which trundle along sidewalks at around five miles per hour, must be as reliable as possible. “The best way we can do our job is by arriving exactly when we told you we were going to arrive,” says Rash. And that means not getting lost. The problem Coco faces is that it cannot rely on GPS, which can be weak in cities because radio signals bounce off buildings and interfere with each other. “We do deliveries in a lot of dense areas with high-rises and underpasses and freeways, and those are the areas where GPS just never really works,” says Rash. “The urban canyon is the worst place in the world for GPS,” says McClendon. “If you look at that blue dot on your phone, you’ll often see it drift 50 meters, which puts you on a different block going a different direction on the wrong side of the street.” That’s where Niantic Spatial comes in. For the last few years, Niantic Spatial has been taking the data collected from players of Pokémon Go and Ingress (Niantic’s previous phone-based AR game, launched in 2013) and building a visual positioning system, technology that tells you where you are based on what you can see. “It turns out that getting Pikachu to realistically run around and getting Coco’s robot to safely and accurately move through the world is actually the same problem,” says John Hanke, CEO of Niantic Spatial. “Visual positioning is not a very new technology,” says Konrad Wenzel at ESRI, a company that develops digital mapping and geospatial analysis software. “But it’s obvious that the more cameras we have out there, the better it becomes.” Niantic Spatial has trained its model on 30 billion images captured in urban environments. In particular, the images are clustered around hot spots—places that served as important locations in Niantic’s games that players were encouraged to visit, such as Pokémon battle arenas. “We had a million-plus locations around the world where we can locate you precisely,” says McClendon. “We know where you’re standing within several centimeters of accuracy and, most importantly, where you’re looking.” The upshot is that for each of those million locations, Niantic Spatial has many thousands of images taken in more or less the same place but from different angles, at different times of day, and in different weather conditions. Each of those images comes with detailed metadata that pinpoints where in space the phone was at the time it captured the image, including which way the phone was facing, which way up it was, whether or not it was moving, how fast and in which direction, and more. The firm has used this data set to train a model to predict exactly where it is by taking into account what it is looking at—even for locations other than those million hot spots, where good sources of image and location data are scarcer.
In addition to GPS, Coco’s robots, which are fitted with four cameras, will now use this model to try to figure out where they are and where they are headed. The robots’ cameras are hip-height and point in all directions at once, so their viewpoint is a little different from a Pokémon Go player’s, but adapting the data was straightforward, says Rash. Rival companies use visual positioning systems too. For example, Starship Technologies, a robot delivery firm founded in Estonia in 2014, says its robots use their sensors to build a 3D map of their surroundings, plotting the edges of buildings and the position of streetlights. But Rash is betting that Niantic Spatial’s tech will give Coco an edge. He claims it will allow his robots to position themselves in the correct pickup spots outside restaurants, making sure they don’t get in anybody’s way, and stop just outside the customer’s door instead of a few steps away, which might have happened in the past. A Cambrian explosion in robotics When Niantic Spatial started work on its visual positioning system, the idea was to apply it to augmented reality, says Hanke. “If you are wearing AR glasses and you want the world to lock in to where you’re looking, then you need some method for doing that,” he says. “But now we’re seeing a Cambrian explosion in robotics.” Some of those robots may need to share spaces with humans—spaces such as construction sites and sidewalks. “If robots are ever going to assimilate into that environment in a way that’s not disruptive for human beings, they’re going to have to have a similar level of spatial understanding,” says Hanke. “We can help robots find exactly where they are when they’ve been jostled and bumped.” The Coco Robotics partnership is the start. What Niantic Spatial is putting in place, says Hanke, are the first pieces of what he calls a living map: a hyper-detailed virtual simulation of the world that changes as the world changes. As robots from Coco and other firms move about the world, they will provide new sources of map data, feeding into more and more detailed digital replicas of the world. But the way Hanke and McClendon see it, maps are not only becoming more detailed; they are being used more and more by machines. That shifts what maps are for. Maps have long been used to help people locate themselves in the world. As they moved from 2D to 3D to 4D (think of real-time simulations, such as digital twins), the basic principle hasn’t changed: Points on the map correspond to points in space or time. And yet maps for machines may need to become more like guidebooks, full of information that humans take for granted. Companies like Niantic Spatial and ESRI want to add descriptions that tell machines what they’re actually looking at, with every object tagged with a list of its properties. “This era is about building useful descriptions of the world for machines to comprehend,” says Hanke. “The data that we have is a great starting point in terms of building up an understanding of how the connective tissue of the world works.” There is a lot of buzz about world models right now—and Niantic Spatial knows it. LLMs may seem like know-it-alls, but they have very little common sense when it comes to interpreting and interacting with everyday environments. World models aim to fix that. Some firms, such as Google DeepMind and World Labs, are developing models that generate virtual fantasy worlds on the fly, which can then be used as training dojos for AI agents. Niantic Spatial says it is coming at the problem from a different angle. Push map-making far enough and you’ll end up capturing everything, says McClendon: “I’m very focused on trying to re-create the real world. We’re not there yet, but we want to be there.”
The Download: AI’s role in the Iran war, and an escalating legal fight
This is today’s edition of The Download, our weekday newsletter that provides a daily dose of what’s going on in the world of technology. How AI is turning the Iran conflict into theater Much of the spotlight on AI in the Iran conflict has focused on models like Claude helping the US military decide where to strike. But a wave of “vibe-coded” intelligence dashboards—and the ecosystem surrounding them—reflect a new role that AI is playing in wartime: mediating information, often for the worse. These sorts of intelligence tools have much promise. Yet there are real reasons to be suspicious of their data feeds. Read the full story. —James O’Donnell
This story is from The Algorithm, our weekly newsletter on AI. Sign up to receive it in your inbox every Monday. The must-reads
I’ve combed the internet to find you today’s most fun/important/scary/fascinating stories about technology. 1 Anthropic has sued the US government The AI firm wants to stop the Pentagon from blacklisting it. (Reuters) + The White House is preparing a new executive order to weed out the company’s technology. (Axios) + Defense experts are alarmed. (CNBC) +.Google and OpenAI staff have filed a legal brief backing Anthropic against Trump. (Wired $) + The company’s stance won many supporters. (MIT Technology Review) 2 GPS jamming has become a crucial battleground in the Middle East The interference is endangering—and protecting—ships and planes. (BBC) + Signal jamming has made navigating the Strait of Hormuz even more difficult. (Bloomberg) + Quantum navigation offers a potential solution. (MIT Technology Review) 3 A tech journalist found his AI clone editing for Grammarly It’s providing AI-generated feedback “inspired by” real writers without their consent. (Platformer) + Could ChatGPT do the jobs of journalists and copywriters? (MIT Technology Review) 4 Nvidia plans to launch an open-source platform for AI agents It’s already pitching the “NemoClaw” product to enterprise software firms. (Wired $) + But don’t let the AI agents hype get ahead of reality (MIT Technology Review) 5 A startup wants to launch a space mirror that reflects sunlight onto Earth Reflect Orbital reckons it could power solar panels at night. Scientists are appalled. (NYT) 6 Yann LeCun’s AI startup has raised over $1bn in Europe’s largest seed round Meta’s former chief AI scientist plans to build systems that “understand the world.” (Bloomberg) 7 Hinge’s CEO insists the app doesn’t rate users’ attractiveness Jackie Jantos’ strategy has helped Hinge defy the decline in dating apps. (FT $) + AI companions are stealing hearts—and it’s getting weird. (New Yorker $) + It’s surprisingly easy to fall into a relationship with a chatbot. (MIT Technology Review) 8 “AI psychosis” could be afflicting your loved ones If so, here’s how you can help them. (404 Media) + One solution: AI should be able to “hang up” on you. (MIT Technology Review)
9 Nintendo is suing Trump over illegal tariffs The gaming giant has joined a lawsuit seeking over $200 billion in refunds. (Ars Technica) 10 Bio-tech is turning ancient poop into a map of lost civilizations Molecular sensors are finding human traces where physical ruins have vanished. (Nature) Quote of the day “I don’t think any of us, whether it’s me or Dario [Amodei], Sam Altman, or Elon Musk, has any legitimacy to decide for society what is a good or bad use of AI.” —Yann LeCun gives Wired his take on the Anthropic’s spat the Pentagon. One More Thing This giant microwave may change the future of war YOSHI SODEOKA armed forces are hunting for a weapon that disables drones en masse—and they want it fast. One solution focuses on microwaves: high-powered electronic devices that push out kilowatts of power to zap the circuits of a drone as if it were the tinfoil you forgot to take off your leftovers when you heated them up. Defense tech startup Epirus may have the winning formula. The company has developed a cutting-edge, cost-efficient drone zapper that’s sparking the interest of the US military. And drones are just one of its targets. Read the full story.
—Sam Dean We can still have nice things
A place for comfort, fun and distraction to brighten up your day. (Got any ideas? Drop me a line.) + Werner Herzog’s magnificent movie about Africa’s ghost elephants has arrived on Disney+ and Hulu. + A “city killer” asteroid won’t hit Earth after all. Phew. + The Met is publishing high-definition 3D scans of over 100 iconic works. + Marty and Doc from Back to the Future are still BFFs in real life. Top image credit: MIT TECHNOLOGY REVIEW (ILLUSTRATION) | PHOTO OF MISSILE (US NAVY), AI-GENERATED IMAGE OF RUBBLE VIA X, SCREENSHOTS VIA WORLDMONITOR, GLOBALTHREATMAP Send asteroids to [email protected]. You can follow me on LinkedIn. Thanks for reading! —Thomas

Prioritizing energy intelligence for sustainable growth
In partnership withEverpure Loudoun County, Virginia, once known for its pastoral scenery and proximity to Washington, DC, has earned a more modern reputation in recent years: The area has the highest concentration of data centers on the planet. Ten years ago, these facilities powered email and e-commerce. Today, thanks to the meteoric rise in demand for AI-infused everything, local utility Dominion Energy is working hard to keep pace with surging power demands. The pressure is so acute that Dulles International Airport is constructing the largest airport solar installation in the country, a highly visible bid to bolster the region’s power mix. Data center campuses like Loudoun’s are cropping up across the country to accommodate an insatiable appetite for AI. But this buildout comes at an enormous cost. In the US alone, data centers consumed roughly 4% of national electricity in 2024. Projections suggest that figure could stretch to 12% by 2028. To put this in perspective, a single 100-megawatt data center consumes roughly as much electricity as 80,000 American homes. Data centers being built today are gearing up for gigawatt scale, enough to power a mid-sized city. For enterprise leaders, energy costs associated with AI and data infrastructure are quickly becoming both a budget concern and a potential bottleneck on growth. Meeting this moment calls for a capability most organizations are only beginning to develop: energy intelligence. The emerging discipline refers to understanding where, when, and why energy is consumed, and using that insight to optimize operations and control costs.
These efforts stand to address both immediate financial pressures and longer-term reputational risks, as communities like Loudoun County grow increasingly concerned about the energy demands associated with nearby data center development. In December 2025, MIT Technology Review Insights conducted a survey of 300 executives to understand how companies are thinking about energy intelligence today, as well as where they’re anticipating challenges in the future.
Here are five of our most notable findings: Energy intelligence is becoming a universal business priority. One hundred percent of executives surveyed expect the ability to measure and strategically manage power consumption to become an important business metric in the next two years. AI workloads are already driving measurable cost increases, and the surge is just beginning. Two-thirds of executives (68%) report their companies have faced energy cost increases of 10% or more in the past 12 months due to AI and data workloads. Nearly all respondents (97%) anticipate their organization’s AI-related energy consumption will increase over the next 12-18 months. Mounting costs are the top energy-related threat to AI innovation. Half of executives (51%) rank rising costs as the single greatest energy-related risk to their digital and AI initiatives. Most companies currently tracking and attempting to optimize data center energy consumption are motivated by cost management. Organizations are responding through infrastructure optimization and energy-efficient partnerships. To address mounting energy demands, three in four leaders (74%) are optimizing existing infrastructure, while 69% are partnering with energy-efficient cloud and storage providers. More than half are also implementing AI workload scheduling (61%) and investing in more efficient hardware (56%). Closing the measurement gap is the next frontier. Most enterprises still lack the granular data needed for true energy intelligence. This gap is especially pronounced for companies relying on third-party cloud providers and managed services for their data compute and storage needs, where 71% say rising consumption-based costs originate, yet energy metrics are often opaque. Download the full report. This content was produced by Insights, the custom content arm of MIT Technology Review. It was not written by MIT Technology Review’s editorial staff. It was researched, designed, and written by human writers, editors, analysts, and illustrators. This includes the writing of surveys and collection of data for surveys. AI tools that may have been used were limited to secondary production processes that passed thorough human review.

Tech layoffs surpass 45,000 in early 2026
Layoffs spread across tech sectors Beyond Amazon, Meta, and Block, several technology vendors and platform companies have also announced sizable layoffs this year. According to the RationalFX report: Semiconductor and electronics company ams OSRAM has announced 2,000 layoffs. Telecommunications vendor Ericsson has announced 1,900 job cuts. Semiconductor equipment manufacturer ASML has reduced its workforce by 1,700 employees. Enterprise software and platform companies are also reducing headcount. Enterprise software providers Autodesk and Salesforce have each cut about 1,000 jobs. Online grocery technology company Ocado has also eliminated around 1,000 roles. eBay reduced its headcount by about 800 jobs. Social media company Pinterest has cut about 675 positions. The layoffs span multiple segments of the technology sector, including cloud services, enterprise software, semiconductor manufacturing, and digital platforms, according to RationalFX. Layoffs tied to restructuring, emerging tech According to RationalFX, the layoffs often reflect broader corporate restructuring efforts rather than financial distress. Many companies are consolidating teams, reducing management layers, and shifting resources toward emerging technologies and strategic priorities. “A key driver behind many of these reductions remains the growing integration of artificial intelligence and automation,” said RationalFX’s Cohen. “Companies are increasingly restructuring teams and workflows around AI-assisted systems, often reducing headcount in areas where tasks can be automated or handled more efficiently with new tools.”

Hustlers are cashing in on China’s OpenClaw AI craze
Feng Qingyang had always hoped to launch his own company, but he never thought this would be how—or that the day would come this fast. Feng, a 27-year-old software engineer based in Beijing, started tinkering with OpenClaw, a popular new open-source AI tool that can take over a device and autonomously complete tasks for a user, in January. He was immediately hooked, and before long he was helping other curious tech workers with less technical proficiency install the AI agent. Feng soon realized this could be a lucrative opportunity. By the end of January, he had set up a page on Xianyu, a secondhand shopping site, advertising “OpenClaw installation support.” “No need to know coding or complex terms. Fully remote,” reads the posting. “Anyone can quickly own an AI assistant, available within 30 minutes.” At the same time, the broader Chinese public was beginning to catch on—and the tool, which had begun as a niche interest among tech workers, started to evolve into a popular sensation.
Feng quickly became inundated with requests, and he started chatting with customers and managing orders late into the night. At the end of February, he quit his job. Now his side gig has now grown into a full-fledged professional operation with over 100 employees. So far, the store has handled 7,000 orders, each worth about 248 RMB or approximately $34. “Opportunities are always fleeting,” says Feng. “As programmers, we are the first to feel the winds shift.”
Feng is among a small cohort of savvy early adopters turning China’s OpenClaw craze into cash. As users with little technical background want in, a cottage industry of people offering installation services and preconfigured hardware has sprung up to meet them. The sudden rise of these tinkerers and impromptu consultants shows just how eager the general public in China is to adopt cutting-edge AI—even when there are huge security risks. A “lobster craze” “Have you raised a lobster yet?” Xie Manrui, a 36-year-old software engineer in Shenzhen, says he has heard this question nonstop over the past month. “Lobster” is the nickname Chinese users have given to OpenClaw—a reference to its logo. Xie, like Feng, has been experimenting with OpenClaw since January. He’s built new open-source tools on top of the ecosystem, including one that visualizes the agent’s progress as an animated little desktop worker and another that lets users voice-chat with it. “I’ve met so many new people through ‘lobster raising,’” says Xie. “Many are lawyers or doctors, with little technical background, but all dedicated to learning new things.” Lobsters are indeed popping up everywhere in China right now—on and offline. In February, for instance, the entrepreneur and tech influencer Fu Sheng hosted a livestream showing off OpenClaw’s capabilities that got 20,000 views. And just last weekend, Xie attended three different OpenClaw events in Shenzhen, each drawing more than 500 people. These self-organized, unofficial gatherings feature power users, influencers, and sometimes venture capitalists as speakers. The biggest event Xie attended, on March 7, drew more than 1,000 people; in the packed venue, he says, people were shoulder to shoulder, with many attendees unable to even get a seat. Now China’s AI giants are starting to piggyback on the trend too, promoting their models, APIs, and cloud services (which can be used with OpenClaw), as well as their own OpenClaw-like agents. Earlier this month, Tencent held a public event offering free installation support for OpenClaw, drawing long lines of people waiting for help, including elderly users and children.
This sudden burst in popularity has even prompted local governments to get involved. Earlier this month the government of Longgang, a district in Shenzhen, released several policies to support OpenClaw-related ventures, including free computing credits and cash rewards for standout projects. Other cities, including Wuxi, have begun rolling out similar measures. These policies only catalyze what’s already in the air. “It was not until my father, who is 77, asked me to help install a ‘lobster’ for him that I realized this thing is truly viral,” says Henry Li, a software engineer based in Beijing. A programmer gold rush What’s making this moment particularly lucrative for people with technical skills, like Feng, is that so many people want OpenClaw, but not nearly as many have the capabilities to access it. Setting it up requires a level of technical knowledge most people do not possess, from typing commands into a black terminal window to navigating unfamiliar developer platforms. On the hardware side, an older or budget laptop may struggle to run it smoothly. And if the tool is not installed on a device separate from someone’s everyday computer, or if the data accessible to OpenClaw is not properly partitioned, the user’s privacy could be at risk—opening the door to data leaks and even malicious attacks. Chris Zhao, known as “Qi Shifu” online, organizes OpenClaw social media groups and events in Beijing. On apps like Rednote and Jike, Zhao routinely shares his thoughts on AI, and he asks other interested users to leave their WeChat ID so he can invite them to a semi-private group chat. The proof required to join is a screenshot that shows your “lobster” up and running. Zhao says that even in group chats for experienced users, hardware and cloud setup remain a constant topic of discussion. The relatively high bar for setting up OpenClaw has generated a sense of exclusivity, creating a natural opening for a service industry to start unfolding around it. On Chinese e-commerce platforms like Taobao and JD, a simple search for “OpenClaw” now returns hundreds of listings, most of them installation guides and technical support packages aimed at nontechnical users, priced anywhere from 100 to 700 RMB (approximately $15 to $100). At the higher end, many vendors offer to come to help you in person. Like Feng, most providers of these services are early adopters with some technical ability who are looking for a side gig. But as demand has surged, some have found themselves overwhelmed. Xie, the developer in Shenzhen who created tools to layer on OpenClaw, was asked by a friend who runs one such business to help out over the weekend; the friend had a customer who worked in e-commerce and had little technical experience, so Xie had to show up in person to get it done. He walked away with 600 RMB ($87) for the afternoon. The growing demand has also pushed vendors like Feng to expand quickly. He has now standardized his operation into tiers: a basic installation, a custom package where users can make specific requests like configuring a preferred chat app, and an ongoing tutoring service for those who want a hand to hold as they find their footing with the technology.
Other vendors in China are making money combining OpenClaw with hardware. Li Gong, a Shenzhen-based seller of refurbished Mac computers, was among the first online sellers to do this—offering Mac minis and MacBooks with OpenClaw preinstalled. Because OpenClaw is designed to operate with deep access to a hard drive and can run continuously in the background unattended, many users prefer to install it on a separate device rather than on the one they use every day. This would help prevent bad actors from infiltrating the program and immediately gaining access to a wide swathe of someone’s personal information. Many turn to secondhand or refurbished options to keep the cost down. Li says that in the last two weeks, orders have increased eightfold. Though OpenClaw itself is a new technology, the general practice of buying software bundles, downloading third-party packages, and seeking out modified devices is nothing new for many Chinese internet users, says Tianyu Fang, a PhD candidate studying the history of technology at Harvard University. Many users pay for one-off IT support services for tasks from installing Adobe software to jailbreaking a Kindle.
Still, not everyone is getting swept up. Jiang Yunhui, a tech worker based in Ningbo, worries that ordinary users who struggle with setup may not be the right audience for a technology that is still effectively in testing. “The hype in first-tier cities can be a little overblown,” he says. “The agent is still a proof of concept, and I doubt it would be of any life-changing use to the average person for now.” He argues that using it safely and getting anything meaningful out of it requires a level of technical fluency and independent judgment that most new users simply don’t have yet. He’s not alone in his concerns. On March 10, the Chinese cybersecurity regulator CNCERT issued a warning about the security and data risks tied to OpenClaw, saying it heightens users’ exposure to data breaches. Despite the potential pitfalls, though, China’s enthusiasm for OpenClaw doesn’t seem to be slowing. Feng, now flush with the earnings from his operation, wants to use the momentum—and the capital—to keep building out his own venture with AI tools at the center of it. “With OpenClaw and other AI agents, I want to see if I can run a one-person company,” he says. “I’m giving myself one year.”

The Download: Pokémon Go to train world models, and the US-China race to find aliens
This is today’s edition of The Download, our weekday newsletter that provides a daily dose of what’s going on in the world of technology. How Pokémon Go is giving delivery robots an inch-perfect view of the world Pokémon Go was the world’s first augmented-reality megahit. Released in 2016 by Niantic, the AR twist on the juggernaut Pokémon franchise fast became a global phenomenon. “500 million people installed that app in 60 days,” says Brian McClendon, CTO at Niantic Spatial, an AI company that Niantic spun out last year. Now Niantic Spatial is using that vast trove of crowdsourced data to build a kind of world model—a buzzy new technology that grounds the smarts of LLMs in real environments. The firm wants to use it to help robots navigate more precisely. Read the full story. —Will Douglas Heaven
MIT Technology Review Narrated: America was winning the race to find Martian life. Then China jumped in. In July 2024, after more than three years on Mars, the Perseverance rover came across a peculiar rocky outcrop. Instead of the usual crystals or sedimentary layers, this one had spots. Those specks were the best hint yet of alien life. NASA began a new mission to bring the rocks back to Earth to study. But now, just over a year and a half later, the project is on life support. As a result, those oh-so-promising rocks may be stuck out there forever.
This also means that, in the race to find evidence of alien life, America has effectively ceded its pole position to its greatest geopolitical rival: China. The superpower is moving full steam ahead with its own version of NASA’s mission. —Robin George Andrews This is our latest story to be turned into an MIT Technology Review Narrated podcast, which we’re publishing each week on Spotify and Apple Podcasts. Just navigate to MIT Technology Review Narrated on either platform, and follow us to get all our new content as it’s released. The must-reads I’ve combed the internet to find you today’s most fun/important/scary/fascinating stories about technology. 1 Viral AI fakes of the Iran war are flooding X And Grok is failing to flag them. (Wired $) + The conflict could wreak havoc on data centers and electricity costs. (The Verge) + Pro-Iran bots are weaponizing posts about Epstein. (Gizmodo) + AI is turning the Iran conflict into a show. (MIT Technology Review) 2 Anthropic fears the loss of billions due to the Pentagon’s blacklisting That’s what the company has told a judge as it seeks to block its designation as a supply-chain risk. (Bloomberg $) + Microsoft has backed the company in its legal fight with the Pentagon. (FT $) + OpenAI’s “compromise” with the DoD dealt a big blow to Anthropic. (MIT Technology Review) 3 Meta has bought a social network that’s exclusively for bots Moltbook is a Reddit-like site where AI agents interact with each other. (NYT $) + The platform is AI theater. (MIT Technology Review) 4 Ukraine is eagerly offering the US its expertise and tech to counter Iranian drones Kyiv has sent drones and UAV specialists to military bases in Jordan. (WSJ $) + A radio-obsessed civilian is shaping Ukraine’s drone defense. (MIT Technology Review) 5 OnlyFans “chatters” are earning $2 per hour to impersonate models A worker in the Philippines described the job as “heartbreaking” and “icky.” (BBC) 6 The DHS has removed officials who objected to “illegal” orders about surveillance tech The officers had refused to mislabel records about the technologies in order to block their release. (Wired) 7 This startup is building data centers run on brain cells The “biological data centers” are coming to Melbourne and Singapore. (New Scientist $) 8 Anduril is expanding into space defense The company is buying ExoAnalytic, which specializes in missile defense tracking. (Reuters) + We saw a demo of an AI system powering Anduril’s vision for war. (MIT Technology Review) 9 Big tech has a new big idea: AI compute as compensation Silicon Valley is pitching it as a job perk. (Business Insider) 10 Wordle’s creator is back with a new game It’s inspired by cryptic crosswords. (The New Yorker $) Quote of the day “You come for the Epstein content, and you stay for the propaganda.” —Bret Schafer, an expert on information manipulation, tells the Washington Post how pro-Iran networks are gaining traction with posts about Epstein.
One More Thing MEREDITH MIOTKE | PHOTO: NASA/JPL-CALTECH/MSSS The quest to figure out farming on Mars If ever a blade of grass grew on Mars, those days are over. But could they begin again? What would it take to grow plants to feed future astronauts on Mars? To grow food there, we can’t just drop seeds in the ground and add water. We will need to create a layer of soil that can support life. And to do that, we first have to get rid of the red planet’s toxic salts. Researchers recently discovered a potential solution—and the early signs are promising. Read the full story. We can still have nice things A place for comfort, fun and distraction to brighten up your day. (Got any ideas? Drop me a line) + Finally, a rebellion arises against mint’s tyranny over our teeth: Peanut Butter Cup toothpaste. + DIY decorators rejoice! The humble paint tray has received an ingeniously simple renovation. + Saudi surgeons have successfully separated two conjoined twins. + If you’re looking for real innovation, check out British Pie Week’s beef rendang, jerk chicken, and double-size pasties.

Eridu exits stealth with $200M to rebuild AI networking
That gap is not static. Promode Nedungadi, Chief Technology Officer, said the architectural and algorithmic trends driving AI are making the network problem harder, not easier. Techniques like mixture-of-experts models and the disaggregation of inference into separate prefill and decode stages all require more data movement. “Every one of those requires more data to be moved around,” he said. “The amount of data being moved per token is growing.” The scale challenge also has more than one dimension. Perkins described three: scale-up, which refers to interconnecting GPUs within a single training domain; scale-out, which covers the broader cluster fabric; and what he called scale-across, an emerging requirement that standards bodies are beginning to address. “We think that scale-across is quite interesting as well,” Perkins said. Architecture: silicon, packaging, and software A key differentiator for Eridu will come from silicon. “There’s no doubt that we are developing our own silicon. We’re developing the most advanced silicon in the networking sector, bar none, period, and that’s absolutely necessary,” Perkins said. “You don’t get to an order-of-magnitude higher scale using off-the-shelf silicon.” Eridu has a partnership with TSMC for process technology and advanced system integration. Perkins said TSMC sees the networking bottleneck as tied directly to its own business. The silicon approach is likely to benefit from chiplet-based architecture and advanced packaging. “We believe you need to be on a different technology arc than what the mainstream technology is,” Omar Hassen, Chief Product Officer, told Network World. “In terms of things like advanced packaging, you’ve got to take advantage of everything you can from chiplet-based architecture, clean-sheet design, and advanced packaging. We believe we’re on the right technology arc that can take us beyond what the existing incumbents are doing.” Fundamentally, Eridu’s approach is an attempt to break through the architectural ceiling facing
From games to biology and beyond: 10 years of AlphaGo’s impact
Catalyzing breakthroughs in scienceBy proving it could navigate the massive search space of a Go board, AlphaGo demonstrated the potential for AI to help us better understand the vast complexities of the physical world. We started by attempting to solve the protein folding problem, a 50-year grand challenge of predicting the 3D structure of proteins – information that is crucial for understanding diseases and developing new drugs.In 2020, we finally cracked this longstanding scientific problem with our AlphaFold 2 system. From there, we folded the structures for all 200 million proteins known to science and made them freely available to scientists in an open-source database. Today, over 3 million researchers around the world use the AlphaFold database to accelerate their important work on everything from malaria vaccines to plastic-eating enzymes. And in 2024, it was the honor of a lifetime for John Jumper and I to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for leading this project, on behalf of the entire AlphaFold team.Since AlphaGo’s win, we’ve applied its groundbreaking approach to many other areas of science and mathematics, including:Mathematical reasoning: The most direct descendant of AlphaGo’s architecture, AlphaProof learned to prove formal mathematical statements using a combination of language models and AlphaZero’s reinforcement learning and search algorithms. Alongside AlphaGeometry 2, it became the first system to achieve a medal-standard (silver) at the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO), proving AlphaGo’s methods could unlock advanced mathematical reasoning and laying the foundation for our most capable general models.Gemini, our largest and most capable model, recently went even further. An advanced version of its Deep Think mode achieved gold-medal level performance at the 2025 IMO using an approach inspired by AlphaGo. Since then, Deep Think has been applied to even more complex, open-ended challenges across science and engineering.Algorithm discovery: Just as AlphaGo searched for the best move in a game, our coding agent AlphaEvolve explores the space of computer code to discover more efficient algorithms. It had its own Move 37 moment when it found a novel way to multiply matrices, a fundamental mathematical operation powering nearly all modern neural networks. AlphaEvolve is now being tested on problems ranging from data center optimization to quantum computing.Scientific collaboration: We are integrating the search and reasoning principles pioneered with AlphaGo into an AI co-scientist. By having agents ‘debate’ scientific ideas and hypotheses, this system acts as a collaborator capable of performing the rigorous thinking necessary to identify patterns in data and solve sophisticated problems. In validation studies at Imperial College London, it analyzed decades of literature and independently arrived at the same hypothesis about antimicrobial resistance that researchers had spent years developing and validating experimentally.We’ve also used AI to better understand the genome, advance fusion energy research, improve weather prediction and more.As impressive as our scientific models are, they are highly specialized. To achieve fundamental breakthroughs like creating limitless clean energy or solving diseases that we don’t understand today, we need general AI systems that can find underlying structure and connections between different subject areas, and help us to come up with new hypotheses like the best scientists do.Future of intelligenceFor an AI to be truly general, it needs to understand the physical world. We built Gemini to be multimodal from the beginning so it could understand not just language, but also audio, video, images and code to build a model of the world.To think and reason across these modalities, the latest Gemini models use some of the techniques we pioneered with AlphaGo and AlphaZero.The next generation of AI systems will also need to be able to call upon specialized tools. For example, if a model needed to know the structure of a protein it could use AlphaFold for that.We think the combination of Gemini’s world models, AlphaGo’s search and planning techniques, and specialized AI tool use will prove to be critical for AGI.True creativity is a key capability that such an AGI system would need to exhibit. Move 37 was a glimpse of AI’s potential to think outside the box, but true original invention will require something more. It would need to not only come up with a novel Go strategy, as AlphaGo impressively did, but actually invent a game as deep and elegant, and as worthy of study as Go.Ten years after AlphaGo’s legendary victory, our ultimate goal is on the horizon. The creative spark first seen in Move 37 catalyzed breakthroughs that are now converging to pave the path towards AGI – and usher in a new golden age of scientific discovery.

How Pokémon Go is helping robots deliver pizza on time
Pokémon Go was the world’s first augmented-reality megahit. Released in 2016 by the Google spinout Niantic, the AR twist on the juggernaut Pokémon franchise fast became a global phenomenon. From Chicago to Oslo to Enoshima, players hit the streets in the urgent hope of catching a Jigglypuff or a Squirtle or (with a huge amount of luck) an ultra-rare Galarian Zapdos hovering just out of reach, superimposed on the everyday world. In short, we’re talking about a huge number of people pointing their phones at a huge number of buildings. “Five hundred million people installed that app in 60 days,” says Brian McClendon, CTO at Niantic Spatial, an AI company that Niantic spun out in May last year. According to the video-game firm Scopely, which bought Pokémon Go from Niantic at the same time, the game still drew more than 100 million players in 2024, eight years after it launched. Now Niantic Spatial is using that vast and unparalleled trove of crowdsourced data—images of urban landmarks tagged with super-accurate location markers taken from the phones of hundreds of millions of Pokémon Go players around the world—to build a kind of world model, a buzzy new technology that grounds the smarts of LLMs in real environments. The company’s latest product is a model that it says can pinpoint your location on a map to within a few centimeters, based on a handful of snapshots of the buildings or other landmarks in view. The firm wants to use it to help robots navigate with greater precision in places where GPS is unreliable.
In the first big test of its technology, Niantic Spatial has just teamed up with Coco Robotics, a startup that deploys last-mile delivery robots in a number of cities across the US and Europe. “Everybody thought that AR was the future, that AR glasses were coming,” says McClendon. “And then robots became the audience.” From Pikachu to pizza delivery Coco Robotics deploys around 1,000 flight-case-size robots—built to carry up to eight extra-large pizzas or four grocery bags—in Los Angeles, Chicago, Jersey City, Miami, and Helsinki. According to CEO Zach Rash, the robots have made more than half a million deliveries to date, covering a few million miles in all weather conditions.
But to compete with human couriers, Coco’s robots, which trundle along sidewalks at around five miles per hour, must be as reliable as possible. “The best way we can do our job is by arriving exactly when we told you we were going to arrive,” says Rash. And that means not getting lost. The problem Coco faces is that it cannot rely on GPS, which can be weak in cities because radio signals bounce off buildings and interfere with each other. “We do deliveries in a lot of dense areas with high-rises and underpasses and freeways, and those are the areas where GPS just never really works,” says Rash. “The urban canyon is the worst place in the world for GPS,” says McClendon. “If you look at that blue dot on your phone, you’ll often see it drift 50 meters, which puts you on a different block going a different direction on the wrong side of the street.” That’s where Niantic Spatial comes in. For the last few years, Niantic Spatial has been taking the data collected from players of Pokémon Go and Ingress (Niantic’s previous phone-based AR game, launched in 2013) and building a visual positioning system, technology that tells you where you are based on what you can see. “It turns out that getting Pikachu to realistically run around and getting Coco’s robot to safely and accurately move through the world is actually the same problem,” says John Hanke, CEO of Niantic Spatial. “Visual positioning is not a very new technology,” says Konrad Wenzel at ESRI, a company that develops digital mapping and geospatial analysis software. “But it’s obvious that the more cameras we have out there, the better it becomes.” Niantic Spatial has trained its model on 30 billion images captured in urban environments. In particular, the images are clustered around hot spots—places that served as important locations in Niantic’s games that players were encouraged to visit, such as Pokémon battle arenas. “We had a million-plus locations around the world where we can locate you precisely,” says McClendon. “We know where you’re standing within several centimeters of accuracy and, most importantly, where you’re looking.” The upshot is that for each of those million locations, Niantic Spatial has many thousands of images taken in more or less the same place but from different angles, at different times of day, and in different weather conditions. Each of those images comes with detailed metadata that pinpoints where in space the phone was at the time it captured the image, including which way the phone was facing, which way up it was, whether or not it was moving, how fast and in which direction, and more. The firm has used this data set to train a model to predict exactly where it is by taking into account what it is looking at—even for locations other than those million hot spots, where good sources of image and location data are scarcer.
In addition to GPS, Coco’s robots, which are fitted with four cameras, will now use this model to try to figure out where they are and where they are headed. The robots’ cameras are hip-height and point in all directions at once, so their viewpoint is a little different from a Pokémon Go player’s, but adapting the data was straightforward, says Rash. Rival companies use visual positioning systems too. For example, Starship Technologies, a robot delivery firm founded in Estonia in 2014, says its robots use their sensors to build a 3D map of their surroundings, plotting the edges of buildings and the position of streetlights. But Rash is betting that Niantic Spatial’s tech will give Coco an edge. He claims it will allow his robots to position themselves in the correct pickup spots outside restaurants, making sure they don’t get in anybody’s way, and stop just outside the customer’s door instead of a few steps away, which might have happened in the past. A Cambrian explosion in robotics When Niantic Spatial started work on its visual positioning system, the idea was to apply it to augmented reality, says Hanke. “If you are wearing AR glasses and you want the world to lock in to where you’re looking, then you need some method for doing that,” he says. “But now we’re seeing a Cambrian explosion in robotics.” Some of those robots may need to share spaces with humans—spaces such as construction sites and sidewalks. “If robots are ever going to assimilate into that environment in a way that’s not disruptive for human beings, they’re going to have to have a similar level of spatial understanding,” says Hanke. “We can help robots find exactly where they are when they’ve been jostled and bumped.” The Coco Robotics partnership is the start. What Niantic Spatial is putting in place, says Hanke, are the first pieces of what he calls a living map: a hyper-detailed virtual simulation of the world that changes as the world changes. As robots from Coco and other firms move about the world, they will provide new sources of map data, feeding into more and more detailed digital replicas of the world. But the way Hanke and McClendon see it, maps are not only becoming more detailed; they are being used more and more by machines. That shifts what maps are for. Maps have long been used to help people locate themselves in the world. As they moved from 2D to 3D to 4D (think of real-time simulations, such as digital twins), the basic principle hasn’t changed: Points on the map correspond to points in space or time. And yet maps for machines may need to become more like guidebooks, full of information that humans take for granted. Companies like Niantic Spatial and ESRI want to add descriptions that tell machines what they’re actually looking at, with every object tagged with a list of its properties. “This era is about building useful descriptions of the world for machines to comprehend,” says Hanke. “The data that we have is a great starting point in terms of building up an understanding of how the connective tissue of the world works.” There is a lot of buzz about world models right now—and Niantic Spatial knows it. LLMs may seem like know-it-alls, but they have very little common sense when it comes to interpreting and interacting with everyday environments. World models aim to fix that. Some firms, such as Google DeepMind and World Labs, are developing models that generate virtual fantasy worlds on the fly, which can then be used as training dojos for AI agents. Niantic Spatial says it is coming at the problem from a different angle. Push map-making far enough and you’ll end up capturing everything, says McClendon: “I’m very focused on trying to re-create the real world. We’re not there yet, but we want to be there.”
Stay Ahead with the Paperboy Newsletter
Your weekly dose of insights into AI, Bitcoin mining, Datacenters and Energy indusrty news. Spend 3-5 minutes and catch-up on 1 week of news.
